Blog
Rahsaan Roland Kirk (born Ronald Theodore Kirk; August 7, 1935 – December 5, 1977), known earlier in his career simply as Roland Kirk, was an American jazz multi-instrumentalist who played tenor saxophone, flute, and many other instruments. He was renowned for his onstage vitality, during which virtuoso improvisation was accompanied by comic banter, political ranting, and the ability to play several instruments simultaneously.
Kirk was born Ronald Theodore Kirk in Columbus, Ohio, where he lived in a neighborhood known as Flytown. He became blind at two years old, which he said was a result of improper medical treatment. As a teenager, Kirk studied at the Ohio State School for the Blind. By age fifteen he was on the road playing rhythm and blues on weekends with Boyd Moore’s band. According to saxophonist Hank Crawford, “He would be like this 14 year-old blind kid playing two horns at once. They would bring him out and he would tear the joint up.” Hank heard him during this period and said he was unbelievable. He remarked, “Now they had him doing all kinds of goofy stuff but he was playing the two horns and he was playing the shit out of them. He was an original from the beginning.” Kirk felt compelled by a dream to transpose two letters in his first name to make ‘”Roland”.[2] In 1970, Kirk added “Rahsaan” to his name after hearing it in a dream.
more...George Van Eps (August 7, 1913 – November 29, 1998) was an American swing and mainstream jazz guitarist.
George Van Eps was born in Plainfield, New Jersey, into a family of musicians. His three brothers were musicians. His mother was a classical pianist and his father, Fred Van Eps, was a ragtime banjoist and sound engineer. George Van Eps began playing banjo when he was eleven years old. After hearing Eddie Lang on the radio, he put down the banjo and devoted himself to guitar. By the age of thirteen, in 1926, he was performing on the radio. Through the middle of the 1930s, he played with Harry Reser, Smith Ballew, Freddy Martin, Benny Goodman, and Ray Noble.
Van Eps moved to California and spent most of his remaining career as a studio musician, playing on many commercials and movie soundtracks.
In the 1930s, he invented a model of guitar with another bass string added to the common six-string guitar. The seven-string guitar allowed him to play basslines below his chord voicings, unlike the single-string style of Charlie Christian and Django Reinhardt. He called his technique “lap piano”. It anticipated the fingerpicking style of country guitarists Chet Atkins and Merle Travis and inspired jazz guitarists Bucky Pizzarelli, John Pizzarelli, and Howard Alden to pick up the seven-string.
more...Charles Luckyth Roberts (August 7, 1887 – February 5, 1968), better known as Luckey Roberts, was an American composer and stride pianist who worked in the jazz, ragtime, and blues styles.
Luckey Roberts was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and was playing piano and acting professionally with traveling Negro minstrel shows in his childhood. He settled in New York City about 1910 and became one of the leading pianists in Harlem, and started publishing some of his original rags.
Roberts toured France and the UK with James Reese Europe during World War I, then returned to New York where he wrote music for various shows and recorded piano rolls.
With James P. Johnson, Roberts developed the stride piano style of playing about 1919.
