Blog
Friday August 30th 2024 6pm Temple Israel Erev Shabbat Service with Inbal Sharett-Singer, Jayson Rodovsky, Jeff Bailey, Pete Whitman and mick laBriola.
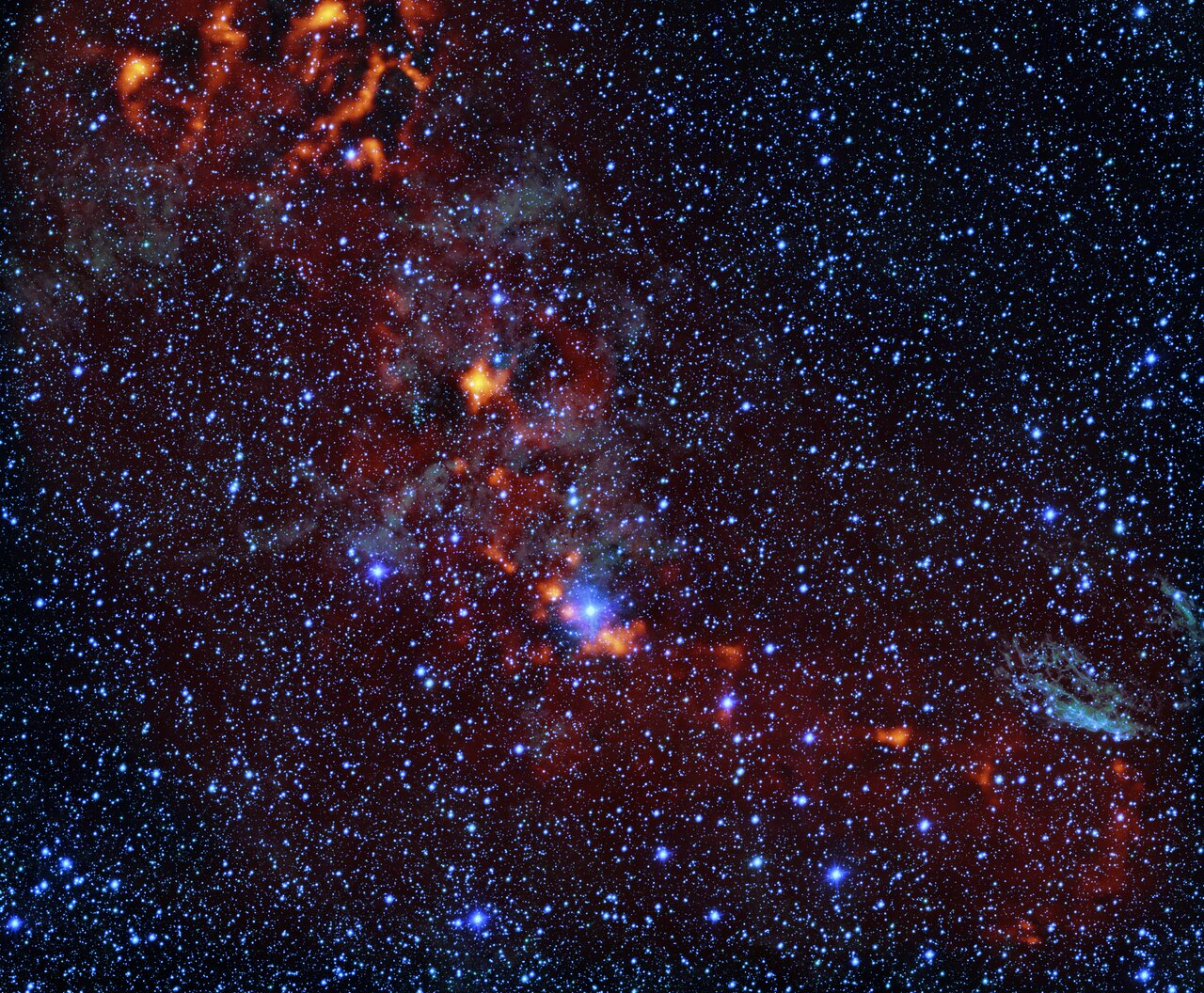
more...The glowing red clouds seen in this Picture of the Week show dense gas regions where new stars are being born in the RCW 106 region. But only 1% of this gas will actually go on to create stars, and astronomers don’t know why this percentage is so low. We do know that star formation takes place when regions of these huge clouds of cold gas are able to clump together and eventually collapse into newborn stars, which happens at a critical density. But once we go past that density, do even denser regions produce even more stars, and could this help to explain the 1% mystery? New results from the Atacama Pathfinder Experiment (APEX), accepted for publication in Astronomy & Astrophysics (link accessible from 20 August), suggest this is not the case: denser regions are not more efficient at forming stars. This is perhaps explained by the way these denser clouds fragment into filamentary structures and cores out of which stars will form, but leaves many questions still to be answered. This Picture of the Week highlights these areas of interest. The image imposes a red map of dense gas, imaged with the ArTéMiS camera at APEX, over an optical image taken with the VLT Survey Telescope. While APEX continues to investigate this stellar mystery, we can expect to see many more stunning images like this.

