Blog
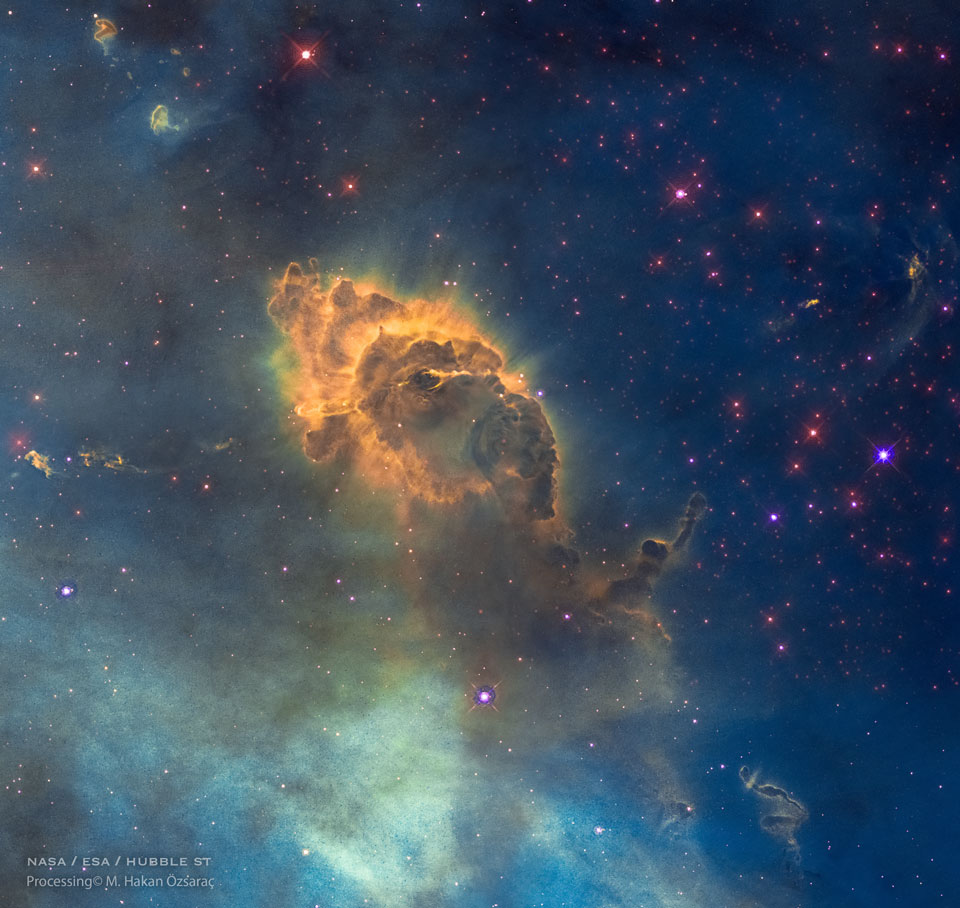
the Hubble Space Telescope captures a cosmic pillar of dust, over two-light years long, inside of which is Herbig-Haro 666 — a young star emitting powerful jets. The structure lies within one of our galaxy’s largest star forming regions, the Carina Nebula, shining in southern skies at a distance of about 7,500 light-years. The pillar‘s layered outline are shaped by the winds and radiation of Carina’s young, hot, massive stars, some of which are still forming inside the nebula. A dust-penetrating view in infrared light better shows the two, narrow, energetic jets blasting outward from a still hidden infant star.
Christopher William Parkening (born December 14, 1947) is an American classical guitarist. He holds the Chair of Classical Guitar at Pepperdine University under the title Distinguished Professor of Music.
Parkening was born in Los Angeles, California. His cousin Jack Marshall, a studio musician active in the 1960s, introduced Parkening to the recordings of Andrés Segovia when he was 11 and encouraged his classical guitar studies. By the age of 19 he had embarked on a professional career of regular touring and recording.
Segovia has stated that, “Christopher Parkening is a great artist—-he is one of the most brilliant guitarists in the world.” The Washington Post stated, Christopher Parkening is “the leading guitar virtuoso of our day, combining profound musical insight with complete technical mastery of his instrument.”
more...Phineas Newborn Jr. (December 14, 1931 – May 26, 1989) was an American jazz pianist, whose principal influences were Art Tatum, Oscar Peterson, and Bud Powell.