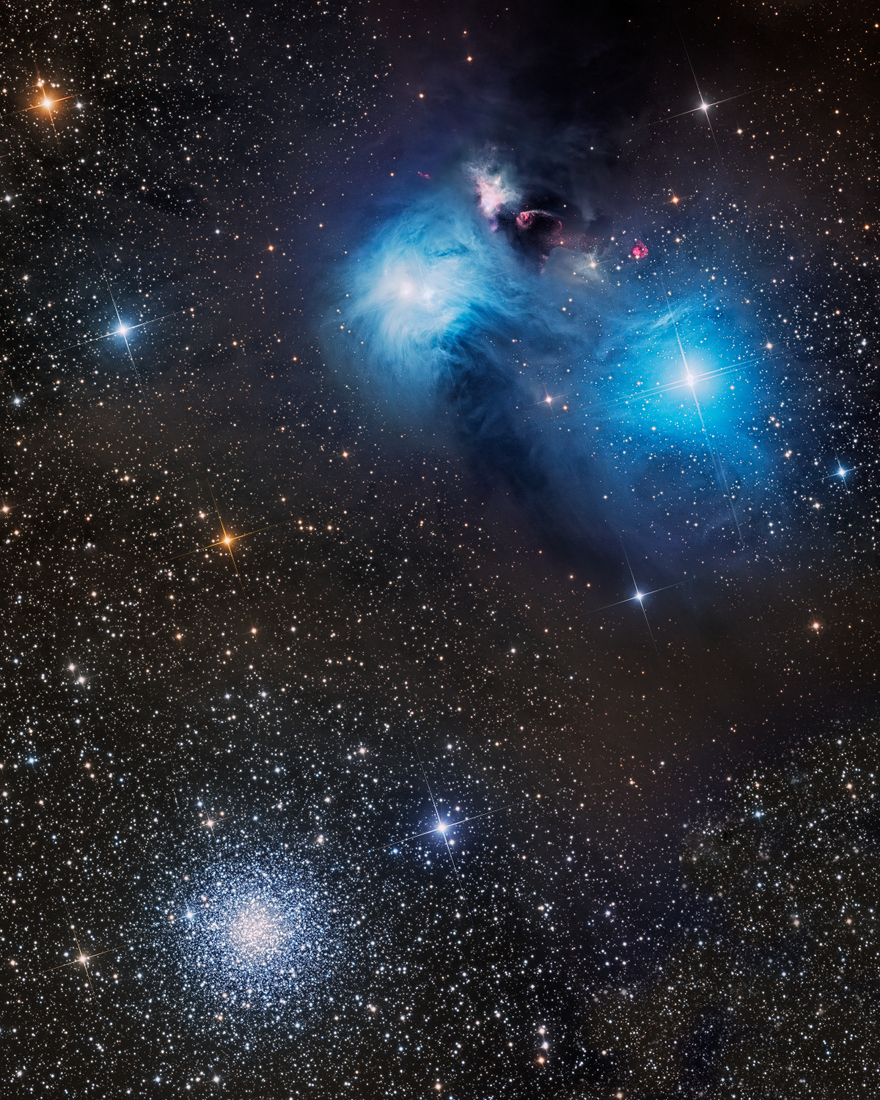
more...Cosmic dust clouds cross a rich field of stars in this telescopic vista near the northern boundary of Corona Australis, the Southern Crown. Less than 500 light-years away the dust clouds effectively block lightfrom more distant background stars in the Milky Way. Top to bottom the frame spans about 2 degrees or over 15 light-years at the clouds’ estimated distance. At top right is a group of lovely reflection nebulae cataloged asNGC 6726, 6727, 6729, and IC 4812. A characteristic blue color is produced as light from hot stars is reflected by the cosmic dust. The dust also obscures from view stars in the region still in the process of formation. Just above the bluish reflection nebulae a smaller NGC 6729 surrounds young variable star R Coronae Australis. To its right are telltale reddish arcs and loops identified as Herbig Haro objects associated with energetic newborn stars. Magnificent globular star cluster NGC 6723 is at bottom left in the frame. Though NGC 6723 appears to be part of the group, its ancient stars actually lie nearly 30,000 light-years away, far beyond the young stars of the Corona Australis dust clouds.

Regina Carter (Detroit, August 6, 1966) is an American jazz violinist. She is the cousin of jazz saxophonist James Carter.
Carter was born in Detroit and was one of three children in her family. She began piano lessons at the age of two after playing a melody by ear for her brother’s piano teacher. After she deliberately played the wrong ending note at a concert, the piano teacher suggested she take up the violin, indicating that the Suzuki Method could be more conducive to her creativity. Carter’s mother enrolled her at the Detroit Community Music School when she was four years old and she began studying the violin. She still studied the piano, as well as tap and ballet. As a teenager, she played in the youth division of the Detroit Symphony Orchestra. While at school, she was able to take master classes from Itzhak Perlman and Yehudi Menuhin.