Lucious Brinson Johnson (August 30, 1934 – March 18, 1976), known as Luther “Georgia Boy” Johnson, was an American Chicago blues and electric bluesguitarist, singer and songwriter. AllMusic journalist Ron Wynn stated, “Johnson’s own inimitable vocals, raspy lines and tart guitar eventually create his own aura… a good, occasionally outstanding blues artist.”
Johnson was born Lucious Brinson Johnson in Davisboro, Georgia. He was raised on a farm and taught himself to play guitar. After completing his service in the US Army, Johnson played guitar with the Milwaukee Supreme Angels, a local gospel group in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. However, he gravitated towards blues and formed his own trio in Milwaukee. He relocated to Chicago, Illinois, in the early 1960s. He backed Elmore James prior to James’s death in 1963, and joined Muddy Waters‘ backing band in 1966. Johnson worked with various musicians during this period, including Chicago Bob Nelson. He recorded his debut album, Come On Home, in 1968, with Muddy Waters’ band.
more...Robert Dennis Crumb (/krʌm/; born August 30, 1943) is an American cartoonist who often signs his work R. Crumb. His work displays a nostalgia for American folk cultureof the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and satire of contemporary American culture.
Crumb contributed to many of the seminal works of the underground comix movement in the 1960s, including being a founder of the first successful underground comix publication, Zap Comix, contributing to all 16 issues. He was additionally contributing to the East Village Other and many other publications, including a variety of one-off and anthology comics. During this time, inspired by psychedelics and cartoons from the 1920s and 1930s, he introduced a wide variety of characters that became extremely popular, including countercultural icons Fritz the Cat and Mr. Natural, and the images from his Keep On Truckin’ strip. Sexual themes abounded in all these projects, often shading into scatological and pornographic comics. In the mid-1970s, he contributed to the Arcade anthology; following the decline of the underground, he moved towards biographical and autobiographical subjects while refining his drawing style, a heavily crosshatched pen-and-ink style inspired by late 19th- and early 20th-century cartooning. Much of his work appeared in a magazine he founded, Weirdo (1981–1993), which was one of the most prominent publications of the alternative comics era. As his career progressed, his comic work became more autobiographical.
In 1991 Crumb was inducted into the comic book industry’s Will Eisner Comic Book Hall of Fame, and in 1994 the Terry Zwigoff film Crumb explored his artistic career and personal life. He was married to cartoonist Aline Kominsky-Crumb, with whom he frequently collaborated. Their daughter Sophie Crumb has also followed a cartooning career.
more...McKinley Howard “Kenny” Dorham (August 30, 1924 – December 5, 1972) was an American jazz trumpeter, composer, and occasional singer. Dorham’s talent is frequently lauded by critics and other musicians, but he never received the kind of attention or public recognition from the jazz establishment that many of his peers did. For this reason, writer Gary Giddins said that Dorham’s name has become “virtually synonymous with ‘underrated’.” Dorham also composed the jazz standard “Blue Bossa“, which was first recorded by his associate Joe Henderson.