Newborn was born in Whiteville, Tennessee, and came from a musical family: his father, Phineas Newborn Sr., was a drummer in blues bands,and his younger brother, Calvin, a jazz guitarist. He studied piano as well as trumpet, and tenor and baritone saxophone. Before moving on to work with Lionel Hampton, Charles Mingus, and others, Newborn first played in an R&B band led by his father on drums, with his brother Calvin on guitar, Tuff Green on bass, Ben Branch and future Hi Records star Willie Mitchell. The group was the house band at the now famous Plantation Inn Club in West Memphis, Arkansas, from 1947 to 1951, and recorded as B. B. King‘s band on his first recordings in 1949, as well as the Sun Records sessions in 1950. They left West Memphis in 1951 to tour with Jackie Brenston as the “Delta Cats” in support of the record “Rocket 88“, recorded by Sam Phillips and considered by many to be the first ever rock & roll record (it was the first Billboard No. 1 record for Chess Records).
more...Cecil Payne (December 14, 1922 – November 27, 2007) was an American jazz baritone saxophonist born in Brooklyn, New York. Payne also played the alto saxophone and flute. He played with other prominent jazz musicians, in particular Dizzy Gillespie and Randy Weston, in addition to his solo work as bandleader.
Payne received his first saxophone aged 13, asking his father for the instrument after hearing “Honeysuckle Rose” performed by Count Basie with Lester Young soloing. Payne took lessons from a local alto sax player, Pete Brown. He studied at Boys High School, Bedford-Stuyvesant
more...Clark Virgil Terry Jr. (December 14, 1920 – February 21, 2015) was an American swing and bebop trumpeter, a pioneer of the flugelhorn in jazz, and a composer and educator.
He played with Charlie Barnet (1947), Count Basie (1948–51), Duke Ellington (1951–59), Quincy Jones (1960), and Oscar Peterson (1964–96). He was with The Tonight Show Band on The Tonight Show from 1962 to 1972. His career in jazz spanned more than 70 years, during which he became one of the most recorded jazz musicians, appearing on over 900 recordings. Terry also mentored Quincy Jones, Miles Davis, Herbie Hancock, Wynton Marsalis, Pat Metheny, Dianne Reeves, and Terri Lyne Carrington.
Terry was born to Clark Virgil Terry Sr. and Mary Terry in St. Louis, Missouri, on December 14, 1920. He attended Vashon High School and began his professional career in the early 1940s, playing in local clubs. He served as a bandsman in the United States Navy during World War II. His first instrument was valve trombone.
more...https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Tkfkun__n-0
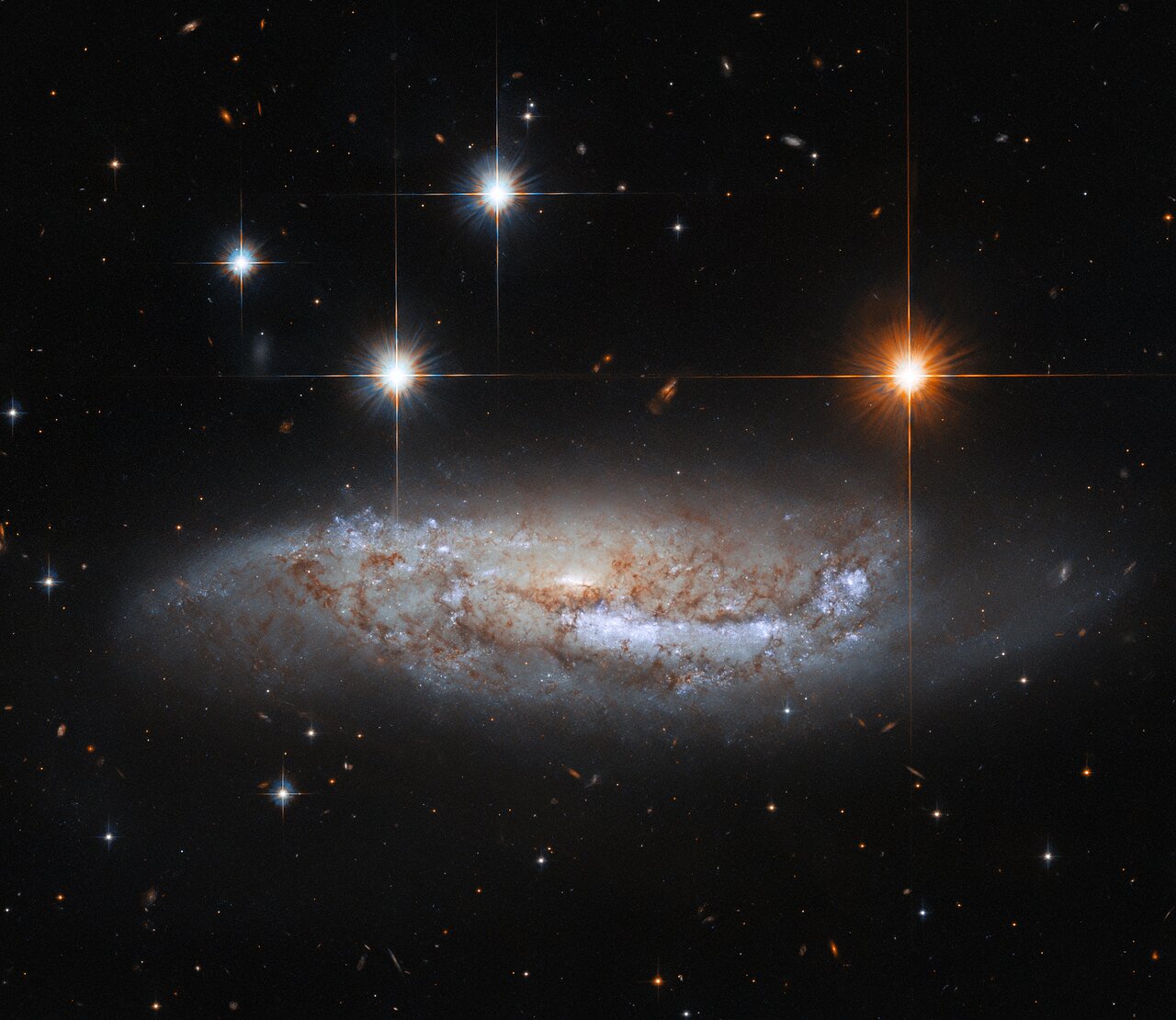
