Blog

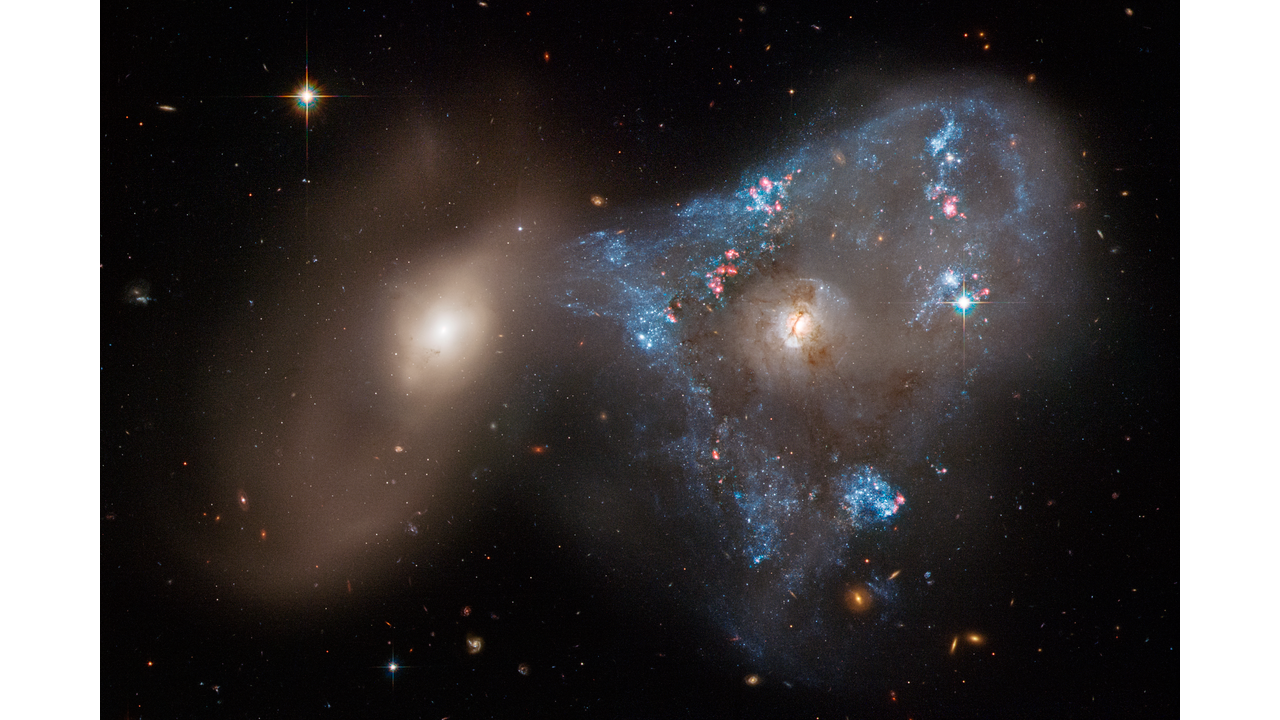
A spectacular head-on collision between two galaxies fueled the unusual triangular-shaped star-birthing frenzy, as captured in a new image from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. The interacting galaxy duo is collectively called Arp 143. The pair contains the glittery, distorted, star-forming spiral galaxy NGC 2445 at right, along with its less flashy companion, NGC 2444 at left.
Astronomers suggest that the galaxies passed through each other, igniting the uniquely shaped star-formation firestorm in NGC 2445, where thousands of stars are bursting to life on the right-hand side of the image. This galaxy is awash in starbirth because it is rich in gas, the fuel that makes stars. However, it hasn’t yet escaped the gravitational clutches of its partner NGC 2444, shown on the left side of the image. The pair is waging a cosmic tug-of-war, which NGC 2444 appears to be winning. The galaxy has pulled gas from NGC 2445, forming the oddball triangle of newly minted stars. 191mly.

Benjamin Earl King (September 28, 1938 – April 30, 2015) was an American soul and R&B singer and record producer. He rose to prominence as one of the principal lead singers of the R&B vocal group the Drifters, notably singing the lead vocals on three of their biggest hit singles “There Goes My Baby“, “This Magic Moment“, and “Save the Last Dance for Me” (their only U.S. No. 1 hit).
