Blog
The final performance of RENT the musical by Theatre 55 performing at the Gremlin Theater in St Paul. Saturday February 11th 2023 at 7pm. Music by Shirley Mier, Jamie Carter, Lyra Olson and mick laBriola.

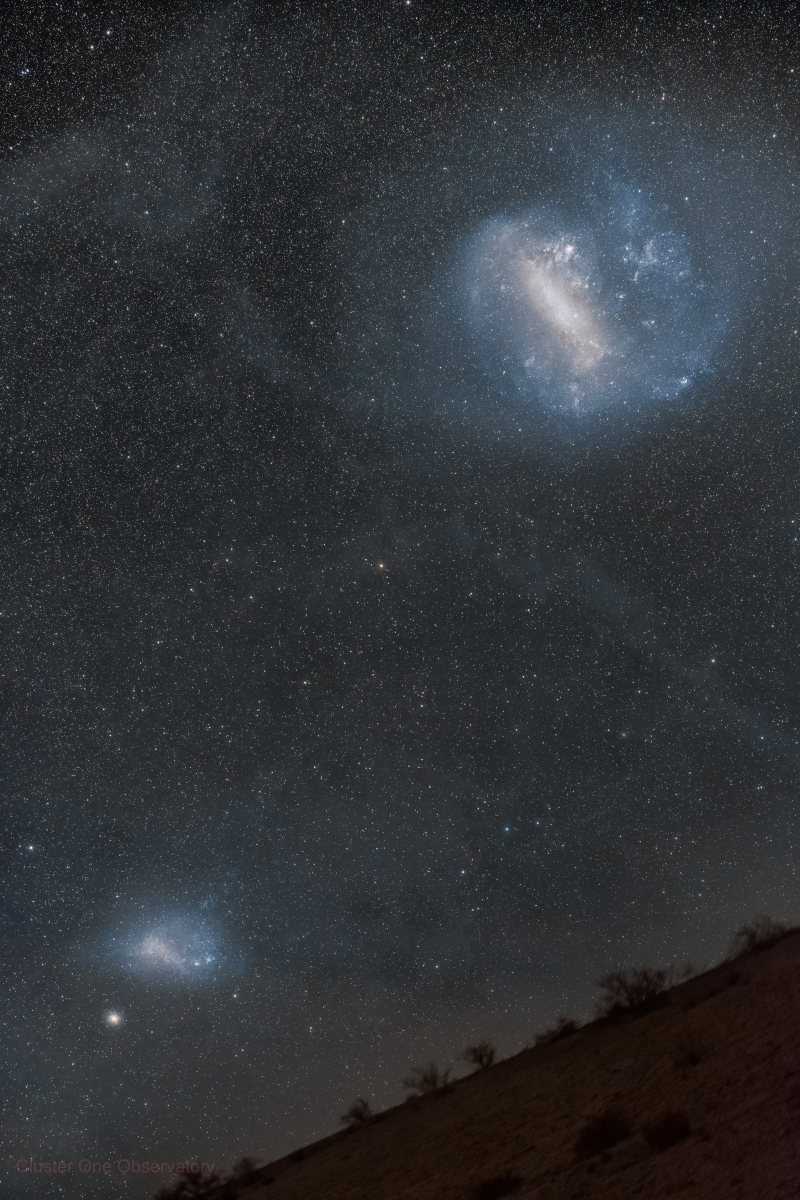
The two prominent clouds in this Chilean Atacama Desert skyscape captured on January 21 actually lie beyond our Milky Way galaxy. Known as the Large and the Small Magellanic Clouds they are so named for the 16th century Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan, leader of the first circumnavigation of planet Earth. Famous jewels of southern hemisphere skies, they are the brightest satellite galaxies of the Milky Way. The larger cloud is some 160,000 light-years, and the smaller 210,000 light-years distant. While both are irregular dwarf galaxies in their own right, they exhibit central barred structures in the deep wide-angle view. Wide and deep exposures also reveal faint dusty galactic cirrus nebulae and the imprints of gravitational tidal interactions between the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds.