Carter attended Cass Technical High School with a close friend, jazz singer Carla Cook, who introduced her to Ella Fitzgerald. In high school, Carter performed with the Detroit Civic Orchestra and played in a pop-funk group named Brainstorm. In addition to taking violin lessons, she also took viola, oboe, and choir lessons. Carter was studying classical violin at the New England Conservatory of Music in Boston when she decided to switch to jazz. She transferred to Oakland University in Rochester, Michigan where she was a jazz major under the direction of Marvin “Doc” Holladay . She also studied and performed with trumpeter Marcus Belgrave Through Belgrave Carter was able to meet a lot of people active in the Detroit jazz scene, including Lyman Woodard. She graduated in 1985. After graduating, she taught strings in Detroit public schools. Needing a change of scene, she moved to Europe and spent two years in Germany. While making connections, she worked as a nanny for a German family and taught violin on a U.S. military base.
more...Ravi Coltrane (born August 6, 1965) is an American jazz saxophonist. Co-owner of the record label RKM Music, he has produced pianist Luis Perdomo, guitarist David Gilmore, and trumpeter Ralph Alessi.
Ravi Coltrane is the son of saxophonist John Coltrane and jazz harpist Alice Coltrane. He is the second of three children; the others were John Jr. and Oran. He is a cousin of experimental music producer Steven Ellison, aka Flying Lotus. He was raised in Los Angeles, California, and was named after sitar player Ravi Shankar. Ravi Coltrane was under two years old in 1967 when his father died.
He is a 1983 graduate of El Camino Real High School in Woodland Hills, California. In 1986, he studied music, concentrating on saxophone at the California Institute of the Arts. He has worked often with Steve Coleman, a significant influence on Coltrane’s musical conception. Coltrane has also played with Geri Allen, Kenny Barron, McCoy Tyner, Pharoah Sanders, Herbie Hancock, Carlos Santana, Stanley Clarke, Chick Corea, and Branford Marsalis.
In 1997, after performing on over thirty recordings as a sideman, Coltrane recorded Moving Pictures, his first album as leader, working with drummer Jeff “Tain” Watts, bassist Lonnie Plaxico, and pianist Michael Cain. This led to touring with his working band, featuring Andy Milne on piano, drummer Steve Hass, and bassist Lonnie Plaxico. Coltrane’s second album, From the Round Box (2000), was recorded with pianist Geri Allen, trumpeter Ralph Alessi, bassist James Genus, and drummer Eric Harland. Mad 6 (2002), Coltrane’s first album for Sony, featured drummer Steve Hass, pianist George Colligan, and bassist James Genus. In Flux (2005) included bassist Drew Gress, pianist Luis Perdomo, and drummer E. J. Strickland.
more...Charles Edward Haden (August 6, 1937 – July 11, 2014) was an American jazz double bass player, bandleader, composer and educator whose career spanned more than 50 years. In the late 1950s, he was an original member of the ground-breaking Ornette Coleman Quartet.
Haden revolutionized the harmonic concept of bass playing in jazz. German musicologist Joachim-Ernst Berendt wrote that Haden’s “ability to create serendipitous harmonies by improvising melodic responses to Coleman’s free-form solos (rather than sticking to predetermined harmonies) was both radical and mesmerizing. His virtuosity lies…in an incredible ability to make the double bass ‘sound out’. Haden cultivated the instrument’s gravity as no one else in jazz. He is a master of simplicity which is one of the most difficult things to achieve.” Haden played a vital role in this revolutionary new approach, evolving a way of playing that sometimes complemented the soloist and sometimes moved independently. In this respect, as did his predecessor bassists Jimmy Blanton and Charles Mingus, Haden helped liberate the bassist from a strictly accompanying role to becoming a more direct participant in group improvisation. In 1969, he formed his first band, the Liberation Music Orchestra, featuring arrangements by pianist Carla Bley. In the late 1960s, he became a member of pianist Keith Jarrett’s trio, quartet and quintet. In the 1980s, he formed his band, Quartet West. Haden also often recorded and performed in a duo setting, with musicians including guitarist Pat Metheny and pianist Hank Jones.
Haden was born in Shenandoah, Iowa. His family was exceptionally musical and performed on the radio as the Haden Family, playing country musicand American folk songs. Haden made his professional debut as a singer on the Haden Family’s radio show when he was just two years old. He continued singing with his family until he was 15 when he contracted a bulbar (brainstem) form of polio affecting his throat and facial muscles.[2] At the age of 14, Haden had become interested in jazz after hearing Charlie Parker and Stan Kenton in concert. Once he recovered from his bout with polio, Haden began in earnest to concentrate on playing the bass. Haden’s interest in the instrument was not sparked by jazz bass alone, but also by the harmonies and chords he heard in compositions by Bach. Haden soon set his sights on moving to Los Angeles to pursue his dream of becoming a jazz musician, and to save money for the trip, took a job as house bassist for ABC-TV’s Ozark Jubilee in Springfield, Missouri.
more...
