Blog
Robert Edward Taylor, Bobby Taylor (February 18, 1934, died 7-23-2017) born in Washington, D.C., was raised in Washington. As a young man, he moved to New York City and sang in doo-wopgroups with singers who later joined successful acts such as Frankie Lymon & the Teenagers and Little Anthony and the Imperials. In 1958 he began his music career as a member of The Four Pharaohs, who released a few locally-selling recordings in the Columbus, Ohio area.
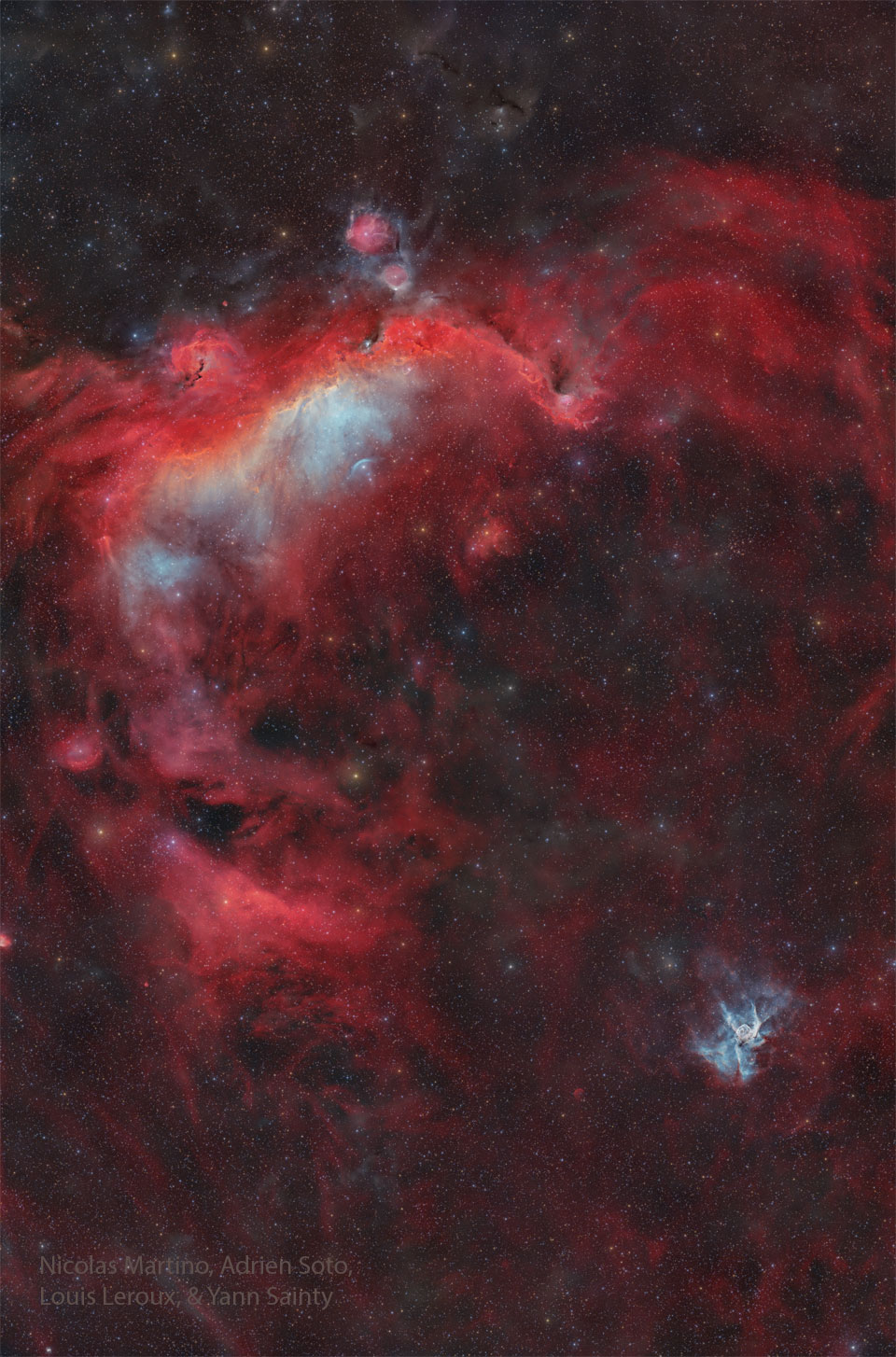
more...Seen as a seagull and a duck, these nebulae are not the only cosmic clouds to evoke images of flight. But both are winging their way across this broad celestial landscape, spanning almost 7 degrees across planet Earth‘s night sky toward the constellation of the Big Dog (Canis Major). The expansive Seagull (top center) is itself composed of two major cataloged emission nebulas. Brighter NGC 2327 forms the head with the more diffuse IC 2177 as the wings and body. Impressively, the Seagull’s wingspan would correspond to about 250 light-years at the nebula’s estimated distance of 3,800 light-years. At the lower right, the Duck appears much more compact and would span only about 50 light-years given its 15,000 light-year distance estimate. Blown by energetic winds from an extremely massive, hot star near its center, the Duck nebula is cataloged as NGC 2359. Of course, the Duck’s thick body and winged appendages also lend it the slightly more dramatic popular moniker, Thor’s Helmet.