As a soloist, King is best known as the singer and co-composer of “Stand by Me“, which became a US Top 10 hit, both in 1961 and later in 1986 (when it was used as the theme to the film of the same name), and a number one hit in the United Kingdom in 1987. The single was also placed on the RIAA‘s list of Songs of the Century. His 1975 single “Supernatural Thing” became a top five hit on the Billboard Hot 100. Additionally, King was the original recording artist of songs such as “Spanish Harlem“, “I (Who Have Nothing)“, “So Much Love“, “Don’t Play That Song (You Lied)“, “We’re Gonna Groove“, and “Till I Can’t Take It Anymore” all of which have been covered by multiple artists to varying degrees of success.
King was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1988, as a member of the Drifters, and has been nominated as a solo artist. Along with the Drifter’s “There Goes My Baby“, King’s songs “Stand by Me” and “Spanish Harlem” also appeared on the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame’s list of 500 Songs That Shaped Rock and Roll.Additionally, he was inducted alongside the Drifters into Vocal Group Hall of Fame in 2000, as well as the Songwriters Hall of Fame in 2012 with the Towering song award.
more...John Gilmore (September 28, 1931 – August 20, 1995) was an American jazz saxophonist, clarinetist, and percussionist. He was known for his tenure with the avant-garde keyboardist/bandleader Sun Ra from the 1950s to the 1990s, and led The Sun Ra Arkestra from Sun Ra’s death in 1993 until his own death in 1995.
Gilmore was raised in Chicago and played clarinet from the age of 14. He took up the tenor saxophone while serving in the United States Air Force from 1948 through 1951.He then pursued a musical career, beginning as a tenor saxophonist on a national tour with the Harlem Globetrotters in an ensemble that included pianist Earl Hines in 1952.
In 1953 Gilmore met pianist and bandleader Sun Ra who had a profound impact on him as a musician. For the next four decades, he recorded and performed almost exclusively with Sun Ra; first as a trio, and then in the Sun Ra Arkestra. This was puzzling to some, who noted Gilmore’s talent, and thought he could be a major star like John Coltrane or Sonny Rollins. Despite being five years older than Gilmore, Coltrane was impressed with his playing, and took informal lessons from Gilmore in the late 1950s. Coltrane’s epochal, proto–free jazz “Chasin’ the Trane” was inspired partly by Gilmore’s sound. The Penguin Guide to Jazz suggests Gilmore remained an influence in Coltrane’s later period, particularly on Sun Ship.
more...Kenneth David Kirkland (September 28, 1955 – November 12, 1998) was an American pianist and keyboardist. Kirkland’s first professional work came with Polish fusion violinist Michal Urbaniak, touring throughout Europe with his group in 1977. Coincidentally, his next high-profile gig was with another Eastern European jazz émigré, Miroslav Vitous. Kirkland is featured on Vitous’ ECM recordings First Meeting and Miroslav Vitous Group.
In 1980, while Kirkland was on tour in Japan with Terumasa Hino, he met Wynton Marsalis, which began his long association with both Wynton and his older brother Branford. On Wynton’s self-titled debut album, Kirkland shared the piano duties with one of his musical influences, Herbie Hancock, but was the sole pianist on Marsalis’s subsequent releases Think of One, Hot House Flowers and Black Codes (From the Underground). Kirkland was found dead in his Queens apartment on Friday, November 13, 1998.
more...
Koko Taylor (born Cora Ann Walton, September 28, 1928 – June 3, 2009) was an American singer whose style encompassed Chicago blues, electric blues, rhythm and blues and soul blues. Sometimes called “The Queen of the Blues”, she was known for her rough, powerful vocals. Over the course of her career, she was nominated for 11 Grammy Awards, winning 1985’s Best Traditional Blues Album for her appearance on Blues Explosion.
Born on a farm near Memphis, Tennessee, Taylor was the daughter of a sharecropper. She left Tennessee for Chicago in 1952 with her husband, Robert “Pops” Taylor, a truck driver. I the late 1950s, she began singing in blues clubs in Chicago. She was spotted by Willie Dixon in 1962, and this led to more opportunities for performing and her first recordings. In 1963 she had a single on USA Records, and in 1964 a cut on a Chicago blues collection on Spivey Records, called Chicago Blues. In 1964 Dixon brought Taylor to Checker Records, a subsidiary label of Chess Records, for which she recorded “Wang Dang Doodle“, a song written by Dixon and recorded by Howlin’ Wolffive years earlier. The record became a hit, reaching number four on the R&B chart and number 58 on the pop chart in 1966, and selling a million copies. She recorded several versions of the song over the years, including a live rendition at the 1967 American Folk Blues Festival, with the harmonica player Little Walter and the guitarist Hound Dog Taylor. Her subsequent recordings, both original songs and covers, did not achieve as much success on the charts.