Anna Marie Wooldridge (August 6, 1930 – August 14, 2010), known professionally as Abbey Lincoln, was an American jazz vocalist, songwriter, and actress. She was a civil rights activist beginning in the 1960s. Lincoln made a career not only out of delivering deeply felt presentations of standards but writing and singing her own material.
Born in Chicago but raised in Calvin Center, Cass County, Michigan, Lincoln was one of many singers influenced by Billie Holiday. Her debut album, Abbey Lincoln’s Affair – A Story of a Girl in Love, was followed by a series of albums for Riverside Records. In 1960 she sang on Max Roach‘s landmark civil rights-themed recording, We Insist! Lincoln’s lyrics were often connected to the civil rights movement in America. After a tour of Africa in the mid-1970s, she adopted the name Aminata Moseka.
During the 1980s, Lincoln’s creative output was smaller and she released only a few albums. Her song “For All We Know” is featured in the 1989 film Drugstore Cowboy. During the 1990s and until her death, however, she fulfilled a 10-album contract with Verve Records.
These albums are highly regarded and represent a crowning achievement in Lincoln’s career. Devil’s Got Your Tongue (1992) featured Rodney Kendrick, Grady Tate, Yoron Israel, J. J. Johnson, Stanley Turrentine, Babatunde Olatunji and The Staple Singers, among others. In 2003, Lincoln received a National Endowment for the Arts Jazz Master Award.
more...Soleares is one of the most basic forms or palos of Flamenco music, probably originated around Cádiz or Seville in Andalusia, the most southern region of Spain. It is usually accompanied by one guitar only, in phrygian mode “por arriba” (fundamental on the 6th string); “Bulerías por soleá” is usually played “por medio” (fundamental on the 5th string). Soleares is sometimes called “mother of palos” although it is not the oldest one (e.g. siguiriyas is older than soleares) and not even related to every other palo (e.g. fandangos family is from a different origin)
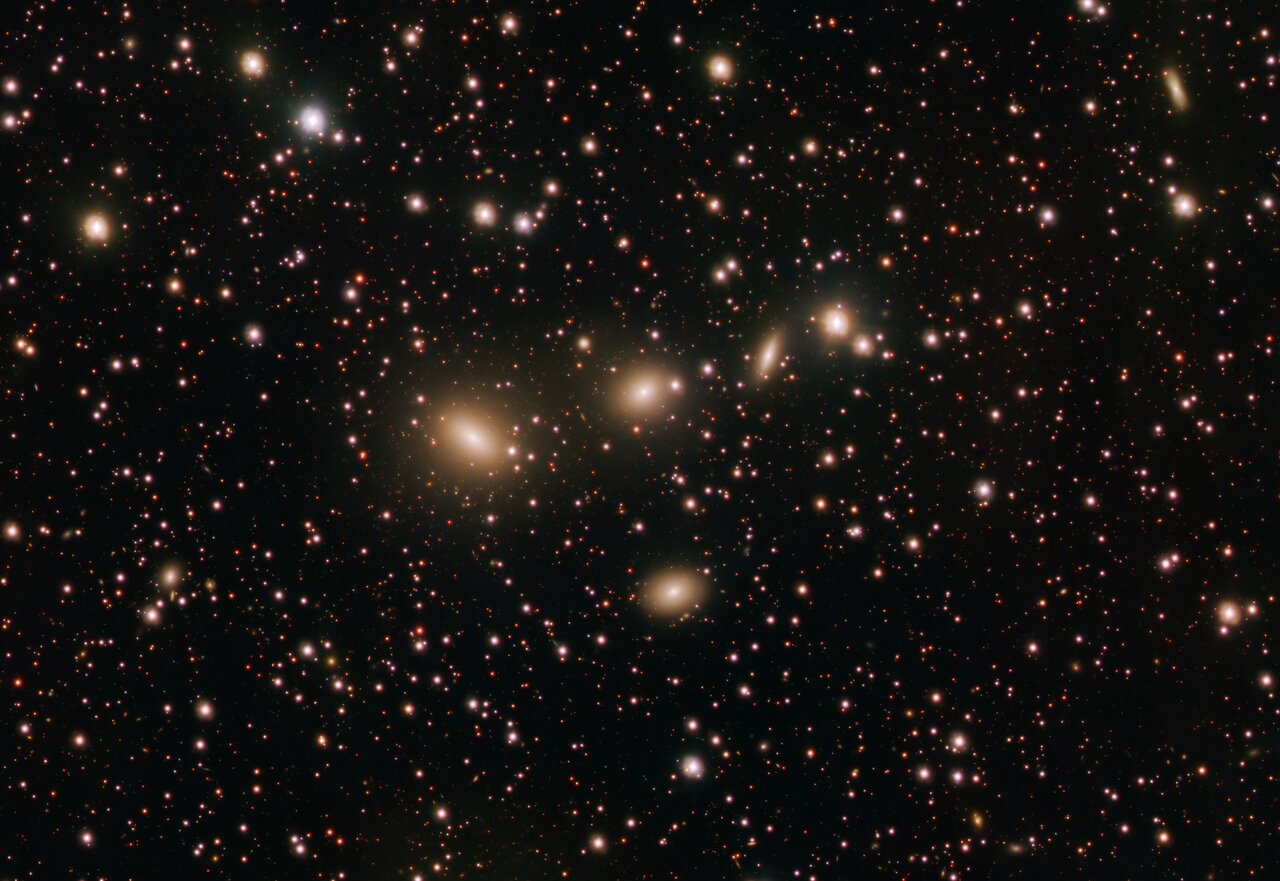