Dorham was one of the most active bebop trumpeters. Early in his career, he played in the big bands of Lionel Hampton, Billy Eckstine, Dizzy Gillespie, and Mercer Ellington, and in Charlie Parker‘s quintet. He joined Parker’s band in December 1948. He was a charter member of the original cooperative the Jazz Messengers. He also recorded as a sideman with Thelonious Monk and Sonny Rollins, and he replaced Clifford Brownin the Max Roach Quintet after Brown’s death in 1956. In addition to sideman work, Dorham led his own groups, including the Jazz Prophets (formed shortly after Art Blakey took over the Jazz Messengers name). The Jazz Prophets, featuring a young Bobby Timmons on piano, bassist Sam Jones, and tenorman J. R. Monterose, with guest Kenny Burrell on guitar, recorded a live album, ‘Round About Midnight at the Cafe Bohemia, in 1956 for Blue Note. During his final years, Dorham suffered from kidney disease, from which he died on December 5, 1972, aged 48.
more...“Rondeña” belong to Malaga’s singing group. “Rondeña” existed before flamenco, joining it in the 19th century. Its origin is in “fandango” from Malaga, more specifically in ” bandolás”. Some authors suggest that this name comes from the nightly rounds. Other authors believe that it comes from the city of Ronda, as “rodeña” was originated in the homonymous mountains. “Rondeña” has greatly extended through Andalusia during the 19th century. “Rondeña” singing has evolved in recent times with with a decrease in melismatic ornamentation. Its composition ad libitum (without “compas”). Lyrics are related to countryside life. Its structure is a couplet of four eight-syllable verses, usually consonant rhyme. They normally turn into five by repetition of the second one, but also without repetition. Dance displays a rhythm of wild abandon. Others have used the rhythm of the “taranto“, which has many similarities but, being rondeña, more open and evocative.
more...
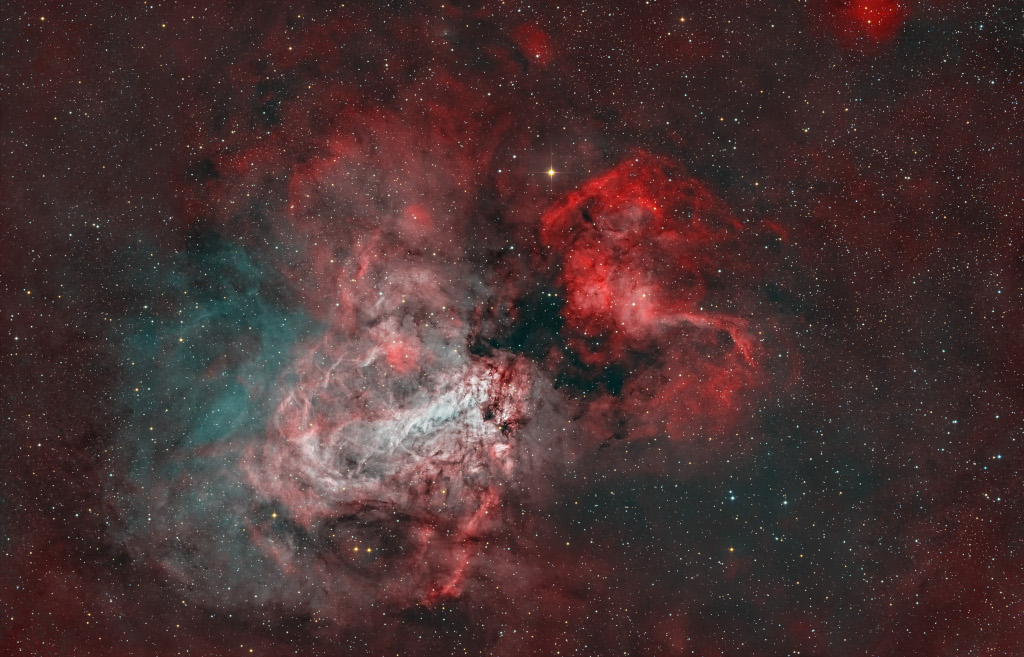
Messier 17 lies some 5,500 light-years away in the nebula-rich constellation Sagittarius. At that distance, this 1.5 degree wide field-of-view would span about 150 light-years. In the sharp color composite image faint details of the region’s gas and dust clouds are highlighted with narrowband image data against a backdrop of central Milky Way stars. The stellar winds and energetic radiation from hot, massive stars already formed from M17’s stock of cosmic gas and dust have slowly carved away at the remaining interstellar material, producing the nebula’s cavernous appearance and the undulating shapes within. A popular stop on telescopic tours of the cosmos, M17 is also known as the Omega or the Swan Nebula.