Didier Lockwood (11 February 1956 – 18 February 2018) was a French violinist. He played in the French rock band Magma in the 1970s, and was known for his use of electric amplification and his experimentation with different sounds on the electric violin.
In 1979, Lockwood released his first album as a leader, New World, and recorded more than 20 albums.In 1994, he moved to New York City for two years. During that time he recorded two albums, New York Rendez Vous and Storyboard. Lockwood’s influences include violinist Jean-Luc Ponty. He started playing electric violin after hearing Ponty on the album King Kong: Jean-Luc Ponty Plays the Music of Frank Zappa. Another important influence was Frenchman Stéphane Grappelli. In 2000, Lockwood recorded a tribute album to Grappelli.
more...Little Johnny Taylor (born Johnny Lamont Merrett; February 11, 1943 – May 17, 2002) was an American blues and soul singer. He made recordings throughout the 1960s and 1970s, and continued public performances through the 1980s and 1990s.
Born in Gregory, Arkansas, United States, he is frequently confused with his contemporary and near namesake Johnnie Taylor, especially since the latter made a cover version of the song that Little Johnny Taylor was most famous for, “Part Time Love” (1963), and the fact that both men began their careers as gospel singers.
Little Johnny Taylor moved to Los Angeles in 1950, and sang with the Mighty Clouds of Joy before moving into secular music. Influenced by Little Willie John, he first recorded as an R&B artist for the Swingin’ record label.
more...Sérgio Santos Mendes (Brazilian Portuguese: [ˈsɛʁʒju ˈsɐ̃tuz ˈmẽdʒis]; born February 11, 1941) is a Brazilian musician. His career took off with worldwide hits by his group Brasil ’66. He has over 55 releases and plays bossa nova heavily crossed with jazz and funk. He was nominated for an Oscar for Best Original Song in 2012 as co-writer of the song “Real in Rio” from the animated film Rio.
Mendes is a unique example of a Brazilian musician primarily known in the United States, where his albums were recorded and where most of his touring took place.
Mendes is married to Gracinha Leporace, who has performed with him since the early 1970s. Mendes has also collaborated with many artists through the years, including The Black Eyed Peas, with whom he re-recorded in 2006 a version of his breakthrough hit “Mas que Nada“.
more...Vincent Eugene Craddock (February 11, 1935 – October 12, 1971), known as Gene Vincent, was an American musician who pioneered the styles of rockabilly and rock and roll. His 1956 top ten hit with his backing band the Blue Caps, “Be-Bop-a-Lula“, is considered a significant early example of rockabilly. His chart career was brief, especially in his home country of the US, where he notched three top 40 hits in 1956 and ’57, and never charted in the top 100 again. In the UK, he was a somewhat bigger star, racking up eight top 40 hits from 1956 to 1961.
Vincent was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame and the Rockabilly Hall of Fame. He is sometimes referred to by his somewhat unusual nickname/moniker the “Screaming End”.
Craddock was born February 11, 1935, in Norfolk, Virginia, to Mary Louise and Ezekiah Jackson Craddock. His musical influences included country, rhythm and blues, and gospel. His favorite composition was Beethoven’s Egmont overture. He showed his first real interest in music while his family lived in Munden Point (now Virginia Beach), in Princess Anne County, Virginia, near the North Carolina line, where they ran a country store. He received his first guitar at the age of twelve as a gift from a friend.
more...The 6th installment of RENT by Theatre 55 performing at the Gremlin Theater Friday February 10th 2023 7pm. Music by Shirley Mier, Jamie Carter, Lyra Olson and mick laBriola.