more...Space can be a lonely place. But not so for this quartet of galaxies making up HCG 86 and observed here with ESO’s VLT Survey Telescope (VST). The four galaxies located approximately 270 million light years from Earth in the Sagittarius constellation, are seen from Earth as arranged in triangular shape, with three of them on a straight line and one underneath; the bright objects to the right of the elongated galaxy are not part of the quartet. HCG stands for Hickson Compact Group, and is used to describe groups of four to ten galaxies where members are physically very close to each other. Because of their compactness, such groups are ideal environments to study galactic interactions, which can sometimes lead to galaxies merging with each other. This image of HCG 86 was taken by a team of astronomers led by Rossella Ragusa of the Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica in Italy as part of the VST Early-type Galaxy Survey (VEGAS) programme. “With VST we are able to investigate very faint structures in the galaxies’ outskirts, which are the relics of past gravitational interactions and merging events,” says Ragusa. In particular, by mapping the light distribution in and around the group’s galaxies in this study, the team concluded that these faint structures are the leftovers of satellite galaxies gobbled by the group approximately seven billion years ago. Located at ESO’s Paranal Observatory in Chile, the VST is one of the world’s largest survey telescopes, devoted to mapping the sky in visible light wavelengths. 2021 marks the anniversary of its first decade of operation, a period during which it has helped to search for planets outside the Solar System and probe the structure of our galaxy and the wider Universe.

Willie Weeks (born August 5, 1947) is an American bass guitarist. He has gained fame performing with famous musicians in a wide variety of genres. He has been one of the most in-demand session musicians throughout his career. Weeks has also gained fame touring with many of rock‘s heavyweights throughout his career.
Weeks was born in Salemburg, North Carolina and began playing the electric bass in the early 1960s. His earliest influences were the country, popand R&B music he heard on the radio. Weeks counts bassists Ron Carter, James Jamerson, and Ray Brown as early influences.
