Blog
Keith Richards (born 18 December 1943), often referred to during the 1960s and 1970s as Keith Richard, is an English musician, singer, and songwriter, who has achieved international fame as the co-founder, guitarist, secondary vocalist, and co-principal songwriter of the Rolling Stones. His songwriting partnership with Mick Jagger is one of the most successful in history. Richards is widely considered one of the greatest guitarists of all time. His career spans over six decades and his guitar playing style has been a trademark of the Rolling Stones throughout the band’s career. Richards gained press notoriety for his romantic involvements, illicit drug use and was often portrayed as a countercultural figure.
Richards was born in and grew up in Dartford, Kent. He studied at the Dartford Technical School and Sidcup Art College. After graduating, Richards befriended Jagger, Bill Wyman, Charlie Watts and Brian Jones, and joined the Rolling Stones. As a member of the Rolling Stones, Richards is the only member, aside from Jagger, to sing lead on some Stones songs. Richards typically sings lead on at least one song a concert, including “Happy“, “Before They Make Me Run“, and “Connection“. Outside of his career with the Rolling Stones, Richards has also played with his own side-project, The X-Pensive Winos. He also appeared in three Pirates of the Caribbean films as Captain Teague, father of Jack Sparrow, whose look and characterization was inspired by Richards himself.
In 1989, Richards was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame, and in 2004 into the UK Music Hall of Fame with the Rolling Stones. Rolling Stone magazine ranked him fourth on its list of 100 best guitarists in 2011. The magazine lists fourteen songs that Richards wrote with the Rolling Stones’ lead vocalist Jagger on its “500 Greatest Songs of All Time” list.
more...Ishmael Wadada Leo Smith (born December 18, 1941) is an American trumpeter and composer, working primarily in the fields of avant-garde jazz and free improvisation. He was one of three finalists for the 2013 Pulitzer Prize for Music for Ten Freedom Summers, released on May 22, 2012.
Smith was born in Leland, Mississippi, United States. He started out playing drums, mellophone, and French horn before he settled on the trumpet. He played in various R&B groups and, by 1967, became a member of the AACM and co-founded the Creative Construction Company, a trio with Leroy Jenkins and Anthony Braxton. In 1971, Smith formed his own label, Kabell. He also formed another band, the New Dalta Ahkri, with members including Henry Threadgill, Anthony Davis and Oliver Lake.
In the 1970s, Smith studied ethnomusicology at Wesleyan University. He played again with Anthony Braxton, as well as recording with Derek Bailey‘s Company. In the mid-1980s, Smith became Rastafarian and began using the name Wadada. In 1993, he began teaching at Cal Arts, a position he held until 2014. In addition to trumpet and flugelhorn, Smith plays several world music instruments, including the koto, kalimba, and atenteben (Ghanaian bamboo flute). He has also taught courses in instrument making. His compositions often use a graphic notation system he calls “Ankhrasmation”, which he developed in 1970.
more...Eddie “Cleanhead” Vinson (born Edward L. Vinson Jr., December 18, 1917 – July 2, 1988) was an American jump blues, jazz, bebop and R&B alto saxophonist and blues shouter. He was nicknamed Cleanhead after an incident in which his hair was accidentally destroyed by lye contained in a hair straightening product, necessitating shaving it off; enamoured of the look, Vinson maintained a shaved head thereafter. Music critic Robert Christgau has called Vinson “one of the cleanest—and nastiest—blues voices you’ll ever hear.”