more...Friday September 27th 2024 6pm. Accompaniment for service with Inbal Sharett-Singer, Jayson Rodovsky, Jeff Bailey, Pete Whitman and mick laBriola
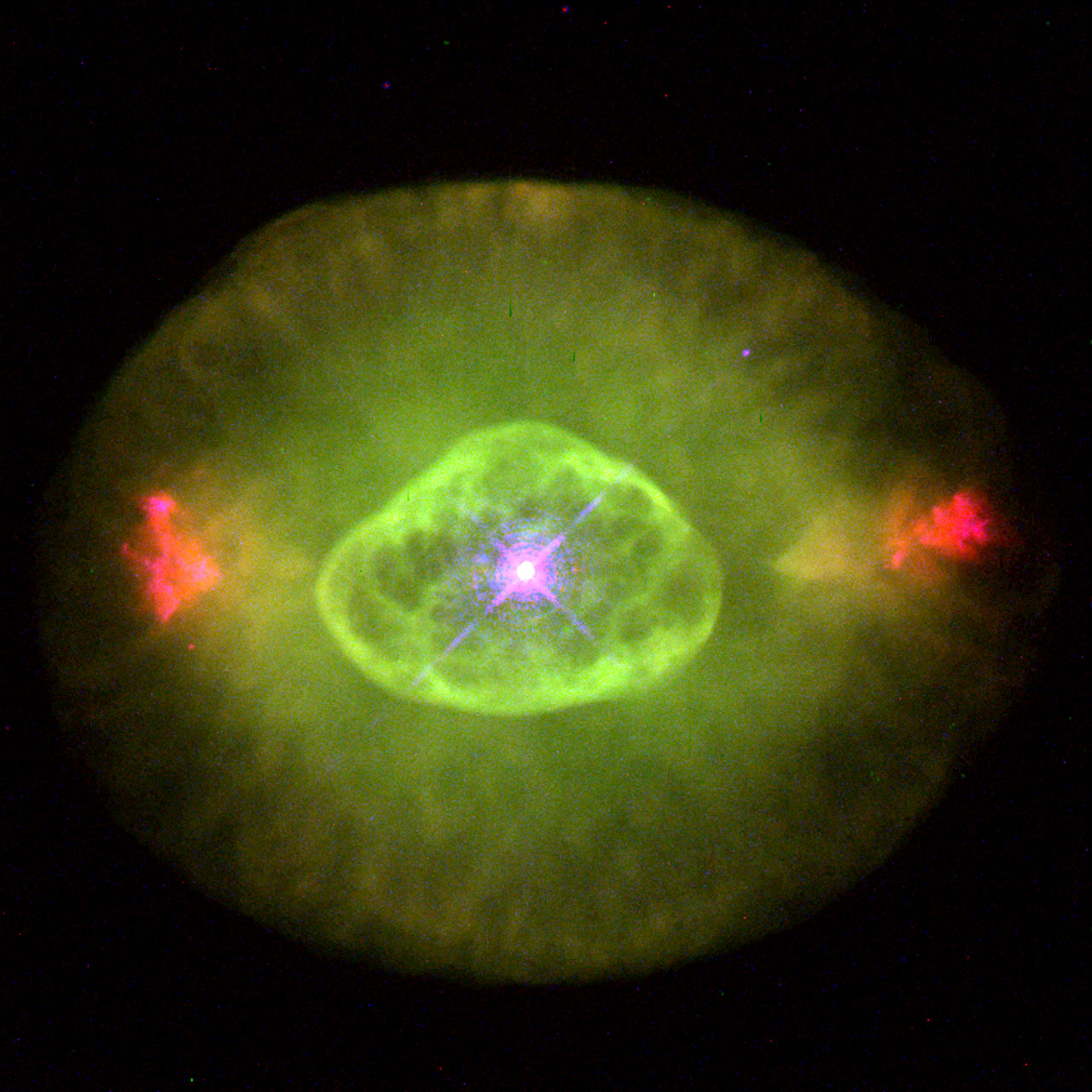
more...NGC 6826’s eye-like appearance is marred by two sets of blood-red ‘fliers’ that lie horizontally across the image. The surrounding faint green ‘white’ of the eye is believed to be gas that made up almost half of the star’s mass for most of its life. The hot remnant star (in the centre of the green oval) drives a fast wind into older material, forming a hot interior bubble which pushes the older gas ahead of it to form a bright rim. (The star is one of the brightest stars in any planetary.) NGC 6826 is 2, 200 light- years away in the constellation Cygnus. The Hubble telescope observation was taken Jan. 27, 1996 with the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2. Blinking Planetary Nebula.
