Blog
Ian Ernest Gilmore Evans (né Green; May 13, 1912 – March 20, 1988) was a Canadian–American jazzpianist, arranger, composer and bandleader. He is widely recognized as one of the greatest orchestrators in jazz, playing an important role in the development of cool jazz, modal jazz, free jazz, and jazz fusion. He is best known for his acclaimed collaborations with Miles Davis.
more...The third week of performances for The Defeat of Jesse James musical at the History Theater. Friday 730pm show. Music by Raymond Berg, Kam Markworth. Christian Wheeler and mick LaBriola. https://www.historytheatre.com/2022-2023/defeat-jesse-james

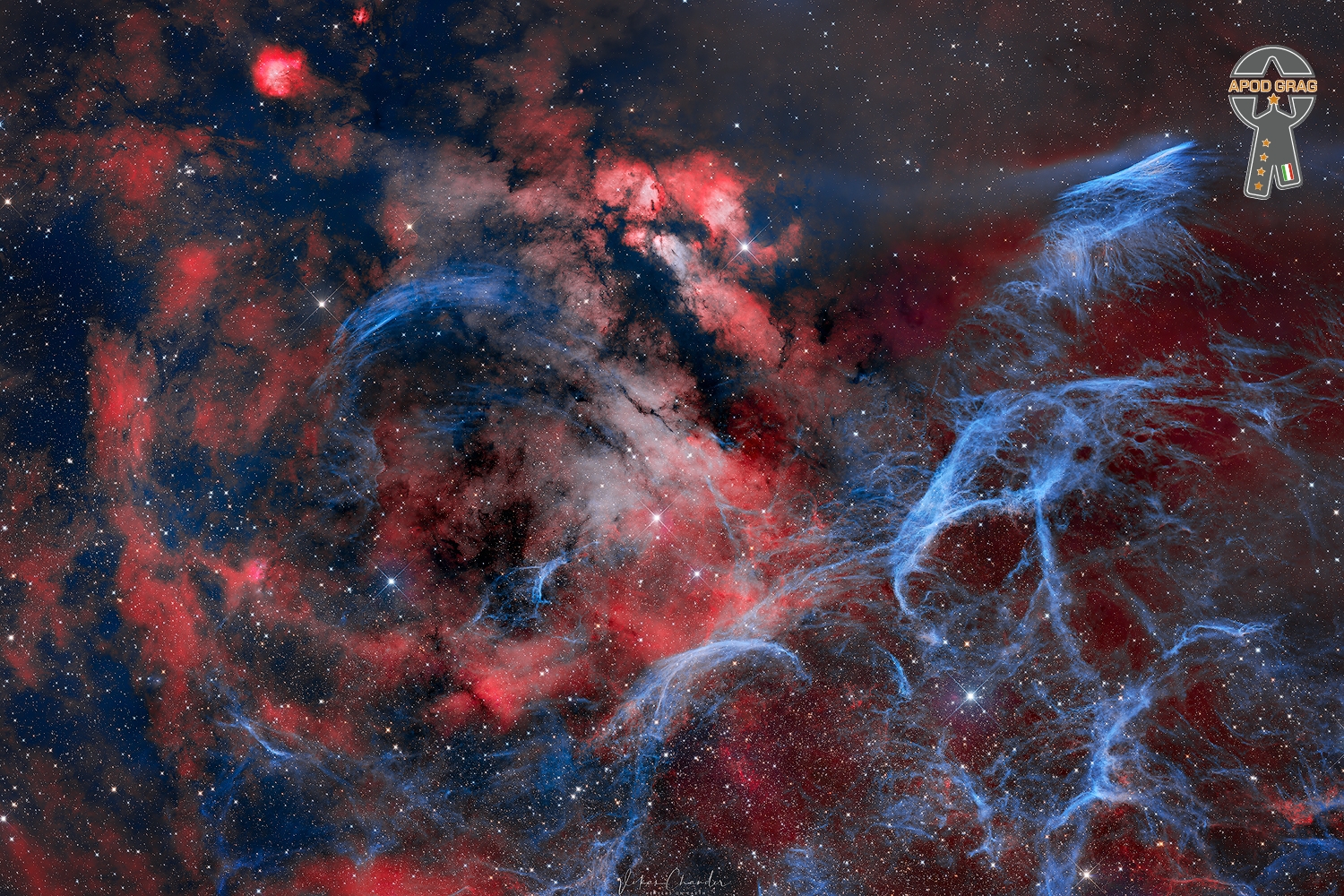
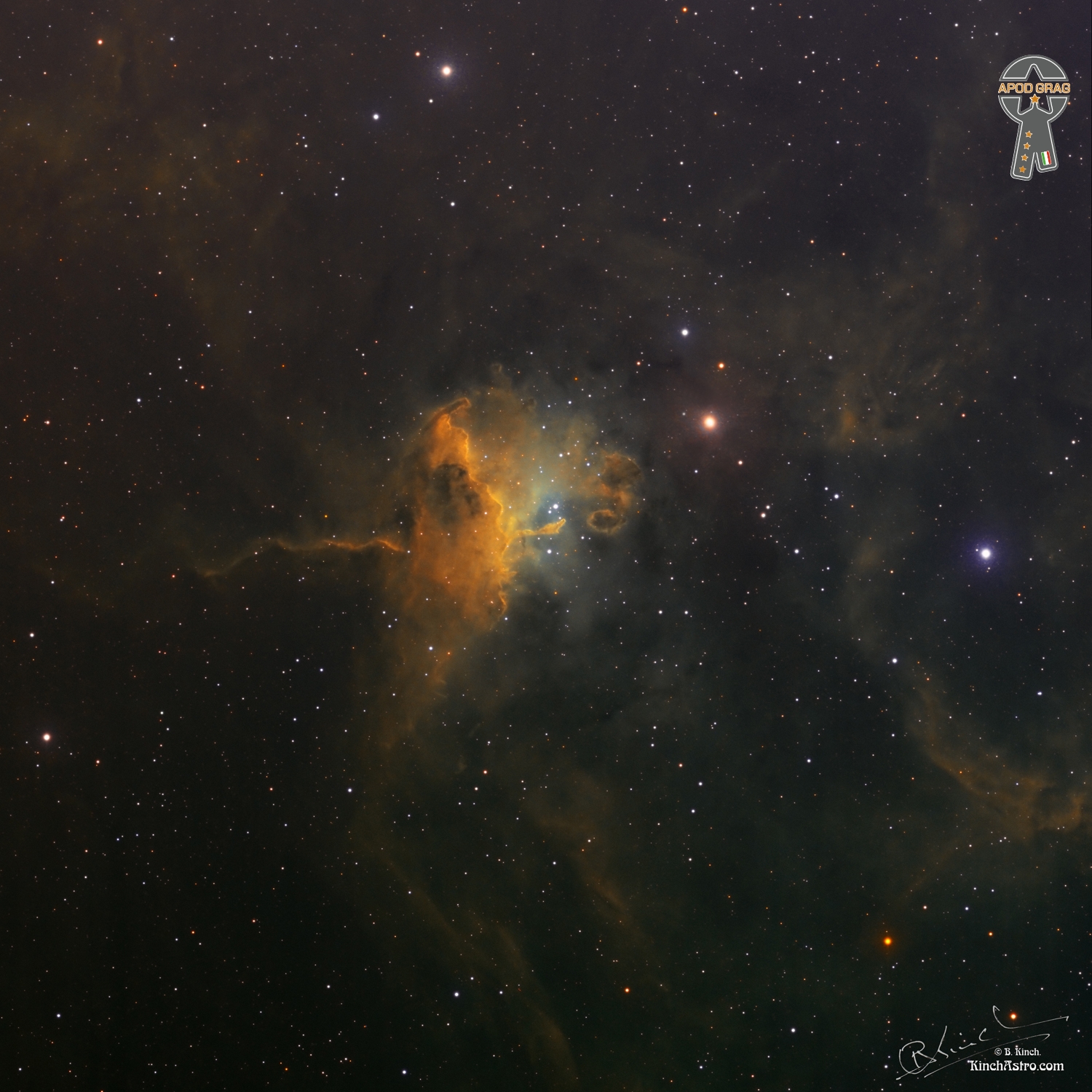
This 2 panel mosaic spans about 6 degrees across a widefield region in the constellation of Vela. The blue gas clouds are from the remnants of the Vela Supernova and one can see NGC 2736, or the Pencil Nebula glow brightly on the right of the frame. The nebula’s shape suggests that it is part of a supernova shock wave that has encountered a region of dense gas. It is this interaction that causes the nebula to glow and form ripples. RCW 38 dominates the center of the frame and is an HII region with dark clouds enshrouding recently formed stars. The gases and clouds come together to form a rich tapestry of glowing reds and dark blacks. Also seen in the image are RCW 39 and 40 amongst lots of other fine details…..