Vinson was born in Houston, Texas. He was a member of the horn section in Milton Larkin‘s orchestra, which he joined in the late 1930s. At various times, he sat next to Arnett Cobb, Illinois Jacquet, and Tom Archia, while other members of the band included Cedric Haywood and Wild Bill Davis. After exiting Larkin’s employment in 1941, Vinson picked up a few vocal tricks while on tour with bluesman Big Bill Broonzy. He then moved to New York and joined the Cootie WilliamsOrchestra from 1942 to 1945, recording such tunes as “Cherry Red”. Vinson struck out on his own in 1945, forming his own large band, signing with Mercury Records, and enjoying a double-sided hit in 1947 with his R&B chart-topper “Old Maid Boogie”, and the song that would prove to be his signature number, “Kidney Stew Blues”.
more...Harold de Vance Land (December 18, 1928 – July 27, 2001) was an American hard bop and post-bop tenor saxophonist. Land developed his hard bop playing with the Max Roach/Clifford Brown band into a personal, modern style; often rivalling Clifford Brown’s instrumental ability with his own inventive and whimsical solos. His tone was strong and emotional, yet hinted at a certain introspective fragility.
Land was born in Houston, Texas, United States and grew up in San Diego, California. He started playing at the age of 16. He made his first recording as the leader of the Harold Land All-Stars, for Savoy Records in 1949. In 1954, he joined the Clifford Brown/Max Roach Quintet, with whom he was at the forefront of the hard-bop/bebop movement. The Land family moved from San Diego to Los Angeles, in 1955. There he played with Curtis Counce, led his own groups, and co-led groups with Bobby Hutcherson, Blue Mitchell, and Red Mitchell. From the 1970s onwards, his style showed the influence of John Coltrane.
In the early 1980s through to the early 1990s he worked regularly with the Timeless All Stars, a group sponsored by the Timeless jazz record label. The group consisted of Land on tenor, Cedar Walton on piano, Buster Williams on bass, Billy Higgins on drums, Curtis Fuller on trombone and Bobby Hutcherson on vibes. Land also toured with his own band during this time, often including his son, Harold Land Jr., on piano and usually featuring Bobby Hutcherson and Billy Higgins as well. During these years he played regularly at Hop Singh’s in Marina Del Rey in the L.A. area and the Keystone Korner in San Francisco.
more...Connie Curtis Crayton (December 18, 1914 – June 25, 1985), known as Pee Wee Crayton, was an American R&B and blues guitarist and singer. On May 8, 2019, Crayton was posthumously inducted into the Blues Hall of Fame by long-time friend Doug MacLeod in a ceremony held in Memphis, Tennessee by the Blues Foundation.