Michael Joseph Jackson (August 29, 1958 – June 25, 2009 Gary, IN) was an American singer, songwriter, dancer, and philanthropist. Dubbed the “King of Pop“, he is regarded as one of the most significant cultural figures of the 20th century. Over a four-decade career, his contributions to music, dance, and fashion, along with his publicized personal life, made him a global figure in popular culture. Jackson influenced artists across many music genres. Through stage and video performances, he popularized street dance moves such as the moonwalk, which he named, and the robot.
He was the eighth child of the Jackson family, and made his public debut in 1964 with his older brothers Jackie, Tito, Jermaine, and Marlon as a member of the Jackson 5(later known as the Jacksons). The Jackson 5 signed with Motown in 1968 and achieved worldwide success with Michael as lead singer. Jackson began his solo career in 1971 while at Motown and recorded multiple successful singles. He became a global solo star with his 1979 album Off the Wall. His music videos, including those for “Beat It“, “Billie Jean“, and “Thriller” from his 1982 album Thriller, are credited with breaking racial barriers and transforming the medium into an art form and promotional tool. He helped popularize MTV and continued to innovate with videos for his albums Bad(1987), Dangerous (1991), HIStory: Past, Present and Future, Book I (1995), and Invincible (2001). Thriller is the best-selling album of all time, while Bad was the first album to produce five US Billboard Hot 100 number-one singles.[nb 1]
From the late 1980s, Jackson became a figure of controversy and speculation due to his changing appearance, relationships, behavior, and lifestyle. In 1993, he was accused of sexually abusing the child of a family friend. The lawsuit was settled out of civil court; Jackson was not indicted due to lack of evidence. In 2005, he was tried and acquitted of further child sexual abuse allegations and several other charges. The Federal Bureau of Investigation found no evidence of criminal conduct by Jackson. In 2009, while he was preparing for a series of comeback concerts, This Is It, Jackson diedfrom an overdose of propofol administered by his personal physician, Conrad Murray, who was convicted in 2011 of involuntary manslaughter for his involvement in Jackson’s death. His death triggered reactions around the world, creating unprecedented surges of internet traffic and a spike in sales of his music. Jackson’s televised memorial service, held at the Staples Center in Los Angeles, was estimated to have been viewed by more than 2.5 billion people.
Jackson is one of the best-selling music artists of all time, with estimated sales of over 500 million records worldwide. He had 13 Billboard Hot 100 number-one singles(fourth highest of any artist in the Hot 100 era) and was the first artist to have a top-ten single on the Billboard Hot 100 in five different decades. His honors include 15 Grammy Awards, six Brit Awards, a Golden Globe Award, and 39 Guinness World Records, including the “Most Successful Entertainer of All Time”. Jackson’s inductions include the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame (twice), the Vocal Group Hall of Fame, the Songwriters Hall of Fame, the Dance Hall of Fame (making him the only recording artist to be inducted) and the National Rhythm & Blues Hall of Fame.
more...Bennie Maupin (born August 29, 1940) is an American jazz multireedist who performs on various saxophones, flute, and bass clarinet.
Maupin was born in Detroit, Michigan, United States. He is known for his participation in Herbie Hancock‘s Mwandishi sextet and Headhunters band, and for performing on Miles Davis‘s seminal fusion record, Bitches Brew. Maupin has collaborated with Horace Silver, Roy Haynes, Woody Shaw, Lee Morgan and many others. He is noted for having a harmonically-advanced, “out” improvisation style, while having a different sense of melodic direction than other “out” jazz musicians such as Eric Dolphy.
Maupin was a member of Almanac, a group with Cecil McBee (bass), Mike Nock (piano) and Eddie Marshall (drums).
more...Dinah Washington ( born Ruth Lee Jones; August 29, 1924 – December 14, 1963 Tuscaloosa, Al) was an American singer and pianist, one of the most popular black female recording artists of the 1950s. Primarily a jazz vocalist, she performed and recorded in a wide variety of styles including blues, R&B, and traditional pop music, and gave herself the title of “Queen of the Blues”. She was also known as “Queen of the Jukeboxes”. She was a 1986 inductee of the Alabama Jazz Hall of Fame, and was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1993.