Weeks has worked in the studio or toured with a wide range of artists, including:
Gregg Allman, David Bowie, Clarence “Gatemouth” Brown, Roy Buchanan, Jimmy Buffett, Kevin Chalfant, Eric Clapton, Hank Crawford, Robert Cray, Pino Daniele, Bo Diddley, The Doobie Brothers, Lou Fellingham, Aretha Franklin, Vince Gill, Buddy Guy, Isaac Hayes, George Harrison, Donny Hathaway, Etta James, Billy Joel, Rickie Lee Jones, Wynonna Judd, Chaka Khan, B.B. King, Lyle Lovett, Gail Davies, David Lee Roth, Michael McDonald, Don McLean, John Mayer, John Mellencamp, Bette Midler, Randy Newman, Pino Palladino, Leon Russell, Boz Scaggs, John Scofield, Carly Simon, Soulive, Rod Stewart, The Rolling Stones, James Taylor, Richard and Linda Thompson, Joe Walsh, Steve Winwood, Bobby Womack, Stevie Wonder, Ronnie Wood and Eikichi Yazawa.
more...Airto Guimorvan Moreira (born August 5, 1941) is a Brazilian jazz drummer and percussionist. He is married to jazz singer Flora Purim, and their daughter Diana Moreira is also a singer. Coming to prominence in the late 1960s as a member of the Brazilian ensemble Quarteto Novo, he moved to the United States and worked in jazz fusion with Miles Davis and Return to Forever.
Airto Moreira was born in Itaiópolis, Brazil, into a family of folk healers, and raised in Curitiba and São Paulo. Showing an extraordinary talent for music at a young age, he became a professional musician at age 13, noticed first as a member of the samba jazz pioneers Sambalanço Trio and for his landmark recording with Hermeto Pascoal in Quarteto Novo in 1967. Shortly after, he followed his wife Flora Purim to the United States.
more...Leonard Harold Breau (August 5, 1941 – August 12, 1984) was a Canadian-American guitarist and music educator. Breau blended many styles of music, including jazz, country, classical, and flamenco. Inspired by country guitarists like Chet Atkins, Breau used fingerstyle techniques not often used in jazz guitar. By using a seven-string guitar and approaching the guitar like a piano, he opened up possibilities for the instrument.
Breau was born August 5, 1941, in Auburn, Maine, but moved with his family to Moncton, New Brunswick in 1948. His francophone parents, Harold Breau and Betty Cody, were professional country and western musicians who performed and recorded from the mid-1930s until the mid-1970s. From the mid to late 1940s they played summer engagements in southern New Brunswick, advertising their performances by playing free programs on radio station CKCW Moncton. Lenny began playing guitar at the age of eight. When he was twelve, he started a small band with friends, and by the age of fourteen he was the lead guitarist for his parents’ band, billed as “Lone Pine Junior”, playing Merle Travis and Chet Atkins instrumentals and occasionally singing. He made his first professional recordings in Westbrook, Maine at Event Records with Al Hawkes at the age of 15 while working as a studio musician. Many of these recordings were released posthumously on the album Boy Wonder. Breau had problems with drugs beginning in the 1960s which he managed to control during the last years of his life. On August 12, 1984, his body was found in a swimming pool at his apartment complex in Los Angeles, California. The coroner reported that Breau had been strangled. Breau’s wife, Jewel, was the chief suspect, but she was not charged.
more...
Rhythm Roots Workshop at Minnesota VA Home Adult Day Center Memory Loss group. The third workshop is a series of nine world percussion sessions for Veterans. Wednesday August 4th 2021 10-noon.