Stephen Lawrence Winwood (born 12 May 1948) is an English musician, singer and songwriter whose genres include blue-eyed soul, rhythm and blues, blues rock and pop rock. Though primarily a guitarist, keyboard player and vocalist prominent for his distinctive, soulful high tenor voice, Winwood plays other instruments proficiently, including drums, mandolin, bass and saxophone.
Winwood was an integral member of three groups of the 1960s and 1970s: the Spencer Davis Group, Trafficand Blind Faith. Beginning in the 1980s, his solo career flourished and he had a number of hit singles, including “While You See a Chance” (1980) from the album Arc of a Diver and “Valerie” (1982) from Talking Back to the Night (“Valerie” became a hit when it was re-released with a remix from Winwood’s 1987 compilation album Chronicles). His 1986 album Back in the High Life marked his career zenith, with hit singles including “Back in the High Life Again“, “The Finer Things” and the US Billboard Hot 100 number one hit “Higher Love“. He found the top of the Hot 100 again with “Roll With It” (1988) from the album of the same name, with “Holding On” also charting highly the same year. While his hit singles ceased at the end of the 1980s, he continued to release new albums up to 2008, when Nine Lives, his latest album, was released.
Winwood was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame as a member of Traffic in 2004. In 2005, Winwood was honoured as a BMI Icon at the annual BMI London Awards for his “enduring influence on generations of music makers.” In 2008, Rolling Stone ranked Winwood No. 33 in its 100 Greatest Singers of All Time. Winwood has won two Grammy Awards. He was nominated twice for a Brit Award for Best British Male Artist: 1988 and 1989. In 2011, he received the Ivor Novello Award from the British Academy of Songwriters, Composers and Authors for Outstanding Song Collection.
more...Gary George Peacock (May 12, 1935 – September 4, 2020) was an American jazz double bassist. He recorded a dozen albums under his own name, and also performed and recorded with major jazz figures such as avant garde saxophonist Albert Ayler, pianists Bill Evans, Paul Bley and Marilyn Crispell, and as a part of Keith Jarrett’s “Standards Trio” with drummer Jack DeJohnette. The trio existed for over thirty years, and recorded over twenty albums together. DeJohnette once stated that he admired Peacock’s “sound, choice of notes, and, above all, the buoyancy of his playing.” Marilyn Crispell called Peacock a “sensitive musician with a great harmonic sense.”
Peacock was born in Burley, Idaho, on May 12, 1935; his father worked as a business consultant for grocery stores, and his mother was a homemaker. He grew up in Yakima, Washington, where he attended Yakima Senior High School, now called A.C. Davis High School. His earliest musical experiences involved playing piano, trumpet, and drums. When he was 15, he heard live jazz for the first time, attending a Jazz at the Philharmonic concert featuring Oscar Peterson and Ray Brown. Peacock graduated in 1953; while playing for his class, he had a profound experience, stating: “I was playing the drums, and had the experience of being played rather than playing… I realized that something transformative had happened… and there was this certainty. From the bottom of my feet to the top of my head, it was totally clear: ‘Oh, this is the direction to go.’
more...Gerald Foster Wiggins (May 12, 1922 – July 13, 2008) was an American jazz pianist and organist. Wiggins was born in New York City on May 12, 1922. He studied classical music, but switched to jazz in his teens.