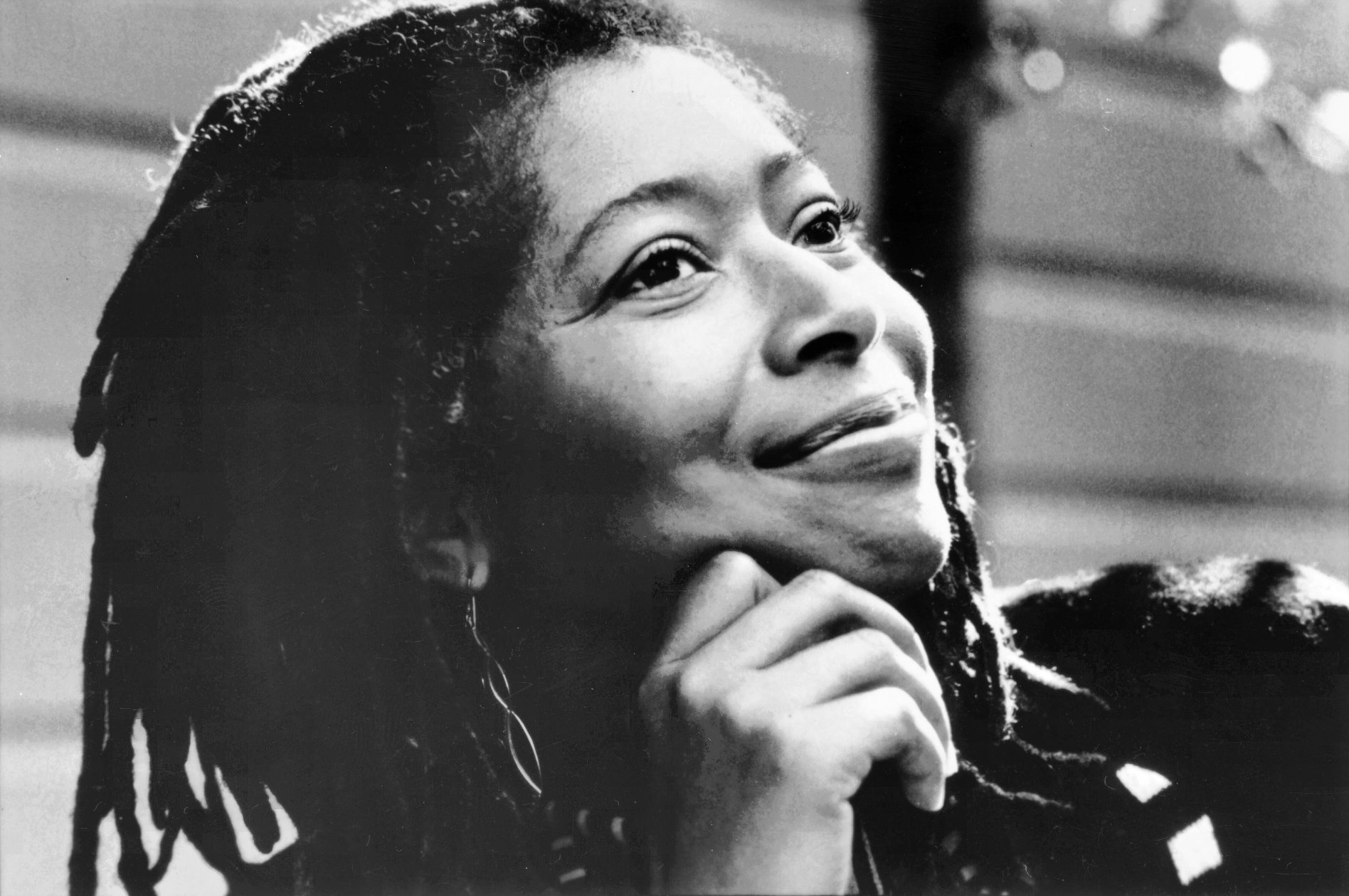
Buddy Cage (February 18, 1946 – February 5, 2020 Toronto, ON) was an American pedal steel guitarist, best known as a longtime member of the New Riders of the Purple Sage.