Early in the morning of December 14, 1963, Washington’s last husband, football player Dick “Night Train” Lane, went to sleep with Washington and awoke later to find her slumped over and not responsive. Dr. B.C. Ross pronounced her dead at the scene at age 39. An autopsy later showed a lethal combination of secobarbital and amobarbital, prescriptions for her insomnia and diet, which contributed to her death. She is buried in the Burr Oak Cemetery in Alsip, Illinois.
more...
Charles Parker Jr. (August 29, 1920 – March 12, 1955 Kansas City, KS), nicknamed “Bird” or “Yardbird“, was an American jazz saxophonist, bandleader, and composer. Parker was a highly influential soloist and leading figure in the development of bebop, a form of jazz characterized by fast tempos, virtuosic technique, and advanced harmonies. He was a virtuoso and introduced revolutionary rhythmic and harmonic ideas into jazz, including rapid passing chords, new variants of altered chords, and chord substitutions. Parker was primarily a player of the alto saxophone.
Parker was an icon for the hipster subculture and later the Beat Generation, personifying the jazz musician as an uncompromising artist and intellectual rather than just an entertainer.
more...
The complex and beautiful Tulip Nebulablossoms about 8,000 light-years away toward the constellation of Cygnus the Swan. Ultraviolet radiation from young energetic stars at the edge of the Cygnus OB3 association, including O star HDE 227018, ionizes the atoms and powers the emission from the Tulip Nebula. Stewart Sharpless cataloged this nearly 70 light-years across reddish glowing cloud of interstellar gas and dust in 1959, as Sh2-101. Also in the featured field of view is the black hole Cygnus X-1, which to be a microquasar because it is one of strongest X-ray sources in planet Earth’s sky. Blasted by powerful jets from a lurking black hole, its fainter bluish curved shock front is only faintly visible beyond the cosmic Tulip’s petals, near the right side of the frame.
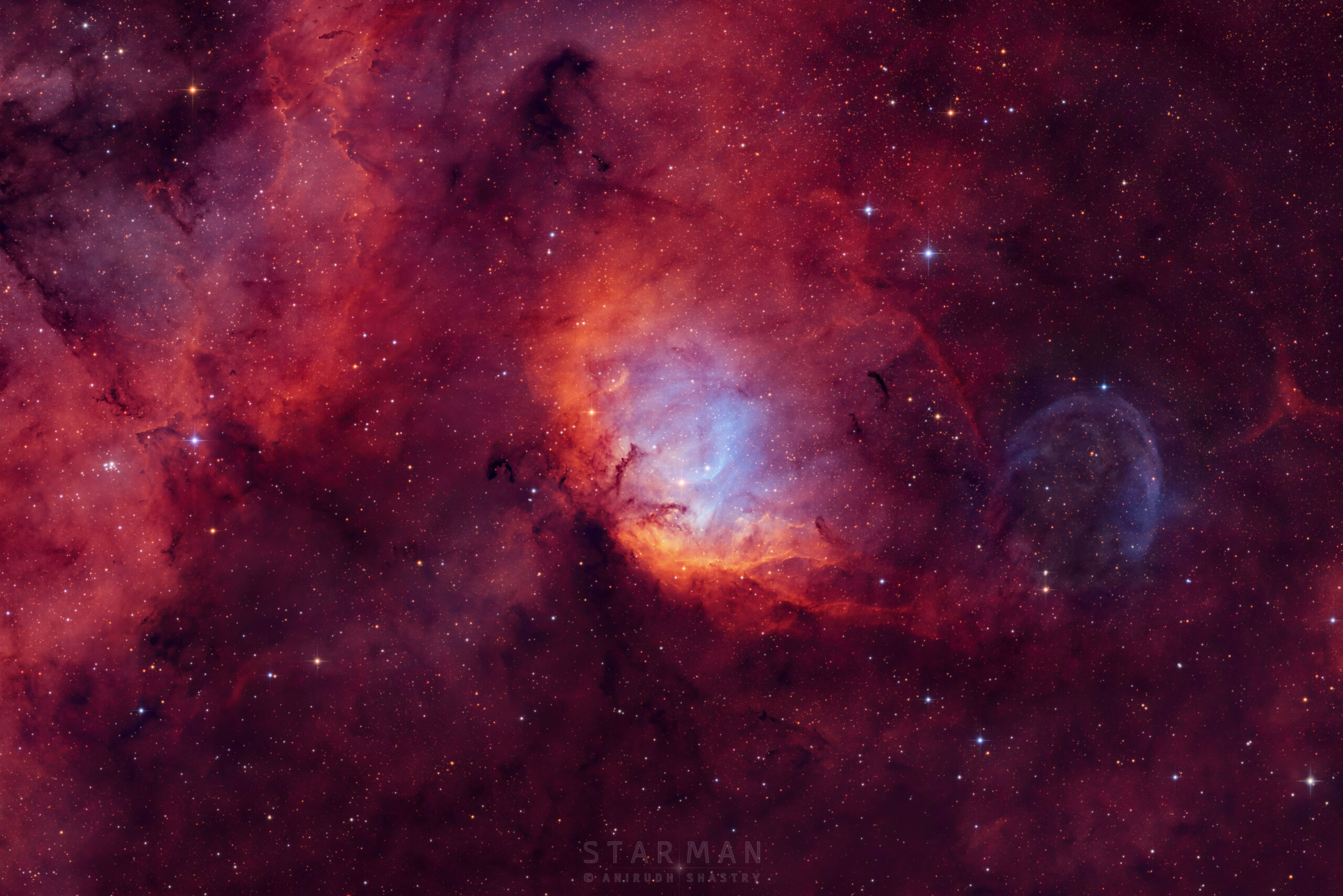
more...
Bhekizizwe Joseph Shabalala (28 August 1940 – 11 February 2020) was a South African singer and musician who was the founder and musical director of the choral group Ladysmith Black Mambazo.