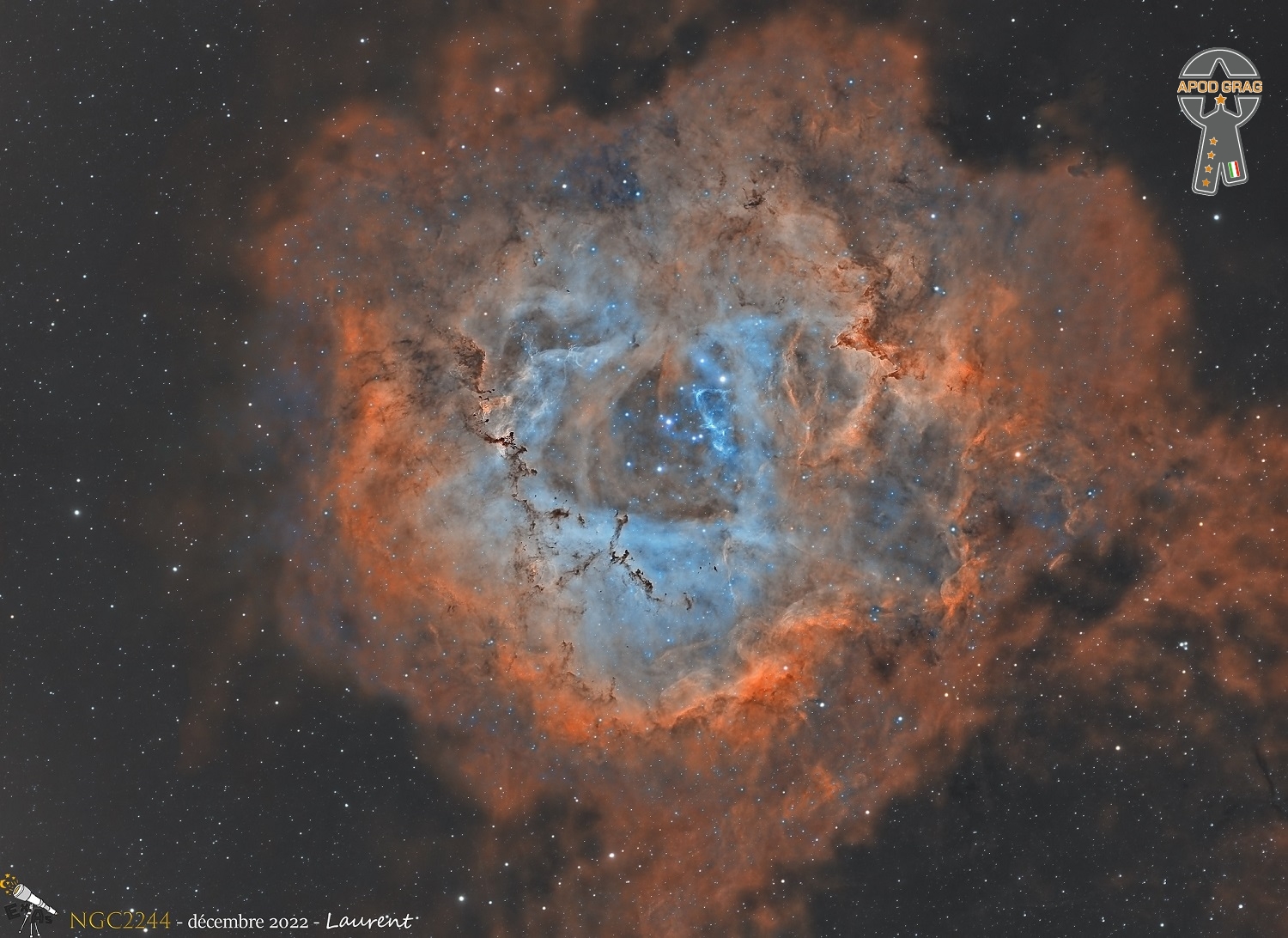
NGC 2244 (also known as Caldwell 50 or the Satellite Cluster) is an open cluster in the Rosette Nebula, which is located in the constellation Monoceros. This cluster has several O-type stars, super hot stars that generate large amounts of radiation and stellar wind.
The age of this cluster has been estimated to be less than 5 million years. The brightest star in the cluster is 12 Monocerotis, a foreground K-class giant. The two brightest members of the cluster are HD 46223 of spectral class O4V, 400,000 times brighter than the Sun, and approximately 50 times more massive, and HD 46150, whose spectral type is O5V, has a luminosity 450,000 time larger than that of our star, and is up to 60 times more massive, but it may actually be a double star.