more...the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope captures a side-on view of NGC 3568, a barred spiral galaxy roughly 57 million light-years from the Milky Way in the constellation Centaurus. In 2014 the light from a supernova explosion in NGC 3568 reached Earth — a sudden flare of light caused by the titanic explosion accompanying the death of a massive star. Whilst most astronomical discoveries are the work of teams of professional astronomers, this supernova was discovered by amateur astronomers from the Backyard Observatory Supernova Search in New Zealand. Dedicated amateur astronomers often make intriguing discoveries — particularly of fleeting astronomical phenomena such as supernovae. This Hubble observation comes from a hoard of data built up to pave the way for future science with the upcoming NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope. By combining ground-based observations with data from Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys and Wide Field Camera 3, astronomers have built a treasure trove of data on the connections between young stars and the clouds of cold gas in which they form. One of Webb’s key science goals is to explore the life cycle of stars — particularly how and where stars are born. Since Webb observes at infrared wavelengths, it will be able to peer through the clouds of gas and dust in stellar nurseries and observe the fledgling stars within. Webb’s superb sensitivity will even allow astronomers to directly investigate faint protostellar cores — the earliest stages of star birth.

more...
Judge Kenneth Peterson (December 13, 1964 – May 17, 2020), known professionally as Lucky Peterson, was an American musician who played contemporary blues, fusing soul, R&B, gospel and rock and roll. He played guitar and keyboards. Music journalist Tony Russell, in his book The Blues – From Robert Johnson to Robert Cray has said, “he may be the only blues musician to have had national television exposure in short pants.”
Peterson’s father, bluesman James Peterson, owned a nightclub in Buffalo called The Governor’s Inn. The club was a regular stop for fellow bluesmen such as Willie Dixon. Dixon saw a five-year-old Lucky Peterson performing at the club and, in Peterson’s words, “Took me under his wing.” Months later, Peterson performed on The Tonight Show, The Ed Sullivan Show and What’s My Line?. Millions of people watched Peterson sing “1-2-3-4”, a cover version of “Please, Please, Please” by James Brown. At the time, Peterson said “his father wrote it”. Around this time he recorded his first album, Our Future: 5 Year Old Lucky Peterson, for Today/Perception Records and appeared on the public television show, Soul!
more...Benjamin M. Tucker (December 13, 1930 – June 4, 2013) was an American jazz bassist who appeared on hundreds of recordings. Tucker played on albums by Art Pepper, Billy Taylor, Quincy Jones, Grant Green, Dexter Gordon, Hank Crawford, Junior Mance, and Herbie Mann.
He was born in Tennessee. As bass player in the Dave Bailey Quintet in 1961, he wrote the instrumental version of the song “Comin’ Home Baby!“, first issued on the album Two Feet in the Gutter. Bob Dorough later wrote a lyric to the song, and the vocal version became a Top 40 hit for jazzsinger Mel Tormé in 1962.