Crayton was born in Rockdale, Texas. He began playing guitar seriously after moving to California in 1935, later settling in Oakland. While there, he absorbed the music of T-Bone Walker but developed his own unique approach. His aggressive playing contrasted with his smooth vocal style and was copied by many later blues guitarists.
In 1948, he signed a recording contract with Modern Records. One of his first recordings was the instrumental “Blues After Hours“, which reached number 1 on the Billboard R&B chart late that year. Its B-side, the pop ballad “I’m Still in Love with You”, and the quicker “Texas Hop” are good examples of his work.
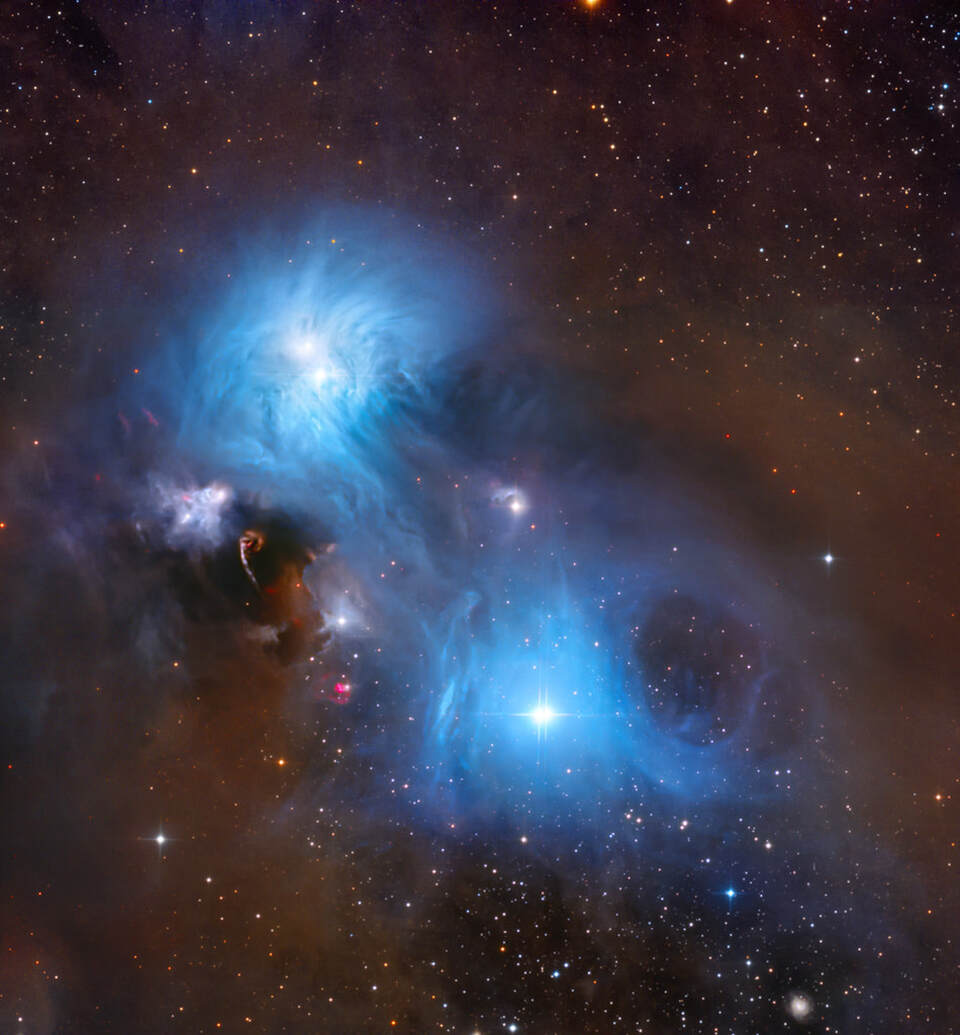
more...NGC 6726 – 27 are 2 nebulae in a huge complex in Corona Australis. This image is only a small section of the complex. A small patch of red nebulosity (HH101) is probably jets emitted from still hidden stars in the dust clouds. The dark nebula (Bernes 157) is so dense that stars cannot shine through.
This colourful complex is approx. 500 light years distance, one of the nearest stat forming regions in the Milky Way.

Paul Vaughn Butterfield (December 17, 1942 – May 4, 1987) was an American blues harmonica player, singer and band leader. After early training as a classical flautist, he developed an interest in blues harmonica. He explored the blues scene in his native Chicago, where he met Muddy Watersand other blues greats, who provided encouragement and opportunities for him to join in jam sessions. He soon began performing with fellow blues enthusiasts Nick Gravenites and Elvin Bishop.
In 1963, he formed the Paul Butterfield Blues Band, which recorded several successful albums and was popular on the late-1960s concert and festival circuit, with performances at the Fillmore West, in San Francisco; the Fillmore East, in New York City; the Monterey Pop Festival; and Woodstock. The band was known for combining electric Chicago blues with a rock urgency and for their pioneering jazz fusion performances and recordings. After the breakup of the group in 1971, Butterfield continued to tour and record with the band Paul Butterfield’s Better Days, with his mentor Muddy Waters, and with members of the roots-rock group the Band. While still recording and performing, Butterfield died in 1987 at age 44 of an accidental drug overdose.
Music critics have acknowledged his development of an original approach that places him among the best-known blues harp players. In 2006, he was inducted into the Blues Hall of Fame. Butterfield and the early members of the Paul Butterfield Blues Band were inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 2015. Both panels noted his harmonica skills and his contributions to bringing blues music to a younger and broader audience.