Popular both as a performer and session musician, he played with many bands and recording artists, including Anne Murray, Bob Dylan, Brewer & Shipley, David Bromberg, and the Zen Tricksters.
more...Irma Thomas (Lee; born February 18, 1941 Ponchatoula, LA) is an American singer from New Orleans. She is known as the “Soul Queen of New Orleans”. Thomas is a contemporary of Aretha Franklin and Etta James, but never experienced their level of commercial success. In 2007, she won the Grammy Award for Best Contemporary Blues Album for After the Rain, her first Grammy in a career spanning over 50 years.
Born Irma Lee, in Ponchatoula, Louisiana, United States, she was the daughter of Percy Lee, a steel chipper, and Vader Lee, who worked as a maid. As a teenager, she sang with a Baptist church choir. She auditioned for Specialty Records at the age of 13. By the time she was 19, she had been married twice and had four children. Keeping her second ex-husband’s surname, she worked as a waitress in New Orleans, occasionally singing with bandleader Tommy Ridgley, who helped her land a record deal with the local Ron label. Her first single, “Don’t Mess with My Man”, was released in late 1959, and reached number 22 on the US Billboard R&B chart.
more...
If you consider yourself a friend of mine please do not try to sell me things or make money from me. I am not interested. There are always exceptions but in general it’s a bad policy. I especially noticed this years ago when people were dealing inebriates and trying to support their habit by selling it to friends. I never liked it and it’s bad mojo! Buena Suerte Estafador


Gene Francis Alan Pitney (February 17, 1940 – April 5, 2006 Hartford, CT) was an American singer, songwriter, and musician.
Pitney charted 16 top-40 hits in the United States, four in the top ten. In the United Kingdom, he had 22 top-40 hit singles, including 11 in the top ten. Among Pitney’s most famous hits are “Town Without Pity“, “(The Man Who Shot) Liberty Valance“, “Twenty Four Hours from Tulsa“, “I’m Gonna Be Strong“, “It Hurts to Be in Love“, and “Something’s Gotten Hold of My Heart“. He also wrote the early-1960s hits “Rubber Ball” recorded by Bobby Vee, “Hello Mary Lou” by Ricky Nelson, and “He’s a Rebel” by the Crystals. In 2002, he was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame.
more...Martyn Bennett (17 February 1971 – 30 January 2005) was a Canadian-Scottish musician who was influential in the evolution of modern Celtic fusion, a blending of traditional Celtic and modern music. He was a piper, violinist, composer and producer. Diagnosis of serious illness at the age of thirty curtailed his live performances, although he completed a further two albums in the studio. He died from cancer in 2005, fifteen months after the release of his fifth album Grit.
more...Noble “Thin Man” Watts (February 17, 1926 – August 24, 2004 DeLand, FL) was an American blues, jump blues and rhythm and bluessaxophonist. He primarily played tenor saxophone. The AllMusic journalist, Bill Dahl, considered Watts “one of the most incendiary […] fire-breathing tenor sax honkers” of the 1950s.
