Blog
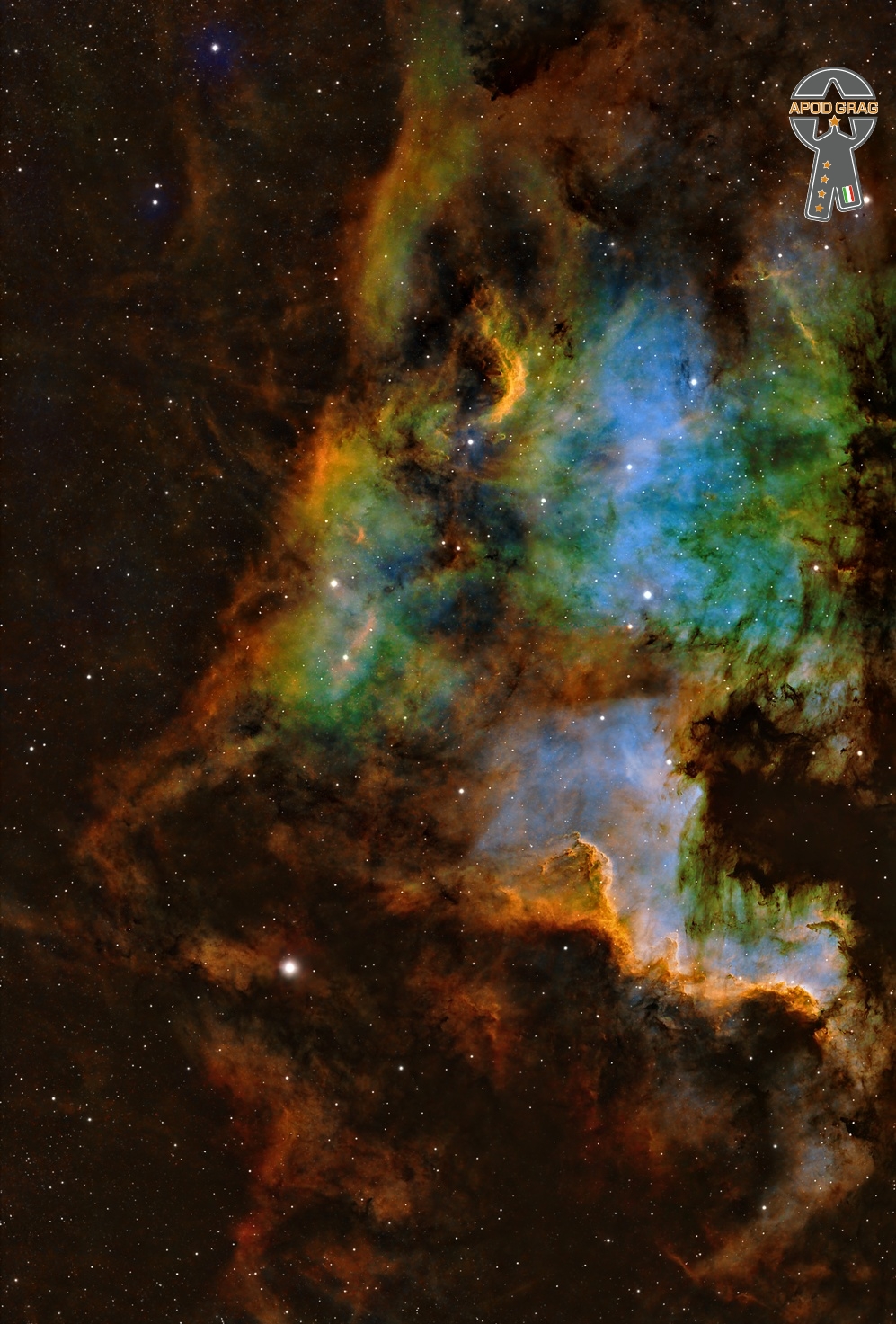
The North America Nebula (NGC 7000 or Caldwell 20) is an emission nebula in the constellation Cygnus, close to Deneb (the tail of the swan and its brightest star). It is named because its shape resembles North America. 2200ly.

Stanley Clarke (born June 30, 1951) is an American bassist, composer and founding member of Return to Forever, one of the first jazz fusion bands. Clarke gave the bass guitar a prominence it lacked in jazz-related music. He is the first jazz-fusion bassist to headline tours, sell out shows worldwide and have recordings reach gold status.
