Blog
This tune commemorates the Sir Henry Clinton’s, Commander of the British forces, storming of Stony Point in 1779. General George Washington managed to outsmart Clinton, and staged to a maneuver to retake Stony Point with the help of General Anthony Wayne, which was eventually successful.
more...https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rlTFKt3tNow
more...Rhoda Scott (born July 3, 1938) is an American soul jazz organist.
Scott was first attracted to the organ in her father’s church at age seven. “It’s really the most beautiful instrument in the world”, she stated in a recent interview. “The first thing I did was take my shoes off and work the pedals.” From then on she always played her church organ in her bare feet, and to this date she has continued the practice.
In 1967 Scott moved to France, where she has since spent most of her career.
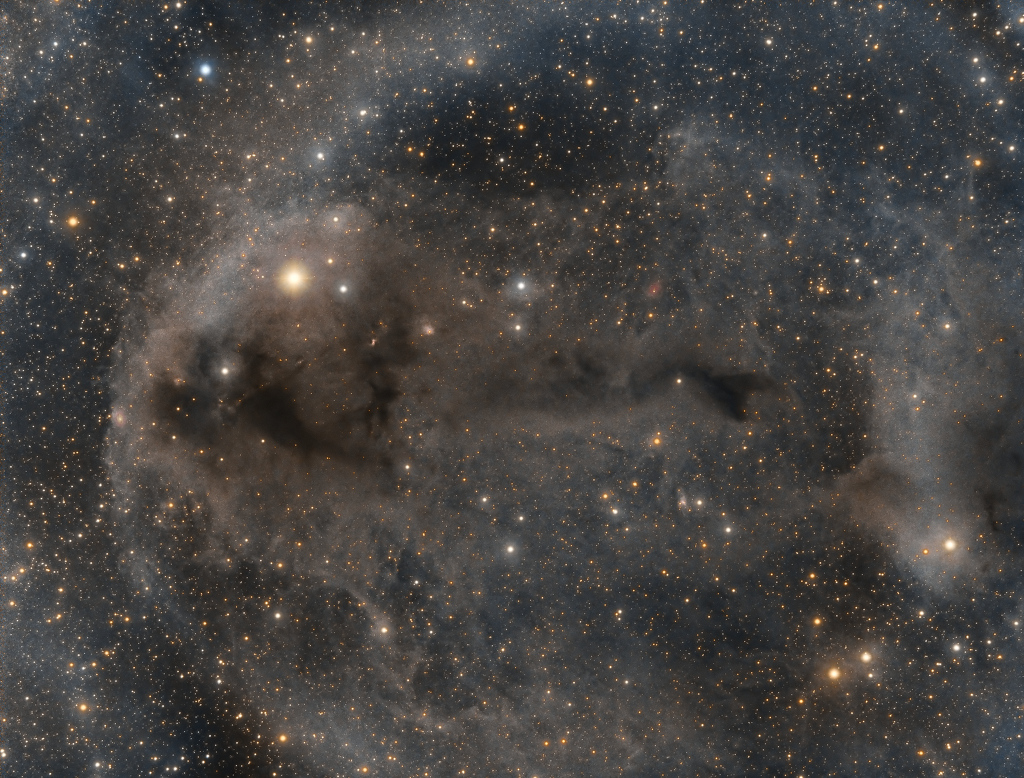
more...Stars are forming in Lynds Dark Nebula (LDN) 1251. About 1,000 light-years away and drifting above the plane of our Milky Way galaxy, the dusty molecular cloud is part of a complex of dark nebulae mapped toward the Cepheus flare region. Across the spectrum, astronomical explorations of the obscuring interstellar clouds reveal energetic shocks and outflows associated with newborn stars, including the telltale reddish glow from scattered Herbig-Haro objects seen in this sharp image. Distant background galaxies also lurk on the scene, buried behind the dusty expanse. This alluring view imaged with a backyard telescope and broadband filters spans about two full moons on the sky, or 17 light-years at the estimated distance of LDN 1251.