Wiggins began as a professional career as a musician accompanying comedian Stepin Fetchit. Wiggins worked with Louis Armstrong and Benny Carter. He was in the military from 1944 to 1946. In the 1940s, he moved to Los Angeles, where he played music for television and film. He also worked with singers like Lena Horne (1950–51), Kay Starr, and Eartha Kitt. In 1960, his best recording as an organist appeared, Wiggin’ Out, known for the quality of its music and fresh, clear sound. He recorded another LP at the organ with saxophonist Teddy Edwards. “In the 1960s he worked as a music director and vocal coach in film studios,” including “a lengthy stint as vocal coach for Marilyn Monroe.” In the 1970s he often collaborated with vocalist Helen Humes.
more...Rumba Flamenca may be the most widely known and least understood of the flamenco forms. Most of the world first heard Rumba Flamenca via the Gypsy Kings in songs like Bamboleo and Volare. In Spain, Rumba Flamenca has come in and out of style since Niña de los Peines first recorded a Rumba in 1918. Since then, artists such as El Chaqueta, Chano Lobato and Miguel Vargas Jiménez (Bambino) have become closely associated with the form. Thanks to the Gypsy Kings and their countless imitators, and to recordings like Paco de Lucia’s Entre Dos Aguas, Rumba Flamenca has become essentially a two guitar form, with one guitar playing a solo melody while the other plays the harmony with the characteristic rumba rasgueado pattern, this often assisted with bass and percussion.
more...
The third week of performances for The Defeat of Jesse James musical at the History Theater. Two Thursday May 11th show with a 10am matinee and a 730pm show. Music by Raymond Berg, Kam Markworth. Christian Wheeler and mick LaBriola. https://www.historytheatre.com/2022-2023/defeat-jesse-james

IC 417 was discovered on 25 September 1892 by the German astronomer Max Wolf. It is an emission and reflection nebula with an embedded star cluster, which is part of an extensive H-II nebula complex and star formation region in the Auriga constellation. The age is estimated to be less than 3 million years.
Claude Hudson “Butch” Trucks (May 11, 1947 – January 24, 2017) was an American drummer. He was best known as a founding member of The Allman Brothers Band, for which he was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1995. Trucks was born and raised in Jacksonville, Florida. He played in various groups before forming the 31st of February while at Florida State University in the mid-1960s. He joined the Allman Brothers Band in 1969. Their 1971 live release, At Fillmore East, represented an artistic and commercial breakthrough. The group became one of the most popular bands of the era on the strength of their live performances and several successful albums. Though the band broke up and re-formed various times, Trucks remained a constant in their 45-year career. Trucks died of a self-inflicted gunshot wound on January 24, 2017. Claude Hudson Trucks was born on May 11, 1947, in Jacksonville, Florida. His father was an optician. He first discovered his talent at drumming when prompted by a band director at Ribault Junior High: “The band director gave three of us sticks and said, ‘Play me something,'” he recalled. He then attended Jean Ribault High School, where he was made first chair as a freshman.
more...Carla Bley (born Lovella May Borg; May 11, 1936) is an American jazz composer, pianist, organist and bandleader. An important figure in the free jazz movement of the 1960s, she is perhaps best known for her jazz opera Escalator over the Hill (released as a triple LP set), as well as a book of compositions that have been performed by many other artists, including Gary Burton, Jimmy Giuffre, George Russell, Art Farmer, John Scofield and her ex-husband Paul Bley.
Bley was born in Oakland, California, United States, to Emil Borg (1899–1990), a piano teacher and church choirmaster, who encouraged her to sing and to learn to play the piano, and Arline Anderson (1907–1944), who died when Bley was eight years old. After giving up the church to immerse herself in roller skating at the age of fourteen, she moved to New York at seventeen and became a cigarette girl at Birdland, where she met jazz pianist Paul Bley. She toured with him under the name Karen Borg, before she changed her name in 1957 to Carla Borg and married Paul Bley the same year adopting the Bley name. He encouraged her to start composing. The couple divorced in 1967, but she kept his surname professionally.