Tucker released the album Baby, You Should Know It (Ava, 1963) with Victor Feldman, Larry Bunker, Bobby Thomas, Ray Crawford, Tommy Tedesco, and Carlos “Patato” Valdes.
By 1972, Tucker owned two radio stations, WSOK-AM, which had over 400,000 listeners, and WLVH-FM. Both of these were located in his hometown of Savannah, Georgia.
He died in a traffic collision in Hutchinson Island, Georgia, on June 4, 2013.
more...Carlos García Montoya (13 December 1903 – 3 March 1993) in Madrid, Spain, was a prominent flamenco guitarist and a founder of the modern-day popular flamenco style of music.
He was the nephew of renowned flamenco guitarist Ramón Montoya. He first learned from his mother, “la Tula”, and then from a neighboring barber, Pepe el Barbero, i.e. Pepe the Barber. After one year Montoya had completed what Pepe was able to teach him. Carlos left to learn what he could from other flamenco guitarists of the time. At fourteen he was playing in the “cafes cantantes,” in the heyday of flamenco singing and dancing, for such artists as Antonio de Bilbao, Juan el Estampío, La Macarrona and La Camisona in Madrid, Spain.
more...William Alexander “Sonny” Greer (December 13, c. 1895 – March 23, 1982) was an American jazz drummer and vocalist, best known for his work with Duke Ellington.
Greer was born in Long Branch, New Jersey, United States, and played with Elmer Snowden‘s band and the Howard Theatre‘s orchestra in Washington, D.C., before joining Duke Ellington, whom he met in 1919. He was Ellington’s first drummer, playing with his quintet, the Washingtonians, and moved with Ellington into the Cotton Club. As a result of his job as a designer with the Leedy Drum Company of Indiana, Greer was able to build up a huge drum kit worth over a then-considerable $3,000, including chimes, a gong, timpani, and vibes.
more...https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FP9hXRgnvu8
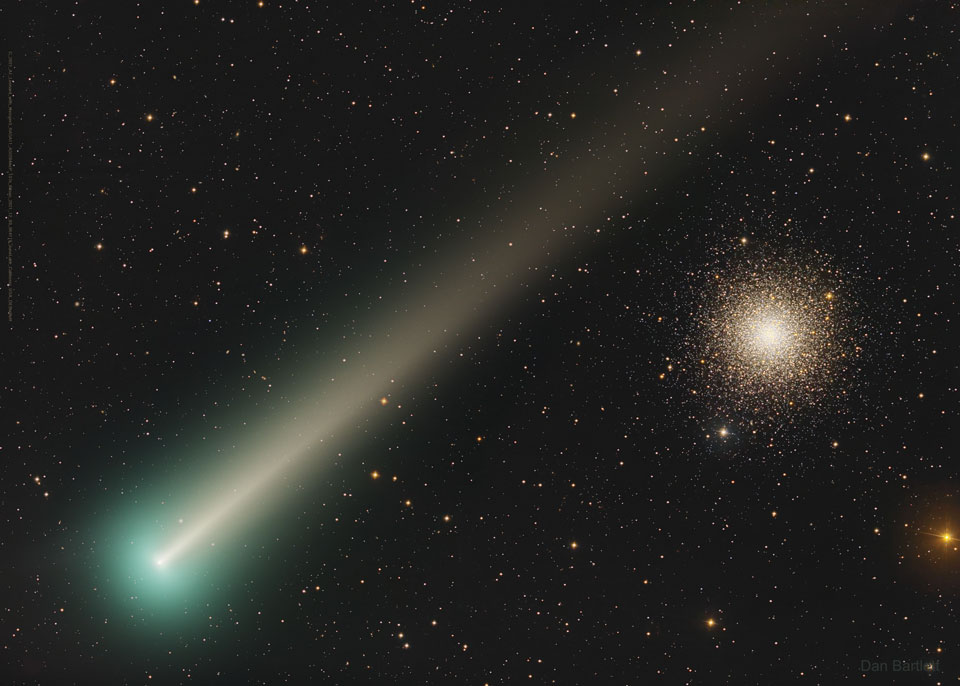
more...Comet Leonard is now visible to the unaided eye — but just barely. Passing nearest to the Earth today, the comet is best seen this week soon after sunset, toward the west, low on the horizon. Currently best visible in the north, by late December the comet will best be seen from south of Earth’s equator. The featured image of Comet C/2021 A1 (Leonard) was taken a week ago from California, USA. The deep exposure shows in great detail the comet’s green gas coma and developing dust tail. The comet — across our inner Solar System and only light-minutes away — was captured passing nearly in front of globular star cluster M3. In contrast, M3 is about 35,000 light-years away. In a week, Comet Leonard will pass unusually close to Venus, but will continue on and be at its closest to the Sun in early January.

