Blog
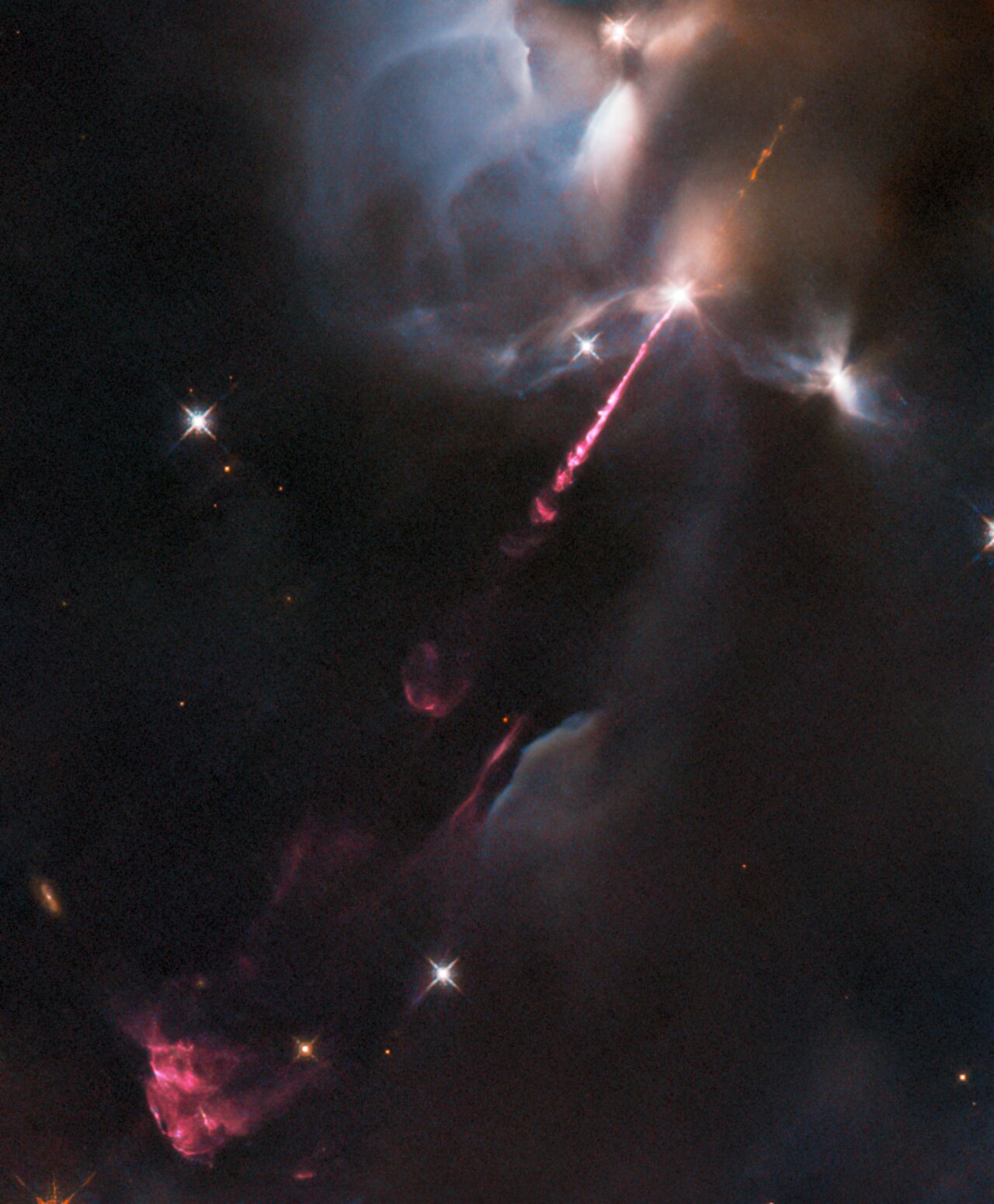
An energetic outburst from an infant star streaks across this image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. This stellar tantrum — produced by an extremely young star in the earliest phase of formation — consists of an incandescent jet of gas travelling at supersonic speeds. As the jet collides with material surrounding the still-forming star, the shock heats this material and causes it to glow. The result is the colourfully wispy structures, which astronomers refer to as Herbig–Haro objects, billowing across the lower left of this image. Herbig–Haro objects are seen to evolve and change significantly over just a few years. This particular object, called HH34, was previously captured by Hubble between 1994 and 2007, and again in glorious detail in 2015. HH34 resides approximately 1250 light-years from Earth in the Orion Nebula, a large region of star formation visible to the unaided eye. The Orion Nebula is one of the closest sites of widespread star formation to Earth, and as such has been pored over by astronomers in search of insights into how stars and planetary systems are born. The data in this image are from a set of Hubble observations of four nearby bright jets with the Wide Field Camera 3 taken to help pave the way for future science with the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope. Webb — which will observe at predominantly infrared wavelengths — will be able to peer into the dusty envelopes surrounding still-forming protostars, revolutionising the study of jets from these young stars. Hubble’s high-resolution images of HH34 and other jets will help astronomers interpret future observations with Webb.