Beginning in 1980, Paul Butterfield underwent several surgical procedures to relieve his peritonitis, a serious and painful inflammation of the intestines. Although strongly opposed to heroin as a bandleader, he developed an addiction to it, which, according to Steve Huey in AllMusic’s Butterfield biography, led to “speculation that he was trying to ease his peritonitis symptoms”. The financial strain of supporting his drug habit was bankrupting him, and the deaths of his friend and one-time musical partner Mike Bloomfield, and manager Albert Grossman had shaken him.[3] On May 4, 1987, at age 44, Paul Butterfield died at his apartment in the North Hollywood district of Los Angeles. An autopsy by the county coroner concluded that he was the victim of an accidental drug overdose, with “significant levels of morphine (heroin), … codeine, the tranquilizer Librium and a trace of alcohol.
more...James Carroll Booker III (December 17, 1939 – November 8, 1983) was a New Orleans rhythm and blues keyboardist born in New Orleans, Louisiana, United States. Booker’s unique style combined rhythm and blues with jazz standards. Musician Dr. John described Booker as “the best black, gay, one-eyed junkie piano genius New Orleans has ever produced.” Flamboyant in personality, he was known as “the Black Liberace”.
Booker was the son and grandson of Baptist ministers, both of whom played the piano. He spent most of his childhood on the Mississippi Gulf Coast, where his father was a church pastor. Booker received a saxophone as a gift from his mother, but he was more interested in the keyboard. He played the organ in his father’s churches.
After returning to New Orleans in his early adolescence, Booker attended the Xavier Academy Preparatory School. He learned some elements of his keyboard style from Tuts Washington and Edward Frank. Booker was highly skilled in classical music and played music by Bach and Chopin, among other composers. He also mastered and memorized solos by Erroll Garner and Liberace. His performances combined elements of stride, blues, gospel and Latin piano styles. Booker died aged 43 on November 8, 1983, while seated in a wheelchair in the emergency room at New Orleans’ Charity Hospital, waiting to receive medical attention. The cause of death, as cited in the Orleans Parish Coroner’s Death Certificate, was renal failure related to chronic abuse of heroin and alcohol.
more...Arthur Lanon Neville Jr. (December 17, 1937 – July 22, 2019) was an American singer, songwriter and keyboardist from New Orleans.
Neville was a staple of the New Orleans music scene for over five decades. He was the founder of the funk band The Meters whose musical style set the tone of New Orleans funk, a co-founder of the rock-soul-jazz band The Neville Brothers, and he later formed the spinoff group The Funky Meters. He performed on many recordings by notable artists from New Orleans and elsewhere, including Labelle (on “Lady Marmalade“), Paul McCartney, Lee Dorsey, Robert Palmer, Dr. John and Professor Longhair.[3][4] He was the recipient of three Grammy awards.
Neville grew up in New Orleans. He was the son of Amelia (Landry) and Arthur Neville Sr. He started on piano and performed with his brothers at an early age. He was influenced by the R&B styles of James Booker, Bill Doggett, Booker T. Jones, Lloyd Glenn and Professor Longhair. In high school he joined and later led The Hawketts. In 1954 the band recorded “Mardi Gras Mambo” with Neville on vocals.The song gained popularity and became a New Orleans carnival anthem. The band toured with Larry Williams. Neville performed regularly in New Orleans, joined the U.S. Navyin 1958, and returned to music in 1962. He released several singles as a lead artist in 1950s and 1960s.
more...Sylvester Kyner Jr. (December 17, 1932 – March 20, 1981), known as Sonny Red, was an American jazz alto saxophonist and composer associated with the hard bop idiom among other styles.
Sonny Red played with Art Blakey, Curtis Fuller, Paul Quinichette, Donald Byrd, Grant Green, Blue Mitchell, Wynton Kelly, Billy Higgins, and Cedar Walton.
In the late 1940s, when he was still in his teens, Sonny Red began to play professionally in Detroit with Barry Harris. He continued to play with Barry Harris until 1952. He went on to play with Art Blakey in 1954, and in 1957 recorded with Curtis Fuller on three albums. Sonny Red first came on the greater jazz scene in the late 1950s with Art Pepper in the album Two Altos.