Rufus Reid (born February 10, 1944, in Atlanta, Georgia) is an American jazz bassist, educator, and composer.
Reid was raised in Sacramento, California, where he played the trumpet through junior high and high school. Upon graduation from Sacramento High School, he entered the United States Air Force as a trumpet player. During that period he began to be seriously interested in the bass.
After fulfilling his duties in the military, Rufus had decided he wanted to pursue a career as a professional bassist. He moved to Seattle, Washington, where he began serious study with James Harnett of the Seattle Symphony. He continued his education at Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois, where he studied with Warren Benfield and principal bassist, Joseph Guastefeste, both of the Chicago Symphony. He graduated in 1971 with a Bachelor of Music Degree as a Performance Major on the Double Bass.
more...Emmanuel N’Djoké “Manu” Dibango (12 December 1933 – 24 March 2020) was a Cameroonian musician and songwriter who played saxophone and vibraphone. He developed a musical style fusing jazz, funk, and traditional Cameroonian music. His father was a member of the Yabassi ethnic group, while his mother was a Duala. He was best known for his 1972 single “Soul Makossa“. He died from COVID-19 on 24 March 2020.
Emmanuel “Manu” Dibango was born in Douala, Cameroon in 1933. His father, Michel Manfred N’Djoké Dibango, was a civil servant. Son of a farmer, he met his wife travelling by pirogue to her residence, Douala. Emmanuel’s mother was a fashion designer, running her own small business. Both her ethnic group, the Douala, and his, the Yabassi, viewed this union of different ethnic groups with some disdain.Dibango had only a stepbrother from his father’s previous marriage, who was four years older than him.In Cameroon, one’s ethnicity is dictated by one’s father, though Dibango wrote in his autobiography, Three Kilos of Coffee, that he had “never been able to identify completely with either of [his] parents”.
more...Jerrald King Goldsmith (February 10, 1929 – July 21, 2004) was an American composer and conductorknown for his work in film and television scoring. He composed scores for five films in the Star Trek franchise and three in the Rambo franchise, as well as for Logan’s Run, Planet of the Apes, Tora! Tora! Tora!, Patton, Chinatown, Alien, Poltergeist, Gremlins, Hoosiers, Total Recall, Air Force One, L.A. Confidential, Mulan, and The Mummy. He also composed the fanfares accompanying the production logos used by multiple major film studios, and music for the Disney attraction Soarin’.
He collaborated with directors including Robert Wise, Howard Hawks, Otto Preminger, Joe Dante, Richard Donner, Ridley Scott, Steven Spielberg, Paul Verhoeven, and Franklin J. Schaffner. His work for Donner and Scott also involved a rejected score for Timeline and a controversially edited score for Alien, where music by Howard Hanson replaced Goldsmith’s end titles and Goldsmith’s own work on Freud: The Secret Passionwas used without his approval in several scenes.
Goldsmith was nominated for six Grammy Awards, five Primetime Emmy Awards, nine Golden Globe Awards, four British Academy Film Awards, and eighteen Academy Awards (winning in 1976 for The Omen).
Goldsmith was born February 10, 1929, in Los Angeles, California. His family was Romanian Jewish. His parents were Tessa (née Rappaport), a school teacher, and Morris Goldsmith, a structural engineer. He started playing piano at age six, but only “got serious” by the time he was eleven. At age thirteen, he studied piano privately with concert pianist and educator Jakob Gimpel (whom Goldsmith would later employ to perform piano solos in his score to The Mephisto Waltz) and by the age of sixteen he was studying both theory and counterpoint under Italian composer Mario Castelnuovo-Tedesco, who also tutored such noteworthy composers and musicians as Henry Mancini, Nelson Riddle, Herman Stein, André Previn, Marty Paich, and John Williams.
more...“The King of the Savoy” reigned supreme over jazz drummers in New York in the 1930’s. He was the consummate showman and with his fluid and rhythmic style, was perfectly suited for the swing era. He raised the standard for drummer awareness, and paved the way for drummer led bands.