John Townes Van Zandt (March 7, 1944 – January 1, 1997 Fort Worth, TX) was an American singer-songwriter. He wrote numerous songs, such as “Pancho and Lefty“, “For the Sake of the Song“, “If I Needed You“, “Tecumseh Valley”, “Rex’s Blues”, and “To Live Is to Fly“, that are widely considered masterpieces of American songwriting. His musical style has often been described as melancholy and features rich, poetic lyrics. During his early years, Van Zandt was respected for his guitar playing and fingerpicking ability.
In 1983, six years after Emmylou Harris had first popularized it, Willie Nelson and Merle Haggard covered Van Zandt’s song “Pancho and Lefty”, reaching number one on the Billboard country music chart. Much of Van Zandt’s life was spent touring various dive bars, often living in cheap motel rooms and backwood cabins. For much of the 1970s, he lived in a simple shack without electricity or a telephone.
Van Zandt’s influence has been cited by countless artists across multiple genres and his music has been recorded or performed by Bob Dylan, Willie Nelson, Lyle Lovett, Merle Haggard, Norah Jones, Emmylou Harris, Counting Crows, Steve Earle, Rodney Crowell, Robert Earl Keen Jr., Nanci Griffith, Guy Clark, Wade Bowen, Gillian Welch, Richard Buckner, Pat Green, Colter Wall, Jason Isbell, Calvin Russell, Natalie Maines, Jason Molina, Kevin Morby, Stephen Duffy, Doc Watson and Frank Turner.
He suffered from a series of drug addictions and alcoholism, and was given a psychiatric diagnosis of bipolar disorder. When he was young, the now-discredited insulin shock therapy erased much of his long-term memory.
Van Zandt died on New Year’s Day 1997 from cardiac arrythmia caused by health problems stemming from years of substance abuse. A revival of interest in Van Zandt blossomed in the 2000s. During the decade, two books, a documentary film (Be Here to Love Me), and numerous magazine articles were written about him. Townes Van Zandt died in the early morning hours of January 1, 1997, at the age of 52. His official cause of death was “natural” cardiac arrhythmia.
more...
Louis Albert Cottrell Jr. (March 7, 1911 – March 21, 1978) was a Louisiana Creole jazz clarinetist and tenor saxophonist. He was the son of the influential drummer Louis Cottrell, Sr., and grandfather of New Orleans jazz drummer Louis Cottrell. As leader of the Heritage Hall Jazz Band, he performed at the famous Carnegie Hall in 1974.
Louis Cottrell was born into an upper-class Creole musical family in New Orleans. His father, Louis “Old Man” Cottrell, Sr., was a famed drummer, and cornetist Manny Perez was his godfather. The young Cottrell grew up around such great musicians as Barney Bigard, John Robichaux, and A.J. Piron. Cottrell studied clarinet under Lorenzo Tio Jr. and Bigard. He began his career in the 1920s with the Golden Rule Orchestra, and then in 1925 played with Paul “Polo” Barnes. Later in the 1920s he worked with Chris Kelly and Kid Rena, then in 1929 found work on the riverboat SS Island Queen with Lawrence Marrero‘s Young Tuxedo Brass Band and Sidney Desvigne. These were the years when he became a prominent union organizer. He joined Don Albert‘s orchestra soon after, recording an album with the orchestra in 1935 under the Vocalion label. He tried his hand at composing, and with Lloyd Glenn and Albert wrote, “You Don’t Love Me (True).”[5] Rhythm and blues bandleader Paul Gayten would later approach Cottrell to record “You Don’t Love Me” and it became one of the first hits of the R & B New Orleans era, having made it to the number 5 spot nationally on the R & B top ten charts. Cottrell toured widely throughout North America with Albert until 1939.
more...Alcide Louis “Slow Drag” Pavageau (March 7, 1888 – January 19, 1969) was an American jazz guitarist and double-bassist.