Clarke is a 5-time Grammy winner, with 15 nominations, 3 as a solo artist, 1 with the Stanley Clarke Band, and 1 with Return to Forever. Clarke was selected to become a 2022 recipient of the National Endowment for the Arts Jazz Masters Fellowship.
A Stanley Clarke electric bass is permanently on display at the National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington, D.C. Clarke was born on June 30, 1951, in Philadelphia.
more...Andrew Hill (June 30, 1931 – April 20, 2007) was an American jazz pianist and composer.
Jazz critic John Fordham described Hill as a “uniquely gifted composer, pianist and educator” although “his status remained largely inside knowledge in the jazz world for most of his career.”
Hill recorded for Blue Note Records for nearly a decade, producing a dozen albums.
Hill was born in Chicago, Illinois, to William and Hattie Hill. He had a brother, Robert, who was a singer and classical violin player. Hill took up the piano at the age of thirteen, and was encouraged by Earl Hines. As a child, he attended the University of Chicago Experimental School. He was referred by jazz composer Bill Russo to Paul Hindemith, with whom he studied informally until 1952.
more...
Lena Mary Calhoun Horne (June 30, 1917 – May 9, 2010) was an American singer, actress, dancer, and civil rights activist. Horne’s career spanned more than seventy years and covered film, television, and theatre. Horne joined the chorus of the Cotton Club at the age of sixteen and became a nightclub performer before moving on to Hollywood and Broadway.
A groundbreaking African-American performer, Horne advocated for civil rights and took part in the March on Washington in August 1963. Later she returned to her roots as a nightclub performer and continued to work on television while releasing well-received record albums. She announced her retirement in March 1980, but the next year starred in a one-woman show, Lena Horne: The Lady and Her Music, which ran for more than 300 performances on Broadway. She then toured the country in the show, earning numerous awards and accolades. Horne continued recording and performing sporadically into the 1990s, retreating from the public eye in 2000.
Lena Horne was born in Bedford–Stuyvesant, Brooklyn. Both sides of her family were biracial African Americans. She belonged to the well-educated upper stratum of Black New Yorkers at the time. She lived the first five years of her life in a brownstone at 519 Macon Street.
more...Prayers are needed and so vitally important immediately. One of my closest partners in crime Van Nixon (singer-songwriter) recently had heart surgery. And Devon Evans (percussionist) was transported back to Abbott for added complications due to a stroke. Please keep these brothers in your thoughts and prayers as they will need your empathy, goodness and healing blessings! Finally my drum buddy Steve Fine passed and we need prayers for his family & friends They are feeling a huge loss to our community!