Earring George Mayweather (September 27, 1927 – February 12, 1995) was an American electric blues and Chicago blues harmonica player, songwriter and singer. He recorded only one solo album, but he played the harmonica on recordings by J. B. Huttoand Eddie Taylor.
AllMusic commented that his album Whup It! Whup It! was “an admirable shot at recreating the ’50s Chicago harp sound”.
George Mayweather Jr. was born in Montgomery County, Alabama. He learned to play the harmonica after receiving the instrument as a Christmas present at the age of six. Inspired by the playing of Sonny Boy Williamson I, Mayweather mainly taught himself the rudiments of the instrument. Upon his relocation to Chicago, Illinois, in September 1949, he befriended Little Walter, who taught him techniques of harmonica playing. He lived in Chicago, next door to J. B. Hutto, and in 1951 he teamed up with Hutto and the percussionist Eddie “Porkchop” Hines to form the Hawks, a trio performing on weekends at the Maxwell Street market. With few opportunities for steady work, Mayweather alternately performed with Hutto and in Bo Diddley‘s backing ensemble. In 1952, when Little Walter left Muddy Waters‘s touring band, Mayweather was offered a job as his replacement, but he declined the potentially lucrative position. By 1954, Mayweather recorded with Hutto in sessions for Chance Records, which produced “Dim Lights”, “Things Are So Slow”,“Combination Boogie”, and “Pet Cream Man”. He later teamed up Eddie Taylor, and together they recorded a number of tracks, including “You’ll Always Have a Home” and “Don’t Knock at My Door”. Several of these were released as singles, but they were not commercial successes.
more...Robert Roland Chudnick (September 27, 1927 – May 27, 1994), known professionally as Red Rodney, was an American jazz trumpeter.
Born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, he became a professional musician at 15, working in the mid-1940s for the big bands of Jerry Wald, Jimmy Dorsey, Georgie Auld, Elliot Lawrence, Benny Goodman, and Les Brown. He was inspired by hearing Dizzy Gillespie and Charlie Parker to change his style to bebop, moving on to play with Claude Thornhill, Gene Krupa, and Woody Herman. He was Jewish.
He accepted an invitation from Charlie Parker to join his quintet. and was a member of the band from 1949 to 1951. Being the only white member of the group, when playing in the southern United States he was billed as “Albino Red” as a ruse to avoid prejudice against mixed race musical combos. During this time he recorded extensively.
During the 1950s, he worked as a bandleader in Philadelphia and recorded with Ira Sullivan. He became addicted to heroin and started a pattern of dropping in and out of jazz.
During 1969, Rodney played in Las Vegas with fellow Woody Herman colleague, trombonist Bill Harris, as part of the Flamingo casino house band led by Russ Black. Similar work continued through 1972.
In the early 1970s he was bankrupted by medical costs following a stroke. He returned to jazz. In 1975 he was incarcerated in Lexington, Kentucky for drug offenses. While jailed he gave music lessons to guitarist Wayne Kramer of the MC5.
more...Earl Rudolph “Bud” Powell (September 27, 1924 – July 31, 1966) was an American jazz pianist and composer. A pioneer in the development of bebop and its associated contributions to jazz theory, Powell’s application of complex phrasing to the piano influenced both his contemporaries and later pianists including Walter Davis, Jr., Toshiko Akiyoshi, and Barry Harris.
Born in the midst of the Harlem Renaissance to a musical family, Powell, during the 1930s, developed an attacking, right-handed approach to the piano, which marked a break from the left-handed approach of stride and ragtime that had been prevalent. Upon joining trumpeter Cootie Williams‘ band in 1943, he received attention from the broader musical community for his fluency and advanced technique. A severe beating by police in 1945 and years of electroconvulsive therapy treatments adversely impacted his mental health, but his recordings and live performances with Charlie Parker, Sonny Stitt, and Max Roach during the late 1940s and early 1950s were instrumental in shaping modern jazz piano technique.