Pavageau was born in New Orleans, Louisiana. He started his career as a dancer, mastering a dance called the Slow Drag which resulted in his nickname. He learned the guitar as a young man from his cousin Ulysses Picou, a singer in New Orleans. Pavageau came from a musical family and was related to families like the Tios, Picous and Pirons who formed some of the earliest jazz bands. He played Buddy Petit, Bunk Johnson, and Herb Morand. Johnson bragged that he taught Louis Armstrong how to play cornet by ear. He started playing bass in 1927 when he was 39 years old and joined George Lewis‘s band from 1943 and also played in Bunk Johnson‘s band in New York City in 1945. He toured with Lewis through the end of the 1950s. In 1961, while playing with the Louis Cottrell Trio, he recorded New Orleans: The Living Legends for Riverside. He worked at Preservation Hall in the 1960s and recorded one album as a leader in 1965 in addition to frequent recording with Lewis.
Pavageau was the son of Ferreol “Joseph” Pavageau and Alice Philippe. He was the descendant of a marriage between two of the oldest Creole families in New Orleans. His family traced their roots to wealthy French planters who were displaced by the Haitian Revolution and friends of Bienville, the founder of New Orleans. For almost 40 years he was the Grand Marshal of the Second Line of the Mardi Gras Parade. The second line is known for twirling ornamental umbrellas during their gatherings. The twirling of umbrellas may have been adapted from the early Italian immigrant custom of using umbrellas at funeral processions. Alcide died in 1969 in New Orleans at the age of 80.
more...Joseph Maurice Ravel (7 March 1875 – 28 December 1937) was a French composer, pianist and conductor. He is often associated with Impressionismalong with his elder contemporary Claude Debussy, although both composers rejected the term. In the 1920s and 1930s Ravel was internationally regarded as France’s greatest living composer.
Born to a music-loving family, Ravel attended France’s premier music college, the Paris Conservatoire; he was not well regarded by its conservative establishment, whose biased treatment of him caused a scandal. After leaving the conservatoire, Ravel found his own way as a composer, developing a style of great clarity and incorporating elements of modernism, baroque, neoclassicism and, in his later works, jazz. He liked to experiment with musical form, as in his best-known work, Boléro (1928), in which repetition takes the place of development. Renowned for his abilities in orchestration, Ravel made some orchestral arrangements of other composers’ piano music, of which his 1922 version of Mussorgsky‘s Pictures at an Exhibition is the best known.
A slow and painstaking worker, Ravel composed fewer pieces than many of his contemporaries. Among his works to enter the repertoire are pieces for piano, chamber music, two piano concertos, ballet music, two operas and eight song cycles; he wrote no symphonies or church music. Many of his works exist in two versions: first, a piano score and later an orchestration. Some of his piano music, such as Gaspard de la nuit (1908), is exceptionally difficult to play, and his complex orchestral works such as Daphnis et Chloé (1912) require skilful balance in performance.
Ravel was among the first composers to recognise the potential of recording to bring their music to a wider public. From the 1920s, despite limited technique as a pianist or conductor, he took part in recordings of several of his works; others were made under his supervision.
more...The final performance of the premier of the Dragon Who Liked to Spit Fire a musical by Sim Glaser. Sunday March 6th 2022 2pm matinee. JCC St Louis Park. Music with Todd Russell, Riley Helgeson, Mark Yannie, Tom Lewis and mick laBriola.