Born in Baltimore, Feb. 10, 1909, William Henry Webb, was an unlikely candidate to become a jazz drummer. Stricken with spinal tuberculosis, he was left with a hunched back, and little use of his legs. He took up drumming as a way to relieve joint stiffness, and never stopped. He saved enough to buy a drum set which he had fit with special pedals for his legs. He joined local band the Jazzola Orchestra, then in 1925 decided to try New York City. He sat in on sessions with Johnny Hodges, Benny Carter, and Duke Ellington, after settling in by 1926 he had his own quintet, and played for five months at the Black Bottom Club. He formed an eight piece band, playing the Paddock Club, moving next to the Savoy with his now called Harlem Stompers, and setting up there in 1927. This band grew to eleven members, and by the end of the ‘20’s they were gigging at all the major jazz clubs in the city as the Cotton Club, the Roseland, and the Strand Roof. In 1930 they toured with the “Hot Chocolate Revue”.
more...
“Mineras” is a flamenco style from the mining area of “Sierra Cartagena-La Union” and developed in the 19th century, together with the rest of “cantos minero-levantinos”. This was the result of the great migrations from Andalusia, specially from Almería.
“Minera” was originated in mid-nineteenth century, emerging as a derivation of local “fandangos”, which already existed in “Sierra de la Union” in Murcia. Creator of this “palo” was Rojo “el Alpargatero”, whose son maintained it, but adding some new variants. In the 50s, “minera” rose again after being gone for some years.
“Minera” is composed by a stanza of four or five eight-syllable verses. Main topics are mining and their workers. It is a serious song, which is difficult to be interpreted. There are two kind of “minera”: the one which is a derivation of local “fandangos” and belongs to “cantos de Levante”, more precisely to “cantes de las minas”. These latter constitute currently a very definite form of “taranta”.
Although “minera” is still present in the area where it originated, current singers do not usually include it in their performances, but some do it in their discography. It is a singing which is very closed to its native place.
more...The 5th of 7 performances of RENT by Theatre 55 at the Gremlin Theater Thursday February 9th 2023 7pm. Music provided by Shirley Mier, Jamie Carter, Lyra Olson and mick laBriola.

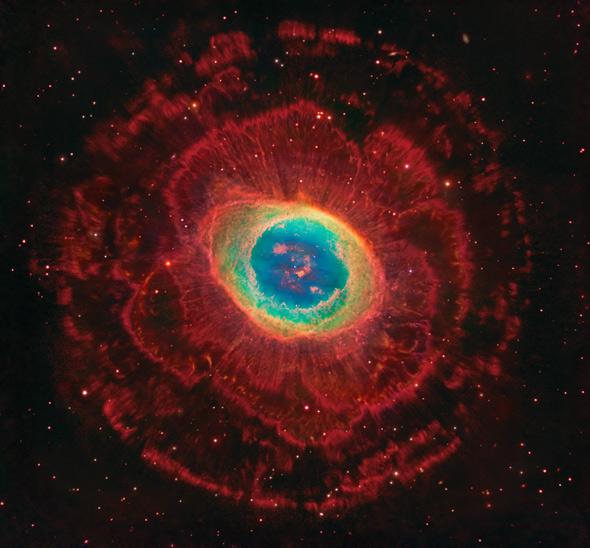
Of all the planetary nebulae in the sky, none is more celebrated than M57, the Ring Nebula. Lying about 2,400 light years away toward the constellation of Lyra, it’s bright enough to be seen in small telescopes, and when long exposures are taken, quite a lot of detail comes out.
Astrophotographer Rob Gendler knows his way around a digital astronomical image. He has been making a habit of creating incredible photographs using multiple observatories, both in space and on the ground, professional and amateur. He took observations from the Hubble Space Telescope, the Large Binocular Telescope, and the monster 8.2-meter Subaru telescope, and combined them to make a stunning image of the Ring. I literally gasped out loud when I saw this.