Following a partial recovery in the mid to late 1950s, Powell’s relocation to Paris in 1959 contributed to the community of African-American expatriates fleeing racism and barriers to a higher standard of living. He returned to a regular recording schedule, toured across Northern and Central Europe, and made records before becoming ill with tuberculosis in 1963.
Despite the friendship and protection of French jazz aficionado Francis Paudras, mental health crises and a troubled return to New York hastened his early death in 1966. The decades following his death saw his career and life story become the inspiration for films and written works, including Bertrand Tavernier‘s Round Midnight. Many Powell compositions, including “Un Poco Loco“, “Bouncing with Bud“, and “Parisian Thoroughfare” have become jazz standards.
more...We know that it’s a four count. Sometimes we can count it in 8’s, but *really* it’s in 4’s. So, it starts on 1 and ends on 3 for the strong ending. I hear it as starting on 2 ending on 4 with a silent one.
1-2-3-4-1-2-3-4-
1-2-3-4-1-2-3
But what *is* a compás of Tangos? Is it one count of 4, two counts of 4, two counts of 8???? I remember being at a workshop with Concha Jareño and she asked the musicians what they thought. All had different answers!!! However, I will say this, I think of one compás as two counts of 4, but a whole measure as 4 counts of 4. Listen to the music enough and you’ll hear it, plus a bunch of variables!!
When danced in tablao, generally, a Tangos dance will be danced one dancer at a time and have the simple format of letra, escobilla, estribillo for each one.
So, an entire Tangos set with multiple dancers might like look like this:
- Falseta (guitar solo)
- Entrada (ay, ay, ay)
- Singer sings a few letras
- Dancer goes out and does llamada and dances a letra, maybe a falseta and maybe short escobilla
- Dancer leaves with estribillo (ending chorus)
- Next dancer, etc
- Perhaps the guitarist plays a falseta in between
- Last dancer calls other dancer to join for the final, which is usually a subida that ends in a llamada on stage.
What I’ve described is what is typical in an American tablao so there are variations- more falsetas, no escobillas, etc.
more...This stunning new mosaic of images from the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope showcases the nearby star-forming cluster, NGC 1333. The nebula is in the Perseus molecular cloud, and located approximately 960 light-years away. Webb’s superb sensitivity allows astronomers to investigate young objects with extremely low masses. Some of the faintest ‘stars’ in the picture are in fact newly born free-floating brown dwarfs with masses comparable to those of giant planets. The same cluster was featured as the 33rd anniversary image of the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope in April of 2023. Hubble’s image just scratched the surface of this region, because clouds of dust obscure much of the star formation process. Observing with larger aperture and in the infrared part of the spectrum, Webb is capable of peering through the dusty veil to reveal newborn stars, brown dwarfs and planetary mass objects. The centre of the image presents a deep peek into the heart of the NGC1333 cloud. Across the image we see large patches of orange, which represent gas glowing in the infrared. These so-called Herbig-Haro objects form when ionised material ejected from young stars collides with the surrounding cloud. They are hallmarks of a very active site of star formation. Many of the young stars in this image are surrounded by disks of gas and dust, which may eventually produce planetary systems. On the right hand side in the image, we can glimpse the shadow of one of these disks oriented edge-on – two dark cones emanating on opposite sides, seen against a bright background. Similar to the young stars in this mosaic, our own Sun and planets formed inside a dusty molecular cloud, 4.6 billion years ago. Our Sun didn’t form in isolation but as part of a cluster, which was perhaps even more massive than NGC 1333. The cluster in the mosaic, only 1-3 million years old, presents us with an opportunity to study stars like our Sun, as well as brown dwarfs and free-floating planets, in their nascent stages. The images were captured as part of the Webb observation programme 1202 (PI: A. Scholz) to survey a large portion of NGC1333. These data constitute the first deep spectroscopic survey of the young cluster, and have identified brown dwarfs down to planetary masses using the observatory’s Near-InfraRed Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (NIRISS). The first results from this survey have been accepted for publication in the Astronomical Journal. [Image Description: Several images of parts of a nebula in space have been aligned to form a single large image of the nebula. It depicts clouds of gas and dust in blue and orange colours as well as brightly shining stars in various sizes. Around the edge there are some black rectangles where there was no image of that region of space.] Links Science paper NGC 1333 (cropped) Pan video: NGC 1333

Victor Edward Jurusz Jr. (September 26, 1953 – December 31, 2019), known professionally as Vic Juris, was an American jazz guitarist.