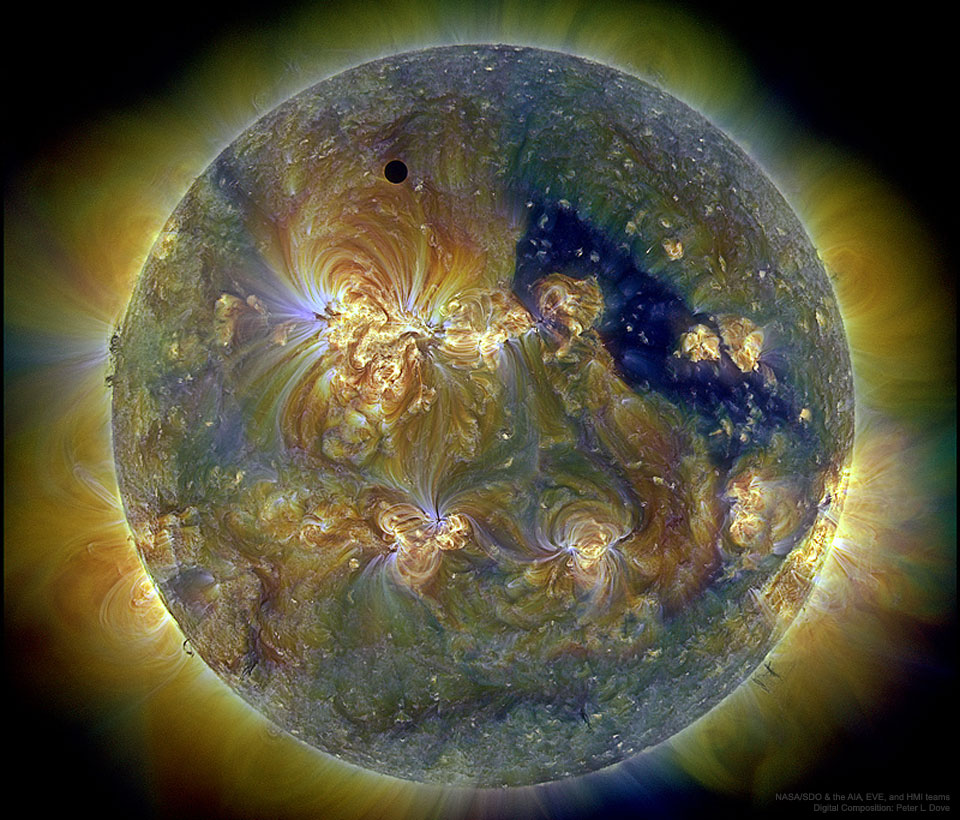
This was a very unusual type of solar eclipse. Typically, it is the Earth’s Moon that eclipses the Sun. In 2012, though, the planet Venus took a turn. Like a solar eclipse by the Moon, the phase of Venus became a continually thinner crescent as Venus became increasingly better aligned with the Sun. Eventually the alignment became perfect and the phase of Venus dropped to zero. The dark spot of Venus crossed our parent star. The situation could technically be labeled a Venusian annular eclipse with an extraordinarily large ring of fire. Pictured here during the occultation, the Sun was imaged in three colors of ultraviolet light by the Earth-orbiting Solar Dynamics Observatory, with the dark region toward the right corresponding to a coronal hole. Hours later, as Venus continued in its orbit, a slight crescent phase appeared again. The next Venusian transit across the Sun will occur in 2117.
David Jon Gilmour CBE (/ˈɡɪlmɔːr/ GHIL-mor; born 6 March 1946) is an English songwriter, guitarist, and singer who was a member of rock band Pink Floyd. He joined as guitarist and co-lead vocalist in 1967, shortly before the departure of founder member Syd Barrett. Pink Floyd achieved international success with the concept albums The Dark Side of the Moon (1973), Wish You Were Here (1975), Animals (1977), and The Wall (1979). By the early 1980s, they had become one of the highest-selling and most acclaimed acts in music history; by 2012, they had sold more than 250 million records worldwide, including 75 million in the United States. Following the departure of Roger Waters in 1985, Pink Floyd continued under Gilmour’s leadership and released three more studio albums.
Gilmour has produced a variety of artists, such as the Dream Academy, and has released four solo studio albums: David Gilmour, About Face, On an Island, and Rattle That Lock. He is also credited for bringing singer-songwriter Kate Bush to public attention. As a member of Pink Floyd, he was inducted into the US Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1996, and the UK Music Hall of Fame in 2005. In 2003, Gilmour was made a Commander of the Order of the British Empire (CBE). He was awarded with the Outstanding Contribution title at the 2008 Q Awards. In 2011, Rolling Stone ranked him number 14 in their list of the greatest guitarists of all time. He was also voted number 36 in the greatest voices in rock by Planet Rock listeners in 2009.