He made two albums as a leader in 1961; both were released by Jazzland Recordings, a subsidiary of Riverside Records. He continued to record in the 1960s, including four albums with Donald Byrd in 1967.
By the 1970s, however, Sonny Red was falling into obscurity. He died in March 1981, at the age of 48.
more...This light and lively song and social dance has roots that extend deeply into many parts of Spanish culture. The dance exudes romanticism, and has a joyous, flirtatious air. Sevillanas first emerged as a distinct form in the late 18th Century as a variant of the Spanish song form seguidillas, appearing simultaneously with the Escuela Bolera, a formalized approach to studying and performing a variety of Spanish regional dances. By the 19th Century, the Sevillanas was an important form in the Escuela Bolera.
The names of many of the steps in the Sevillanas (e.g., el paseo, la pasada, el zapateado, el careo, and las vueltas)are from Escuela Bolera practice. An important detail Sevillanas retains from the Escuela Bolera style is the pose the dancer takes at the end of each copla, known as bien parado, or “standing well.” Sevillanas was eventually folded into the flamenco repertoire, and in the process became aflamencada – “flamenco-ized.” Because it is a partner dance, Sevillanas is often the only Spanish dance non-dancers have learned, contributing to it’s social role within Spanish-speaking and flamenco communities. The Sevillanas is associated with El Rocio, an annual pilgrimage to a sacred shrine in the Coto Doñana. Many of the letras of the Sevillanas are associated with this and other religious subjects. Although Sevillanas have passed through various periods in the evolution of Spanish culture, it’s important to know that these facets of Spanish culture are still alive today, and that Sevillanas is very much a part of each of them.
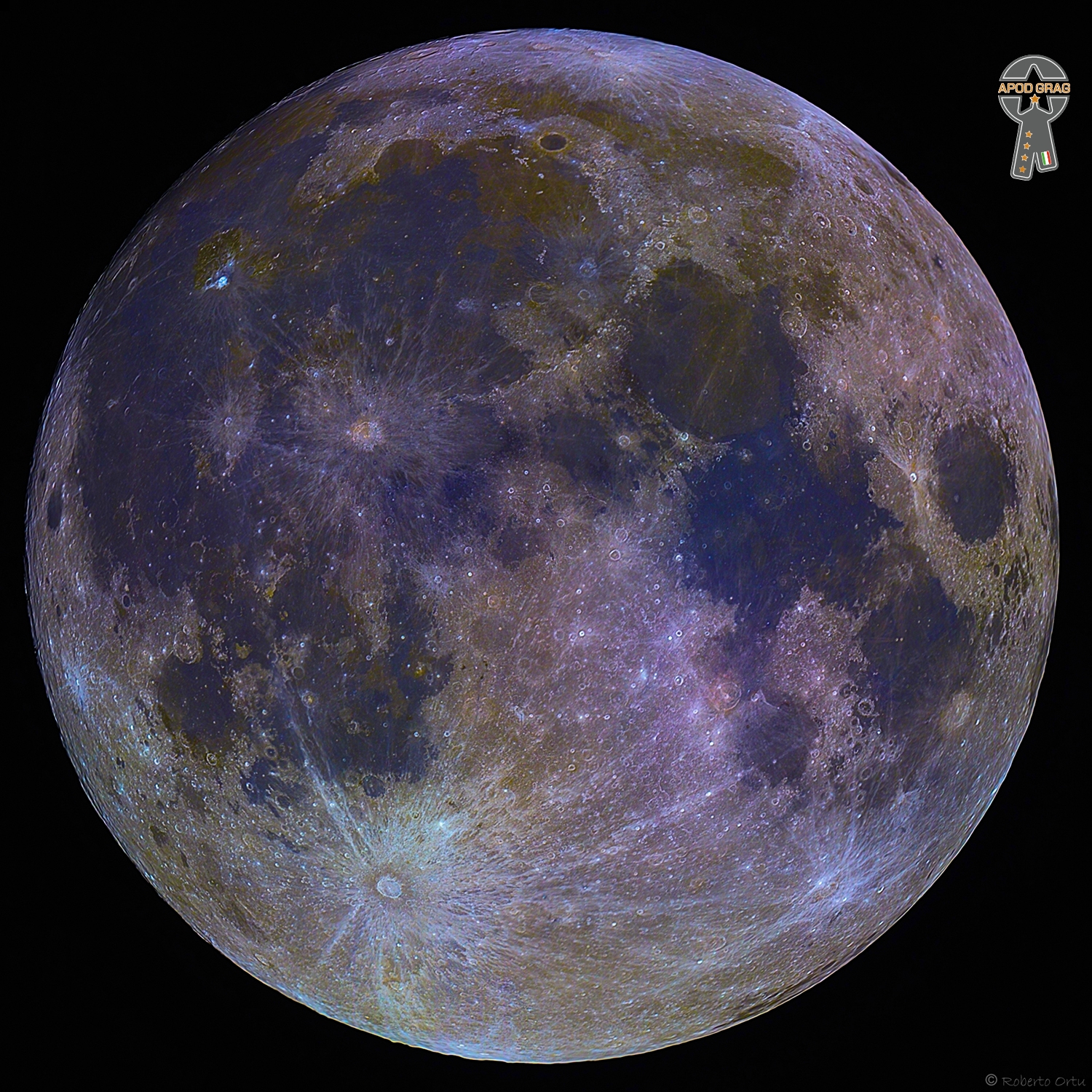
more...The Moon is Earth‘s only natural satellite. At about one-quarter the diameter of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia), it is the largest natural satellite in the Solar System relative to the size of its planet, the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System overall, and is larger than any known dwarf planet. The Moon is a planetary-mass object that formed a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under geophysical definitions of the term.It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth’s (0.1654 g); Jupiter‘s moon Io is the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density.