more...Carlos Eduardo Lyra Barbosa (born 11 May 1933) is a Brazilian singer and composer of numerous bossa nova and Música popular brasileira classics. He and Antonio Carlos Jobim, were the first two music composers, together with lyricists Vinicius de Moraes and Ronaldo Boscoli, to be recorded by João Gilbertoon his first LP entitled Chega de Saudade (1959), which was called the first generation of Bossa Nova.
more...Frederick Roach (May 11, 1931 – October 3, 1980) was an American soul jazz Hammond B3 organist born in The Bronx, New York, United States. Roach’s first commercial recordings were with saxophonist Ike Quebec for Blue Note Records in the fall of 1961. These sessions produced Quebec’s albums Heavy Soul and It Might as Well Be Spring. In March of 1962, Roach recorded as a backing musician for the Thunderbird album by Willis Jackson. From 1962-64, Roach recorded 5 albums as a leader for Blue Note, and also recorded with Donald Byrd on the album I’m Tryin’ to Get Home. Roach’s original writing, steady basslines, and highly musical fleet-fingered right hand set him apart From 1966-67 he recorded three more albums as a leader for Prestige Records, which are in a more commercial vein than his Blue Note dates. Roach’s Prestige albums were his last commercial recordings.
Dean Rudland, in the liner notes to a CD reissue of Roach’s Prestige albums Soul Book and Mocha Motion, wrote that Roach moved to Paris in the 1970s and worked as an arranger for Oliver Lake’s big band. Roach can be heard reciting one of his own poems on a 1974 album by jazz bassist Bob Reid titled Africa Is Calling Me: A Modern Day Black Opera (Kwela Records, 30K010), which was recorded in Paris and featured Oliver Lake.
Roach reportedly later moved to California to work in the film industry. He suffered a heart attack and died in 1980.
more...Seán Keane, one of the finest Irish folk music fiddlers, passed away on May 7, 2023. He was best known as the fiddler for the influential Irish and Celtic music band, The Chieftains.
Keane grew up in Drimnagh, a suburb of Dublin. He was born into a family with a rich musical heritage. His parents, both accomplished fiddle players, were revered members of the traditional music communities in County Longford and County Clare. Their home was a frequent destination for a multitude of traveling traditional players from all across Ireland, who performed in the bustling streets of Dublin. The Keane household became a veritable landmark in Dublin’s traditional music scene in the 1950s and 1960s, and it was here that Seán and his brother James, an accordion player, honed their craft.
Their summer trips to Longford and Clare further fueled their passion for traditional music and introduced them to an array of styles and techniques. These experiences were instrumental in shaping Seán’s musical direction and creative expression.
In 1968, Seán Keane made his foray into the world of professional music by joining the acclaimed Irish traditional music band, The Chieftains. With his virtuosic fiddle playing and his deep-seated passion for traditional music, he quickly became an integral member of the group. Seán’s contributions to The Chieftains’ discography, which spans several decades, are nothing short of remarkable.
more...https://www.legacy.com/us/obituaries/legacyremembers/isaac-russell-hart-obituary?id=51810909&fbclid=IwAR0VTSOvYdh3PApKtv7Vf0TseMNcrFGp7ryqxgHgo2YmlErm_WB_ft_E7qo

Fourth in a nine part series of Rhythm Roots Workshops at Cerenity Humboldt
Senior Care April 19th thru June 14th. https://cerenityseniorcare.org/cerenity-senior-care-humboldt-st-paul-mn/ in St Paul.

More Posts
- Flamenco Fridays with Sabicas
- Daily Roots with Anthony B
- Music for Surviving the Pandemic and Realizing Racial Justice
- The Cosmos with NGC 1300
- Jamaaladeen Tacuma Day
- Bernard Purdie
- Shelly Manne Day
- Hazel Scott Day
- Clarence Pinetop Smith Day
- World Music with Don Pío Alvarado
- Daily Roots with Slyford Walker
- Music for Surviving the Pandemic and Realizing Racial Justice
- The Cosmos with M42
- Gary Thomas Day
- Maxi Priest Day
- João Gilberto Day
- Howlin’ Wolf Day
- World Music with Wardruna
- Daily Roots with Coco Tea
- Music for Surviving the Pandemic & Realizing Racial Justice