Gilmour has taken part in projects related to issues including animal rights, environmentalism, homelessness, poverty, and human rights. He has married twice and is the father of eight children.
more...Flora Purim (born March 6, 1942) is a Brazilian jazz singer known primarily for her work in the jazz fusion style. She became prominent for her part in Return to Forever with Chick Corea and Stanley Clarke. She has recorded and performed with numerous artists, including Dizzy Gillespie, Gil Evans, Opa, Stan Getz, George Duke, Mickey Hart of the Grateful Dead, Santana, Jaco Pastorius, and her husband Airto Moreira.
In 2002, Purim was the recipient of one of Brazil’s highest awards, the 2002 Ordem do Rio Branco for Lifetime Achievement. She has been called “The Queen of Brazilian Jazz”.
Purim was born in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, to Jewish parents who were classical musicians. Her father Naum Purim played violin and her mother Rachel Vaisberg was a pianist. When her father was out of the house, her mother played jazz.
more...John Leslie “Wes” Montgomery (March 6, 1923 – June 15, 1968) was an American jazz guitarist. Montgomery was known for an unusual technique of plucking the strings with the side of his thumb and his extensive use of octaves, which gave him a distinctive sound.
Montgomery often worked with his brothers Buddy (Charles F.) and Monk (William H.) and with organist Melvin Rhyne. His recordings up to 1965 were oriented towards hard bop, soul jazz, and post bop, but around 1965 he began recording more pop-oriented instrumental albums that found mainstream success. His later guitar style influenced jazz fusion and smooth jazz.
Montgomery was born in Indianapolis, Indiana. According to NPR, the nickname “Wes” was a child’s abbreviation of his middle name, Leslie. The family was large, and the parents split up early in the lives of the children. Montgomery and his brothers moved to Columbus, Ohio, with their father and attended Champion High School. His older brother Monk dropped out of school to sell coal and ice, gradually saving enough money to buy his brother Wes a four-string tenor guitar from a pawn shop in 1935. Although Montgomery spent many hours with the guitar, he discounted this time later in life, saying he had to start over when he got his first six-string several years later. Montgomery died of a heart attack on June 15, 1968, while at home in Indianapolis. His grandson is actor Anthony Montgomery, who played Travis Mayweather on Star Trek: Enterprise.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SZkmozm0UII
more...Howard McGhee (March 6, 1918 – July 17, 1987) was one of the first American bebop jazz trumpeters, with Dizzy Gillespie, Fats Navarro and Idrees Sulieman. He was known for his fast fingering and high notes. He had an influence on younger bebop trumpeters such as Fats Navarro.
Howard McGhee was born in Tulsa, Oklahoma, United States, and raised in Detroit, Michigan. During his career, he played in bands led by Lionel Hampton, Andy Kirk, Count Basie and Charlie Barnet. He was in a club listening to the radio when he first heard Charlie Parker and was one of the earliest adopters of the new style, a fact that was disapproved by older musicians like Kid Ory.
In 1946–47, some record sessions for the new label Dial were organized in Hollywood, with Charlie Parker and McGhee. The first was held on July 29, 1946. The musicians were Charlie Parker, Howard McGhee, Jimmy Bunn, Bob Kesterson, and Roy Porter. With Parker’s health near to collapse, he played “Max is Making Wax”, “Lover Man“, and “The Gypsy”
more...James Robert Wills (March 6, 1905 – May 13, 1975 Kosse, TX) was an American Western swing musician, songwriter, and bandleader. Considered by music authorities as the co-founder of Western swing, he was known widely as the King of Western Swing (although Spade Cooley self-promoted the moniker “King of Western Swing” from 1942 to 1969).
Wills formed several bands and played radio stations around the South and West until he formed the Texas Playboys in 1934 with Wills on fiddle, Tommy Duncan on piano and vocals, rhythm guitarist June Whalin, tenor banjoist Johnnie Lee Wills, and Kermit Whalin, who played steel guitar and bass. The band played regularly on Tulsa, Oklahoma, radio station KVOO and added Leon McAuliffe on steel guitar, pianist Al Stricklin, drummer Smokey Dacus, and a horn section that expanded the band’s sound. Wills favored jazz-like arrangements and the band found national popularity into the 1940s with such hits as “Steel Guitar Rag“, “New San Antonio Rose“, “Smoke on the Water“, “Stars and Stripes on Iwo Jima“, and “New Spanish Two Step“.