Orbiting Earth at an average distance of 384,400 km (238,900 mi), or about 30 times Earth’s diameter, its gravitational influence slightly lengthens Earth’s day and is the main driver of Earth’s tides. The Moon’s orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synodic period of 29.5 days, the amount of visible surface illuminated by the Sun varies from none up to 100%, resulting in lunar phases that form the basis for the months of a lunar calendar. The Moon is tidally locked to Earth, which means that the length of a full rotation of the Moon on its own axis causes its same side (the near side) to always face Earth, and the somewhat longer lunar day is the same as the synodic period. That said, 59% of the total lunar surface can be seen from Earth through shifts in perspective due to libration.
Robben Lee Ford (born December 16, 1951) is an American blues, jazz, and rock guitarist. He was a member of the L.A. Express and Yellowjackets and has collaborated with Miles Davis, Joni Mitchell, George Harrison, Larry Carlton, Rick Springfield, Little Feat and Kiss. He was named one of the “100 Greatest Guitarists of the 20th Century” by Musician magazine.
Robben Ford was born in Woodlake, California, United States, and raised in Ukiah, California. He began playing the saxophone at age 10 and the guitar at age 14. Robben and two of his brothers (Patrick and Mark) created the Charles Ford Blues Band in honor of and named after their father. A fourth brother died in the Viet Nam conflict.
more...John Laird Abercrombie (December 16, 1944 – August 22, 2017) was an American jazz guitarist. His work explored jazz fusion, free jazz, and avant-garde jazz. Abercrombie studied at Berklee College of Music in Boston, Massachusetts. He was known for his understated style and his work with organ trios.
John Abercrombie was born on December 16, 1944, in Port Chester, New York. Growing up in the 1950s in Greenwich, Connecticut he was attracted to the rock and roll of Chuck Berry, Elvis Presley, Fats Domino, and Bill Haley and the Comets. He also liked the sound of jazz guitarist Mickey Baker of the vocal duo Mickey and Silvia. He had two friends who were musicians with a large jazz collection. They played him albums by Dave Brubeck and Miles Davis. The first jazz guitar album he heard was by Barney Kessel.