Juris was born in Jersey City, New Jersey, but he moved with his family to Parsippanyearly in his life. In 1963, at the age of 10, he began learning guitar. At 11, he studied guitar at the home of his teacher, Ed Berg, and got interested in jazz listening to Berg’s records of guitarists Django Reinhardt, Jim Hall, Barney Kessel, Jimmy Raney, and Johnny Smith. In his teens he played the rock music of the 1960s. When he was 19, he met blind saxophonist Eric Kloss and they became friends. He made his first recording on Kloss’s album Bodies’ Warmth (Muse, 1975). Around the same time, he met guitarist Pat Martino, who became a friend and mentor.
Juris recorded with Richie Cole during 1976–78 and released his debut album as a leader, Roadsong, in 1979. In the early 1980s, he turned to acoustic guitar in duos with Larry Coryell and Biréli Lagrène, and in the late 1980s he worked with Gary Peacock‘s band. Since 1991 he has spent much of his career with saxophonist David Liebman.
During the 1990s, he worked as sideman with Lee Konitz and Peggy Stern (1992), Benny Waters (1993), Jeanie Bryson (1993–94), Gary Peacock (since 1994), Steve LaSpina (since 1995), Judi Silvano (1996), Ken Serio (1996, 2007, 2019) and Joe Locke (1998).
Juris taught at The New School for Jazz and Contemporary Music, Lehigh University, and Rutgers University and wrote instructional books for guitar.
more...Gary Bartz (born September 26, 1940, in Baltimore) is an American jazz saxophonist.He has won two Grammy Awards. Bartz was first exposed to jazz as the son of the owners of a jazz nightclub in Baltimore. In 1958 he left Baltimore to study at the Juilliard School. In the early 1960s, he performed with Eric Dolphy and McCoy Tyner in Charles Mingus‘ Jazz Workshop. He worked as a sideman with Max Roach and Abbey Lincoln before joining Art Blakey and the Jazz Messengers. In 1968, he was a member of McCoy Tyner‘s band, Expansions.
In mid-1970, he joined Miles Davis‘ band,performing live at the Isle Of Wight festival in August; and at a series of December dates at The Cellar Door club in Washington, D.C. Portions of these shows were initially released on the 1971 Live-Evil album, with the entire six performance/four night run eventually released in full on the 2005 Cellar Door Sessions box set. He later formed the band Ntu Troop, which combined jazz, funk, and soul.
more...George Gershwin (born Jacob Gershwine; September 26, 1898 – July 11, 1937) was an American composer and pianist whose compositions spanned popular, jazz and classical genres. Among his best-known works are the orchestral compositions Rhapsody in Blue (1924) and An American in Paris (1928), the songs “Swanee” (1919) and “Fascinating Rhythm” (1924), the jazz standards “Embraceable You” (1928) and “I Got Rhythm” (1930), and the opera Porgy and Bess (1935), which included the hit “Summertime“.
Gershwin studied piano under Charles Hambitzer and composition with Rubin Goldmark, Henry Cowell, and Joseph Brody. He began his career as a song plugger but soon started composing Broadway theater works with his brother Ira Gershwin and with Buddy DeSylva. He moved to Paris, intending to study with Nadia Boulanger, but she refused him, afraid that rigorous classical study would ruin his jazz-influenced style; Maurice Ravel voiced similar objections when Gershwin inquired about studying with him. He subsequently composed An American in Paris, returned to New York City and wrote Porgy and Bess with Ira and DuBose Heyward. Initially a commercial failure, it came to be considered one of the most important American operas of the 20th century and an American cultural classic.
Gershwin moved to Hollywood and composed numerous film scores. He died in 1937, only 38 years old, of a brain tumor. His compositions have been adapted for use in film and television, with many becoming jazz standards.
more...More Posts
- Daily Roots with Augustus Pablo
- Surviving the Pandemic and Realizing Racial Justice
- The Cosmos with OH 231.8+04.2
- Duane Allman
- Meredith Monk
- Dr. John
- Flamenco Fridays with José Valencia
- Daily Roots with the Upsetters
- Surviving the Pandemic and Realizing Racial Justice
- The Cosmos with NGC 1015
- George Freeman
- Kenny Werner
- Joe Hunter
- Tommy Dorsey
- World Music with Lakha Khan
- Daily Roots with Robert Marley
- Surviving the Pandemic and Realizing Racial Justice
- The Cosmos with NGC 869/884
- Cindy Blackman
- Don Cherry