The Ring Nebula (also catalogued as Messier 57, M57 and NGC 6720) is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation of Lyra. Such a nebula is formed when a star, during the last stages of its evolution before becoming a white dwarf, expels a vast luminous envelope of ionized gas into the surrounding interstellar space.
more...
Carole King Klein (born Carol Joan Klein; February 9, 1942) is an American singer, songwriter, and musician who has been active since 1958, initially as one of the staff songwriters at 1650 Broadway and later as a solo artist. Regarded as one of the most significant and influential musicians of all time, King is the most successful female songwriter of the latter half of the 20th century in the US, having written or co-written 118 pop hits on the Billboard Hot 100. King also wrote 61 hits that charted in the UK, making her the most successful female songwriter on the UK singles charts between 1962 and 2005.
King’s major success began in the 1960s when she and her first husband, Gerry Goffin, wrote more than two dozen chart hits, many of which have become standards, for numerous artists. She has continued writing for other artists since then. King’s success as a performer in her own right did not come until the 1970s, when she sang her own songs, accompanying herself on the piano, in a series of albums and concerts. After experiencing commercial disappointment with her debut album Writer, King scored her breakthrough with the album Tapestry, which topped the U.S. album chart for 15 weeks in 1971 and remained on the charts for more than six years.
King has made 25 solo albums, the most successful being Tapestry, which held the record for most weeks at No. 1 by a female artist for more than 20 years. Her record sales were estimated at more than 75 million copies worldwide. She has won four Grammy Awards and was inducted into the Songwriters Hall of Fame. She has been inducted twice into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame, as a performer and songwriter.She is the recipient of the 2013 Library of Congress Gershwin Prize for Popular Song, the first woman to be so honored. She is also a 2015 Kennedy Center Honoree. King was born Carol Joan Klein on February 9, 1942, in Manhattan, New York City, to Jewish parents Eugenia (née Cammer), a teacher, and Sidney N. Klein, a firefighter.
more...Ernest Dale Tubb (February 9, 1914 – September 6, 1984), nicknamed the Texas Troubadour, was an American singer and songwriter and one of the pioneers of country music. His biggest career hit song, “Walking the Floor Over You” (1941), marked the rise of the honky tonk style of music.
In 1948, he was the first singer to record a hit version of Billy Hayes and Jay W. Johnson’s “Blue Christmas“, a song more commonly associated with Elvis Presley and his late-1950s version. Another well-known Tubb hit was “Waltz Across Texas” (1965) (written by his nephew Quanah Talmadge Tubb, known professionally as Billy Talmadge), which became one of his most requested songs and is often used in dance halls throughout Texas during waltz lessons. Tubb recorded duets with the then up-and-coming Loretta Lynn in the early 1960s, including their hit “Sweet Thang”. Tubb is a member of the Country Music Hall of Fame.
The youngest of five children, Tubb was born on a cotton farm near Crisp, in Ellis County, Texas, United States. His father was a sharecropper and Tubb spent his youth working on farms throughout the state.Tubb’s earliest immigrant ancestor was Edward Tubb, who arrived in Virginia from Northamptonshire, England in 1701.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qfPMMt1tnPI
more...More Posts
- World Music with Franco Luambo Makiadi
- Daily Roots with Karl Bryan & Overproof
- Echos of Freedom by Nelson Mandela
- The Cosmos with the Super Blood Wolf Moon
- Andy Sheppard Day
- Jimmy Cobb Day
- Leadbelly Day
- World Music with Carlos Núñez
- Daily Roots with Tony Scott
- Echos of Freedom by Marcus Garvey
- The Cosmos with NGC 6052
- Robert Palmer Day
- Janis Joplin Day
- Horace Parlan Day
- World Music with Catrin Finch and Seckou Keita
- Daily Roots with Andy Capp
- Mt Zion Shabbat for the Soul Service 1-18-19
- Echos of Freedom by Floyd Westerman
- The Cosmos with NGC 4603
- Bobby Broom Day