He took guitar lessons at the age of ten, asking his teacher to show him what Barney Kessel was playing. After high school, he attended Berklee College of Music. At Berklee, he was drawn to the music of Jim Hall, the 1962 album The Bridge by Sonny Rollins, and Wes Montgomery on his albums The Wes Montgomery Trio (1959) and Boss Guitar (1963). He cites George Benson and Pat Martino as inspirations. He often played with other students at Paul’s Mall, a jazz club in Boston connected to a larger club, Jazz Workshop. Appearing at Paul’s Mall led to meetings with Michael Brecker, Randy Brecker, and organist Johnny Hammond Smith, who invited him to go on tour.
more...Joseph Carl Firrantello (December 16, 1937 – January 10, 1986), known as Joe Farrell, was an American jazz multi-instrumentalist who primarily performed as a saxophonist and flutist. He is best known for a series of albums under his own name on the CTI record label and for playing in the initial incarnation of Chick Corea‘s Return to Forever.
Farrell was born in Chicago Heights, Illinois. As a child, Farrell began playing the flute and clarinet. After graduating from the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign in 1959, he moved to New York City to work as a freelance musician.
more...John Robert “Johnny Hammond” Smith (December 16, 1933 – June 4, 1997) was an American soul jazz and hard bop organist. Born in Louisville, Kentucky, he was a renowned player of the Hammond B-3 organ so earning “Hammond” as a nickname, which also avoided his being confused with jazz guitarist Johnny Smith.
Smith played with Paul Williams and Chris Columbo before forming his own group. His bands featured singers Etta Jones, Byrdie Green, saxophonists Houston Person, Earl Edwards, guitarists Eddie McFadden, Floyd Smith, James Clark, vibist Freddie McCoy. His career took off as he was serving as accompanist to singer Nancy Wilson. One of his last accomplishments also included Nancy Wilson. He wrote the song “Quiet Fire” for her Nancy Now!release in 1988.
After a 10-year spell on Prestige Records throughout the 1960s resulting in a series of albums, he signed for soul/R&B influenced Kudu imprint of Creed Taylor‘s well-regarded CTI Records jazz record label in 1971. His first album for Taylor, Break Out was chosen that year to launch Kudu. The album featured Grover Washington Jr. as a sideman prior to the launch of his career as a solo recording artist. Three further albums followed with Taylor on Kudu, as he decided to refer to himself as “Johnny Hammond”, after deciding to drop “Smith” from his name.
His style had become increasingly funky as he adapted to the style changes in music, culminating in two popular albums with the Mizell Brothers, Gambler’s Life (1974) for the CTI offshoot, Salvation and then in 1975, Gears after switching to another jazz label, Milestone Records. He began using electric and acoustic pianos, starting with Gambler’s Life, in addition to his signature instrument. Hammond’s song “Shifting Gears” was featured on the breakbeat compilation Ultimate Breaks and Beats, and was also featured in the soundtrack of the 2006 video game Driver: Parallel Lines as well.
Smith also taught at the Cal Poly Pomona music department for several years, beginning in January 1987.
He died in Victorville, California of cancer at the age of 63.
more...More Posts
- Mickey Tucker Day
- John Tchicai Day
- Oliver Jackson Day
- World Music with Bakalina Velika
- Daily Roots with Joe Cocker
- The Cosmos with NGC 5128
- Freddie Waits Day
- Jim Keltner Day
- Connie Kay Day
- World Music with Saida Karoli
- Daily Roots with the Stingers
- Community Band performing Arbor Day Celebration
- Happy Arbor Day 2019
- The Cosmos with NGC 4993
- Lakshminarayana Shankar Day
- Teddy Edwards Day
- Johnny Shines Day
- World Music with Manitas de Plata y Jose Reyes
- Daily Roots with Bongo Man Byfield
- The Cosmos with M8