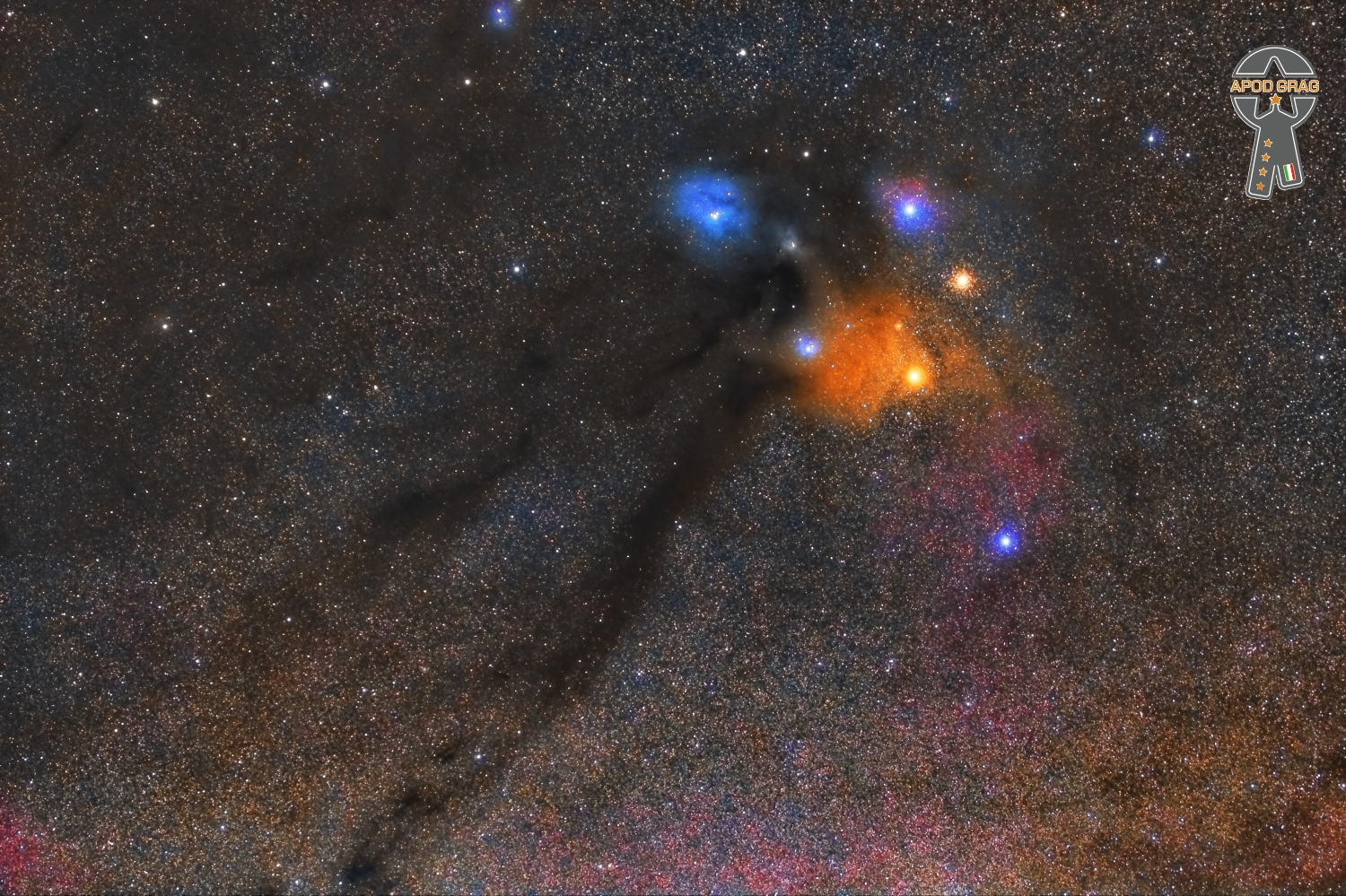
The Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex is a dark nebula of gas and dust that is located 1° south of the star ρ Ophiuchi of the constellation Ophiuchus. At an estimated distance of 131 ± 3 parsecs, it is one of the closest star-forming regions to the Solar System.
This cloud covers an angular area of 4.5° × 6.5° on the celestial sphere. It consists of two major regions of dense gas and dust. The first contains a star-forming cloud (L1688) and two filaments (L1709 and L1755), while the second has a star-forming region (L1689) and a filament (L1712–L1729). These filaments extend up to 10–17.5 parsecs in length and can be as narrow as 0.24 parsecs in width. Some of the structures within the complex appear to be the result of a shock front passing through the clouds from the direction of the neighboring Sco OB2 Association.
More Posts
- Echos of Freedom with Maya Angelou
- The Cosmos with NGC 5963/5965
- Benny Golson Day
- Antonio Carlos Jobim Day
- Sleepy John Estes Day
- World Music with El Indio Gitano
- Daily Roots with the Harmonians
- Echos of Freedom by Nina Simone
- The Cosmos with M51
- Joe Albany Day
- Jimmy Forrest Day
- Avery Parrish Day
- Oliver “Tuku” Mtukudzi Day
- Daily Roots with the Soul Rhythms
- Echos of Freedom by Lincoln
- The Cosmos with the Moon Meteorite Strike
- Gary Burton Day
- Curtis Counce Day
- Django Reinhardt Day
- World Music with Hussein Rassim