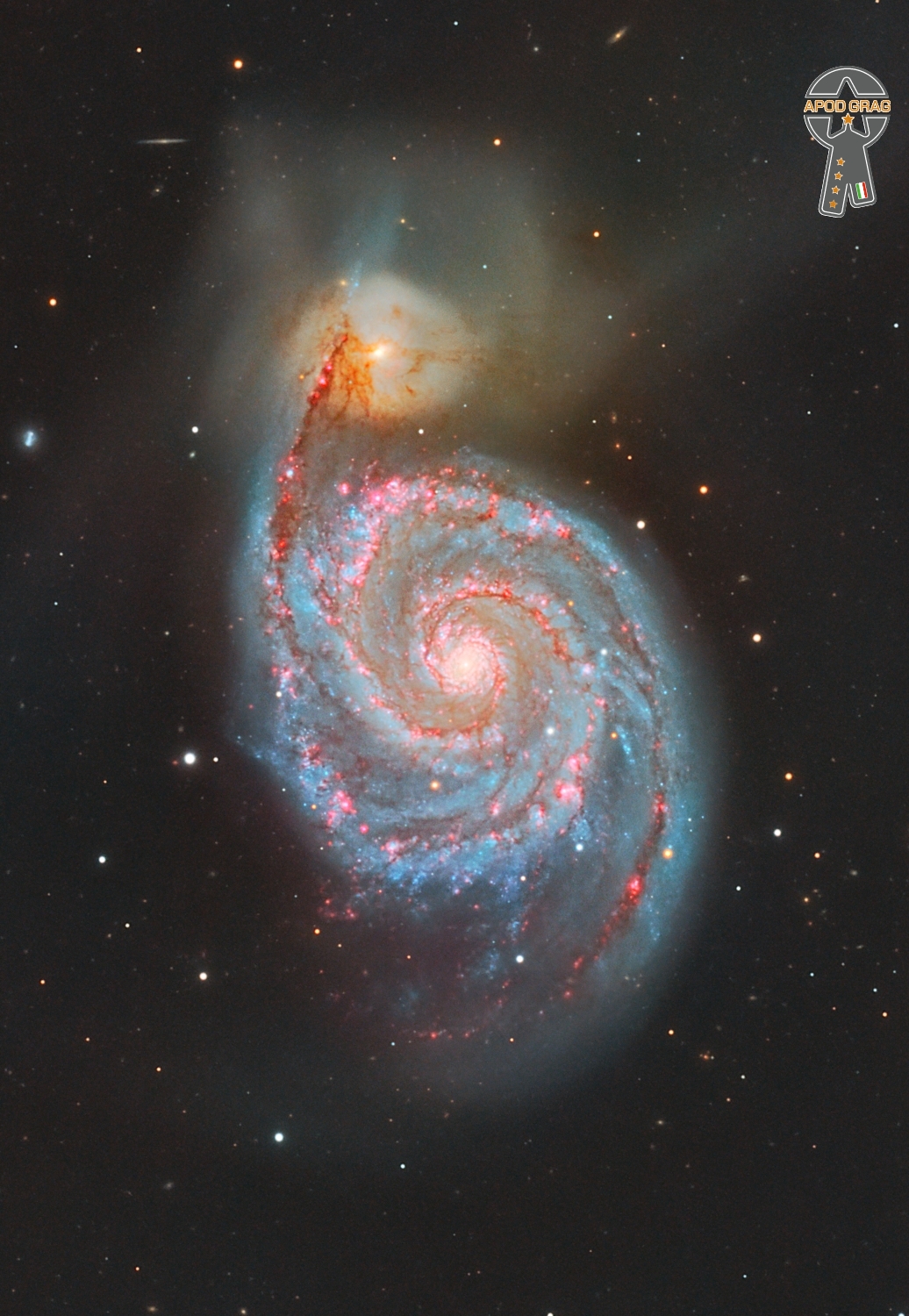
The Whirlpool Galaxy, also known as Messier 51a (M51a) or NGC 5194, is an interacting grand-design spiral galaxy with a Seyfert 2 active galactic nucleus. It lies in the constellation Canes Venatici, and was the first galaxy to be classified as a spiral galaxy. It is 7.22 megaparsecs (23.5 million light-years) away and 23.58 kiloparsecs (76,900 ly) in diameter.

Julian Priester (born June 29, 1935) is an American jazz trombonist and occasional euphoniumist. He is sometimes credited “Julian Priester Pepo Mtoto”. He has played with Sun Ra, Max Roach, Duke Ellington, John Coltrane, and Herbie Hancock.
Biography
He was born in Chicago, Illinois, United States. Priester attended Chicago’s DuSable High School, where he studied under Walter Dyett. In his teens he played with bluesand R&B artists such as Muddy Waters, and Bo Diddley, and had the opportunity to jam with jazz players such as the saxophonist Sonny Stitt.
In the early 1950s, Priester was a member of Sun Ra’s big band, recording several albums with the group, before leaving Chicago in 1956 to tour with Lionel Hampton, and he then joined Dinah Washington in 1958. The following year he settled in New York and joined the group led by drummer Max Roach,[1] who heard him playing on the Philly Joe Jones album, “Blues for Dracula” (1958). While playing in Roach’s group, Priester also recorded two albums as a leader, Keep Swingin’ and Spiritsville, both of which were recorded and released by Riverside (the latter by their Jazzland subsidiary) in 1960.
more...Eva Narcissus Boyd (June 29, 1943 – April 10, 2003), known by the stage name of Little Eva, was an American singer, well known for her 1962 hit “The Loco-Motion“.
Boyd was born in Belhaven, North Carolina in 1943 and had twelve siblings. At the age of fifteen, she moved to the Brighton Beach section of Brooklyn, New York. As a teenager, Boyd worked as a maid and earned extra money as a babysitter for songwriters Carole King and Gerry Goffin (including for the young Louise Goffin).
more...Bernard Herrmann (born Maximillian Herman; June 29, 1911 – December 24, 1975 NY, NY) was an American composer and conductor best known for his work in composing for films. As a conductor, he championed the music of lesser-known composers. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest film composers. Alex Rosswrites that “Over four decades, he revolutionized movie scoring by abandoning the illustrative musical techniques that dominated Hollywood in the 1930s and imposing his own peculiar harmonic and rhythmic vocabulary.”