Grover Washington Jr. (December 12, 1943 – December 17, 1999) was an American jazz-funk / soul-jazz saxophonist. Along with Wes Montgomery and George Benson, he is considered by many to be one of the founders of the smooth jazz genre. He wrote some of his material and later became an arranger and producer.
Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, Washington made some of the genre’s most memorable hits, including “Mister Magic”, “Reed Seed”, “Black Frost”, “Winelight”, “Inner City Blues”, “Let it Flow(For Dr. J)” and “The Best is Yet to Come”. In addition, he performed very frequently with other artists, including Bill Withers on “Just the Two of Us“, Patti LaBelle on “The Best Is Yet to Come” and Phyllis Hyman on “A Sacred Kind of Love”. He is also remembered for his take on the Dave Brubeck classic “Take Five“, and for his 1996 version of “Soulful Strut“. On December 17, 1999, five days after his 56th birthday, Washington collapsed while waiting in the green room after performing four songs for The Saturday Early Show, at CBS Studios in New York City. He was taken to St. Luke’s-Roosevelt Hospital, where he was pronounced dead at about 7:30 pm. His doctors determined that he had suffered a massive heart attack. He is interred at West Laurel Hill Cemetery in Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y9-PRcDwS8Q
more...Anthony Tillmon Williams (December 12, 1945 – February 23, 1997) was an American jazz drummer. Williams first gained fame in the band of trumpeter Miles Davis and pioneered jazz fusion. He was inducted into the Modern Drummer Hall of Fame in 1986. During his lifetime, music critic Robert Christgau described Williams as “probably the best drummer in the world”.
Williams was born in Chicago and grew up in Boston. He was of African, Portuguese, and Chinese descent. He studied with drummer Alan Dawsonat an early age, and began playing professionally at the age of 13 with saxophonist Sam Rivers. Saxophonist Jackie McLean hired Williams when he was 16. At 17 Williams gained attention by joining Miles Davis in what was later dubbed Davis’s Second Great Quintet. Williams was a vital element of the group, called by Davis in his autobiography “the center that the group’s sound revolved around.” His playing helped redefine the role of the jazz rhythm section through the use of polyrhythms and metric modulation. Meanwhile, he recorded his first two albums as leader for Blue Note label, Life Time (1964) and Spring (1965). He also recorded as a sideman for the label including, in 1964, Out to Lunch! with Eric Dolphy and Point of Departurewith Andrew Hill. On February 20, 1997, Williams checked into Seton Medical Center in Daly City, California, suffering from stomach pain. 3 days later, while recuperating from gall bladder surgery, he died of a heart attack. Williams was 51 years old
more...Emmanuel N’Djoké “Manu” Dibango (12 December 1933 – 24 March 2020) was a Cameroonian musician and songwriter who played saxophoneand vibraphone. He developed a musical style fusing jazz, funk, and traditional Cameroonian music. His father was a member of the Yabassi ethnic group, while his mother was a Duala. He was best known for his 1972 single “Soul Makossa“. He died from COVID-19 on 24 March 2020.
Emmanuel “Manu” Dibango was born in Douala, Cameroon in 1933. His father, Michel Manfred N’Djoké Dibango, was a civil servant. Son of a farmer, he met his wife travelling by pirogue to her residence, Douala. Emmanuel’s mother was a fashion designer, running her own small business. Both her ethnic group, the Douala, and his, the Yabassi, viewed this union of different ethnic groups with some disdain. Dibango had only a stepbrother from his father’s previous marriage, who was four years older than him. In Cameroon, one’s ethnicity is dictated by one’s father, though Dibango wrote in his autobiography, Three Kilos of Coffee, that he had “never been able to identify completely with either of [his] parents”
more...More Posts
- Carl Perkins Day
- World Music with Australian Aboriginal Didgeridoo
- Daily Roots with Mystic Eyes
- The Cosmos with IRAS 16399-0937
- Joe Castro Day
- Oscar Peterson Day
- World Music with Aljibe
- Daily Roots with Bunny Rugs
- The Cosmos with M86
- David Crosby Day
- Son Seals Day
- Stuff Smith Day
- World Music with Lingua Franca Ensemble
- Daily Roots with Bunny Wailer
- The Cosmos with NGC 2736
- Mulgrew Miller Day
- George Shearing Day
- World Music with Tabanka
- Daily Roots with Prodigal Creator
- The Cosmos with Meteor M31