Bhekizizwe Joseph Shabalala was born in the town of Ladysmith (eMnambithi district) in the KwaZulu-Natal region of South Africa. His parents, Jonathan Mluwane Shabalala and Nomandla Elina Shabalala, raised Joseph and his six siblings on a white-owned farm called Tugela. His father died in the late 1940s; Joseph, being the eldest, had to take care of the family. He left the farm, however, in 1958 to search for work in the nearby city of Durban.
more...
Joseph Osborn (August 28, 1937 – December 14, 2018) was an American bass guitar player known for his work as a session musician in Los Angeles with the Wrecking Crew and in Nashville with the A-Team of studio musicians during the 1960s through the 1980.
Osborn began his career working in local clubs, then played on a hit record by singer Dale Hawkins. He moved to Las Vegas at age 20, and spent a year playing backup for country singer Bob Luman. With legendary guitar player Roy Buchanan among his bandmates, Osborn switched from guitar to electric bass. In 1960, with Allen “Puddler” Harris, a native of Franklin Parish, also in northeastern Louisiana, and James Burton, originally from Webster Parish, Osborn joined pop star Ricky Nelson‘s backup band, where he spent four years. His playing on such Nelson hits as “Travelin’ Man” began attracting wider notice, and he found opportunities to branch out into studio work with artists such as Johnny Rivers.
more...Kenneth Sidney “Kenny” Drew (August 28, 1928 – August 4, 1993) was an American-Danish jazz pianist.
Drew was born on August 28, 1928, in New York City, United States, and he received piano lessons from the age of five. He attended the High School of Music & Art in Manhattan. His first recording, in 1950, was with Howard McGhee, and over the next two years Drew worked in bands led by Buddy DeFranco, Coleman Hawkins, Lester Young, and Charlie Parker, among others.
more...More Posts
- World Music with Catrin Finch and Seckou Keita
- Daily Roots with Andy Capp
- Mt Zion Shabbat for the Soul Service 1-18-19
- Echos of Freedom by Floyd Westerman
- The Cosmos with NGC 4603
- Bobby Broom Day
- Steve Grossman Day
- Al Foster Day
- World Music with Canut Reyes
- Daily Roots with the Charmers
- Echos of Freedom by W.E.B. DuBois
- The Cosmos with RCW 36
- Cyrus Chestnut Day
- Billy Harper Day
- Cedar Walton Day
- World Music with Mdou Moctar
- Daily Roots with the Creations
- Clyde Bellecourt Vigil
- Echos of Freedom by Phillis Wheatley
- The Cosmos with IC 342