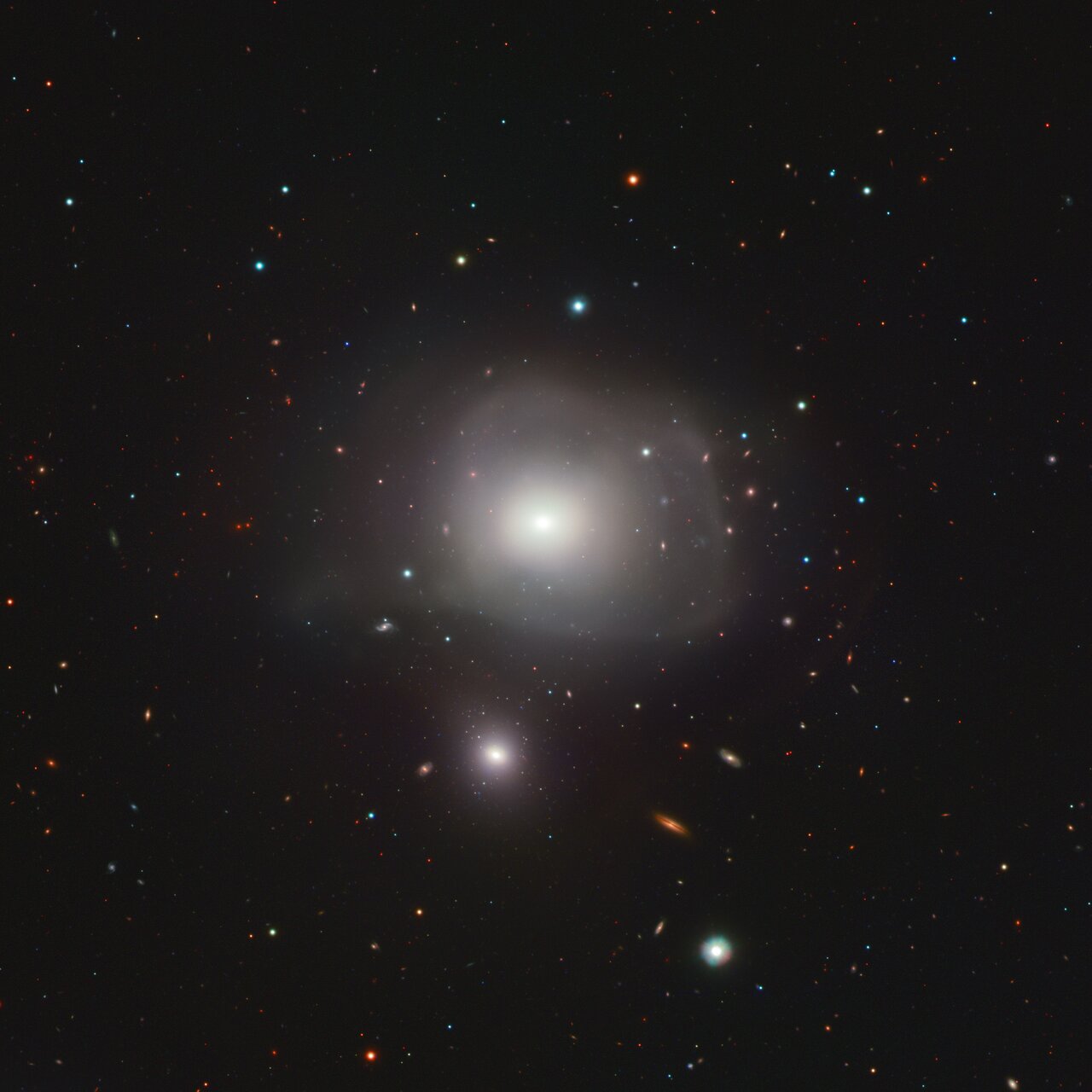
more...This Picture of the Week shows NGC 3640, an unusual elliptical galaxy 88 million light-years away. The image, taken with the VLT Survey Telescope hosted at ESO’s Paranal Observatory, reveals a menagerie of galaxies of all shapes and sizes, ranging from slight blue smudges to the fried-egg shape of NGC 3640. But amidst this colourful cosmic neighbourhood, one thing stands out — this egg has a double yolk: a smaller galaxy that might be too close for its comfort.