Wills and the Texas Playboys recorded with several publishers and companies, including Vocalion, Okeh, Columbia, and MGM, frequently moving. In 1950, he had two top 10 hits, “Ida Red Likes the Boogie” and “Faded Love“, which were his last hits for a decade. Throughout the 1950s, he struggled with poor health and tenuous finances, but continued to perform frequently despite the decline in popularity of his earlier music as rock and roll took over. Wills had a heart attack in 1962 and a second one the next year, which forced him to disband the Playboys, although Wills continued to perform solo.
The Country Music Hall of Fame inducted Wills in 1968 and the Texas State Legislature honored him for his contribution to American music.
In 1972, Wills accepted a citation from the American Society of Composers, Authors and Publishers in Nashville. He was recording an album with fan Merle Haggard in 1973 when a stroke left him comatose until his death in 1975. The Rock and Roll Hall of Fame inducted Wills and the Texas Playboys in 1999
more...STOP THE WAR IN UKRAINE
more...Last weekend of this original musical by Sim Glaser. Performing Saturday 2pm matinee and 630pm evening shows. JCC St Louis Park. Music with Todd Russell, Riley Helgeson, Mark Yannie, Tom Lewis and mick laBriola.

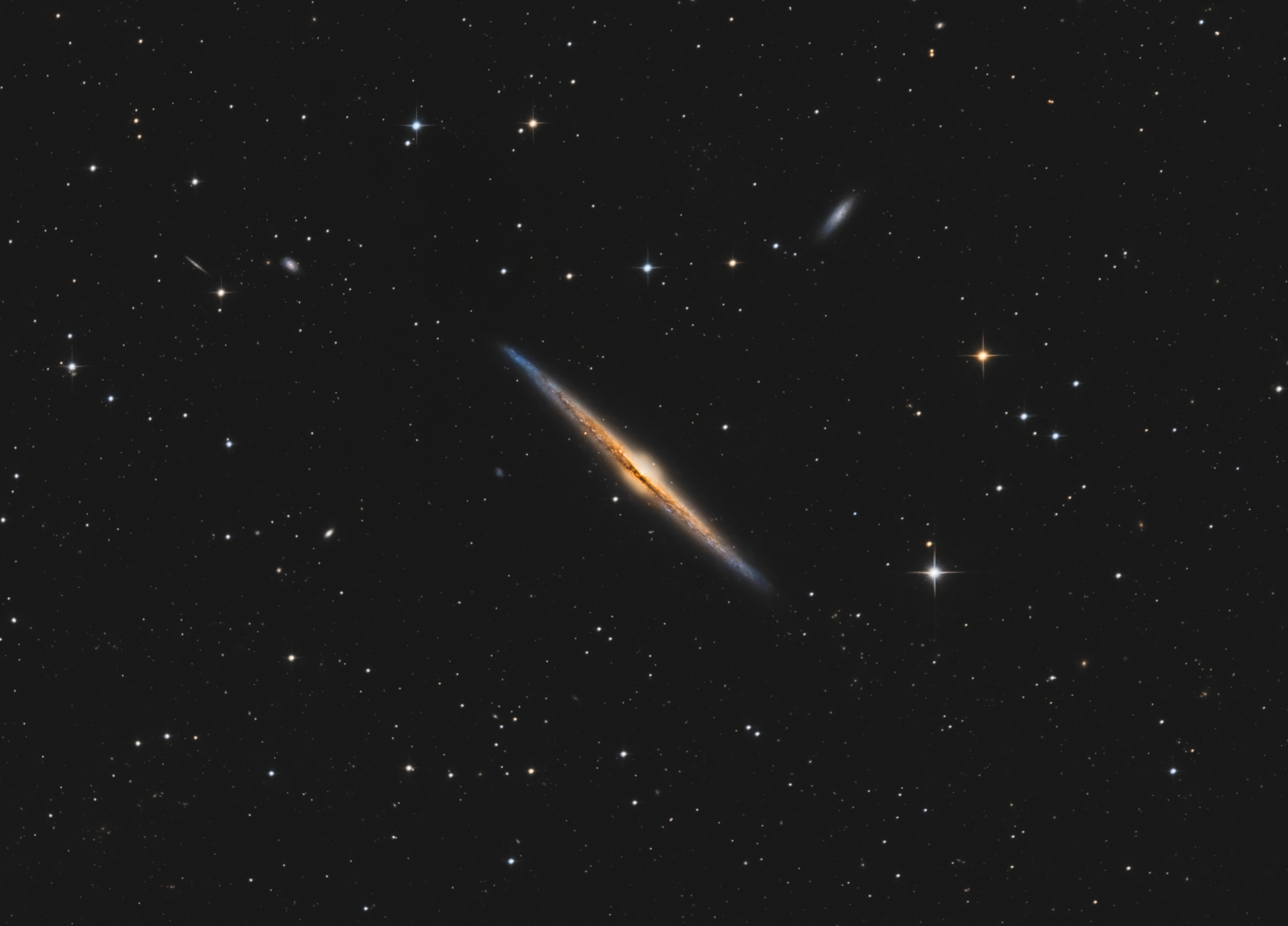
NGC 4565 (also known as the Needle Galaxy or Caldwell 38) is an edge-on spiral galaxy about 30 to 50 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. It lies close to the North Galactic Poleand has a visual magnitude of approximately 10. It is known as the Needle Galaxy for its narrow profile. First recorded in 1785 by William Herschel, it is a prominent example of an edge-on spiral galaxy.

Edmond Montague Grant (born 5 March 1948) is a Guyanese–British singer, songwriter and multi-instrumentalist, known for his genre-blending sound; his music has blended elements of electronic pop, reggae, British rock, African polyrhythms, soul, funk and Latin samba, among many others. In addition to this, he also helped to pioneer the genre of ringbang. He was a founding member of The Equals, one of the United Kingdom’s first racially-integrated pop groups. His subsequent solo career included the platinum single “Electric Avenue“, which is his biggest international hit.