An Academy Award-winner for The Devil and Daniel Webster(1941), Herrmann is known for his collaborations with Alfred Hitchcock, notably The Man Who Knew Too Much (1956) (where he makes a cameo as the conductor at Royal Albert Hall), Vertigo(1958), North by Northwest (1959), Psycho (1960), The Birds(1963) (as “sound consultant”) and Marnie (1964). He worked in radio drama, composing for Orson Welles‘s The Mercury Theater on the Air, and his first film score was for Welles’s film debut, Citizen Kane (1941). His other credits include Jane Eyre (1943), Anna and the King of Siam (1946), The Ghost and Mrs. Muir(1947), The Day the Earth Stood Still (1951), Cape Fear (1962), Fahrenheit 451 (1966) and Twisted Nerve (1968). Herrmann scored films that were inspired by Hitchcock, like François Truffaut‘s The Bride Wore Black (1968) and Brian De Palma‘s Sisters (1972) and Obsession (1976). He composed the scores for several fantasy films by Ray Harryhausen, and composed for television, including Have Gun – Will Travel and Rod Serling‘s The Twilight Zone. His last score, recorded shortly before his death, was for Martin Scorsese‘s Taxi Driver (1976).
more...
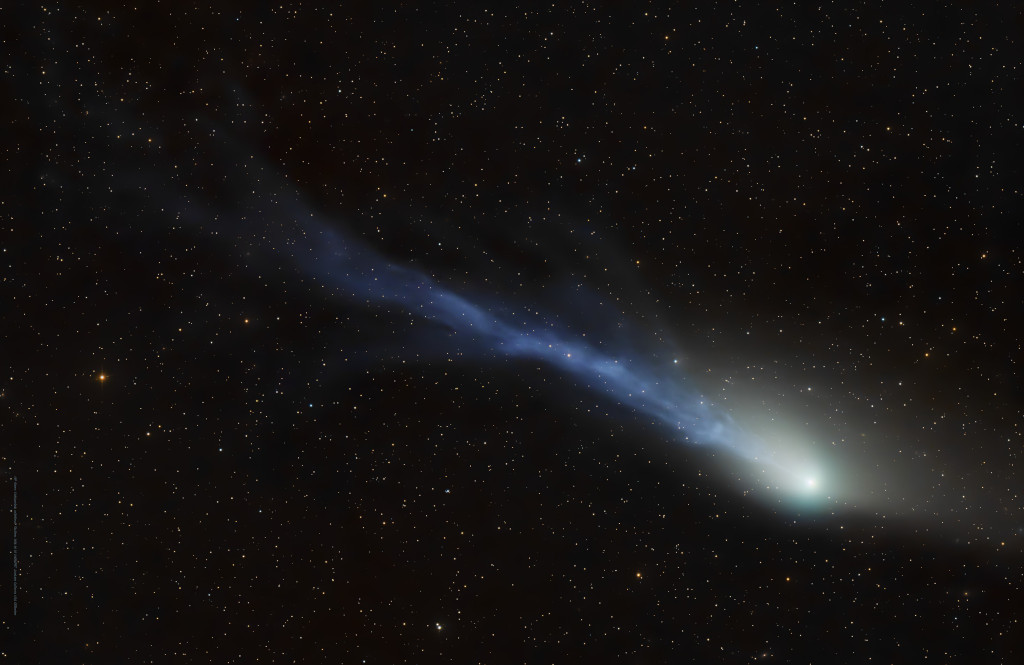
Comet 13P/Olbers is returning to the inner Solar System after 68 years. The periodic, Halley-type comet will reach its next perihelion or closest approach to the Sun on June 30 and has become a target for binocular viewing low in planet Earth’s northern hemisphere night skies. But this sharp telescopic image of 13P is composed of stacked exposures made on the night of June 25. It easily reveals shifting details in the bright comet’s torn and tattered ion tail buffeted by the wind from an active Sun, along with a broad, fanned-out dust tail and slightly greenish coma. The frame spans over two degrees across a background of faint stars toward the constellation Lynx.

More Posts
- Keith Godchaux Day
- Commander Cody Day
- Phil Upchurch Day
- Carmell Jones Day
- World Music with Pedro Sierra
- Daily Roots with Lee Perry & Jah Lloyd
- The Cosmos with NGC 4691
- Knoel Scott Day
- Tatá Güines Day
- Dudu Pukwana Day
- Screamin Jay Hawkins Day
- World Music with Nusrat Fateh Ali Khan
- Daily Roots with Denzil Dennis
- The Cosmos with NGC 70
- Chico Freeman Day
- Vince Guaraldi Day
- Ben Riley Day
- Joe Morello Day
- World Music with Lingling Yu & Guo Gan
- Daily Roots with Rula Brown