Throughout their extremely long lifetime, galaxies change. As they soar through space, they may steal gas and stars from other galaxies, or even engulf and merge with them. After these events, galaxies can become distorted, as exemplified by the misshaped NGC 3640 and the diffuse light around it. The galaxy is then left with ‘scars’ that hint at a violent past, which astronomers can use to know its past and present history.
To trace the history behind this galaxy and its smaller companion, a team of astronomers at the Italian National Institute for Astrophysics used the VST to analyse their globular clusters, spherical and compact aggregations of stars bound by gravity. These usually contain some of the first stars created within a galaxy and can therefore act as fossil markers, revealing the galaxy’s history, even after merging events.
The results confirm that NGC 3640 has engulfed other galaxies before, an ominous sign for the smaller galaxy now in its path, NGC 3641. Yet, this small galactic underdog shows a distinct lack of distortions in its shape or the globular clusters within. This suggests that their interaction, while fast, is not happening close enough for NGC 3640 to pose a threat. NGC 3641 might be safe… for now.

Nicole Mitchell (born February 17, 1967) is an American jazz flautist and composer who teaches jazz at the University of Virginia. She is a former chairwoman of the Association for the Advancement of Creative Musicians (AACM).
more...Jeremy Webster “Fred” Frith (born 17 February 1949) is an English multi-instrumentalist, composer, and improviser. Probably best known for his guitar work, Frith first came to attention as a founding member of the English avant-rock group Henry Cow. He was also a member of the groups Art Bears, Massacre, and Skeleton Crew. He has collaborated with numerous musicians, including Robert Wyatt, Derek Bailey, the Residents, Lol Coxhill, John Zorn, Brian Eno, Mike Patton, Lars Hollmer, Bill Laswell, Iva Bittová, Jad Fair, Kramer, the ARTE Quartett, and Bob Ostertag. He has also composed several long works, including Traffic Continues (1996, performed 1998 by Frith and Ensemble Modern) and Freedom in Fragments (1993, performed 1999 by Rova Saxophone Quartet). Frith produces most of his own music, and has also produced many albums by other musicians, including Curlew, the Muffins, Etron Fou Leloublan, and Orthotonics.
He is the subject of Nicolas Humbert and Werner Penzel’s 1990 documentary Step Across the Border. Frith also appears in the Canadian documentary Act of God, which is about the metaphysical effects of being struck by lightning. He has contributed to a number of music publications, including New Musical Express and Trouser Press, and has conducted improvising workshops across the world. His career spans over four decades and he appears on over 400 albums, and he still performs actively throughout the world.
Frith was awarded the 2008 Demetrio Stratos Prize for his career achievements in experimental music. The prize was established in 2005 in honour of experimental vocalist Demetrio Stratos, of the Italian group Area, who died in 1979. In 2010 Frith received an honorary doctorate from the University of Huddersfield in West Yorkshire, England, in recognition of his contribution to music. Frith was Professor of Composition in the Music Department at Mills College in Oakland, California, until his retirement in 2018. He is the brother of Simon Frith, a music critic and sociologist, and Chris Frith, a psychologist at University College London.
more...
Boniface Ferdinand Leonard “Buddy” DeFranco (February 17, 1923 – December 24, 2014 Camden, NJ) was an American jazz clarinetist. In addition to his work as a bandleader, DeFranco led the Glenn Miller Orchestra for almost a decade in the 1960s and 1970s.
more...More Posts
- Daily Roots with Israel Vibration
- The Cosmos with NGC 1187
- Reggie Workman Day
- Big Bill Broonzy Day
- World Music with Very Be Careful
- Daily Roots with Uwe Banton
- The Cosmos with M20
- Joe Chambers Day
- Clifton Chenier Day
- Johnny Smith Day
- World Music with Haig Yazdjian
- Daily Roots with Peter Tosh
- Your Community Band 6-24-18 2pm
- The Cosmos with NGC 7098
- Jeff Beck Day
- Lester Williams Day
- Terry Riley Day
- World Music with George Abdo
- Daily Roots with Damian Marley and Nas
- Geoffrey Oryema Ugandan musician Passes