Grant was born in Plaisance, British Guiana, later moving to Linden. His father, Patrick, was a trumpeter who played in Nello and the Luckies.[13]While at school, his parents lived and worked in the United Kingdom, sending back money for his education. In 1960, he emigrated to join his parents in London.He lived in Kentish Town and went to school at the Acland Burghley Secondary Modern at Tufnell Park, where he learned to read and write music. He became a big fan of Chuck Berry, and after seeing him play at the Finsbury Park Astoria decided on a career in music.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XNOB2b2puV0
more...J. B. Lenoir March 5, 1929 – April 29, 1967) was an American blues guitarist and singer-songwriter, active in the Chicago blues scene in the 1950s and 1960s.
Lenoir was born in Monticello, Mississippi. His full given name was simply “J. B.”; the letters were not initials. Lenoir’s guitar-playing father introduced him to the music of Blind Lemon Jefferson, which became a major influence. During the early 1940s, Lenoir worked with the blues artists Sonny Boy Williamson II and Elmore James in New Orleans. He was later influenced by Arthur Crudup and Lightnin’ Hopkins.
In 1949, he moved to Chicago, where Big Bill Broonzy helped introduce him to the blues community. He began to perform at local nightclubs, with musicians such as Memphis Minnie, Big Maceo Merriweather, and Muddy Waters, and became an important part of the city’s blues scene. He began recording in 1951 for J.O.B. Records and Chess Records. His recording of “Korea Blues” was licensed to and released by Chess, as having been performed by J. B. and his Bayou Boys. His band included the pianist Sunnyland Slim, the guitarist Leroy Foster, and the drummer Alfred Wallace.
more...More Posts
- Little Johnny Taylor Day
- Otis Clay Day
- World Music with Sali Sidibé Memorial
- Daily Roots with the Pioneers
- HAIR final performance
- Echos of Freedom by Liu Xiaobo
- The Cosmos with NGC 925
- Manu Dibango Day
- Walter Perkins Day
- Chick Webb Day
- World Music with Amina Annabi
- Daily Roots with Rudy Mills
- HAIR Minneapolis Production in NY Times
- HAIR musical Minneapolis matinee & evening Shows
- Echos of Freedom by Benjamin Franklin
- The Cosmos with IC 5146
- Carol King Day
- Ernest Tubb Day
- Walter Page Day
- World Music with King Mensah