Lonnie Smith (born July 3, 1942), styled Dr. Lonnie Smith, is an American jazz Hammond B3 organist who was a member of the George Benson quartet in the 1960s. He recorded albums with saxophonist Lou Donaldson for Blue Note before being signed as a solo act. He owns the label Pilgrimage.
He was born in Lackawanna, New York, into a family with a vocal group and radio program. Smith says that his mother was a major influence on him musically, as she introduced him to gospel, classical, and jazz music. He was part of several vocal ensembles in the 1950s, including the Teen Kings which included Grover Washington Jr., on sax and his brother Daryl on drums. Art Kubera, the owner of a local music store, gave Smith his first organ, a Hammond B3. George Benson Quartet
Smith’s affinity for R&B melded with his own personal style as he became active in the local music scene. He moved to New York City, where he met George Benson, the guitarist for Jack McDuff‘s band. Benson and Smith connected on a personal level, and the two formed the George Benson Quartet, featuring Lonnie Smith, in 1966.
After two albums under Benson’s leadership, It’s Uptown and Cookbook, Smith recorded his first solo album (Finger Lickin’ Good Soul Organ) in 1967, with George Benson and Melvin Sparks on guitar, Ronnie Cuber on baritone sax, and Marion Booker on drums. This combination remained stable for the next five years.
After recording several albums with Benson, Smith became a solo recording artist and has since recorded over 30 albums under his own name. Numerous prominent jazz artists have joined Smith on his albums and in his live performances, including Lee Morgan, David “Fathead” Newman, King Curtis, Terry Bradds, Blue Mitchell, Joey DeFrancesco and Joe Lovano.
more...John Heard is a bass player and artist. He has worked with Pharoah Sanders, playing on his Heart is a Melody album, George Duke playing on the Jean-Luc Ponty Experience with the George Duke Trio album and Oscar Petersons The London Concert album. he also played on the Night Rider by Oscar Peterson and Count Basie.
He was born John William Heard in July 1938.
He also played saxophone in his early years. He began playing bass at the age of 14. His professional career began in a band that included sax player Booker Ervin, drummer J.C. Moses, pianist Horace Parlan and trumpet player Tommy Turrentine. Whilst still at high school, he attended special classes at the Carnegie Museum of Art.
In 1958 he joined the air force and was sent to Germany. Because of his art experience he was given a job of designing posters for events. He also did some art teaching, teaching the wives of officers. He left the air force in 1961 and enrolled at the Art Institute of Pittsburgh. He returned to music and went to Buffalo and later to California.
more...John Coles (July 3, 1926 – December 21, 1997) was an American jazz trumpeter.
Coles was born in Trenton, New Jersey on July 3, 1926. He grew up in Philadelphia and was self-taught on trumpet.
Coles spent his early career playing with R&B groups, including those of Eddie Vinson (1948–1951), Bull Moose Jackson (1952), and Earl Bostic (1955–1956). He was with James Moody from 1956 to 1958, and played with Gil Evans‘s orchestra between 1958 and 1964, including for the album Out of the Cool. After this he spent time with Charles Mingus in his sextet which also included Eric Dolphy, Clifford Jordan, Jaki Byard, and Dannie Richmond. Following this he played with Herbie Hancock (1968–1969), Ray Charles (1969–1971), Duke Ellington (1971–1974), Art Blakey (1976), Dameronia, Mingus Dynasty, and the Count Basie Orchestra under the direction of Thad Jones (1985–1986).
In 1985 Coles settled in the San Francisco Bay area; he recorded with Frank Morgan and Chico Freeman the following year. After his return to Philadelphia in 1989 he again worked with Morgan and was part of Gene Harris‘s Philip Morris Superband. In 1990 he recorded with Charles Earland and Buck Hill. Coles recorded as a leader several times over the course of his career. He died of cancer on December 21, 1997 in Philadelphia.
more...Solea is one of the heavy hitters of all of palos (rhythms) of flamenco. It’s profound, somber and the mother of all palos (imho).
It’s a 12 count, but unlike the other 12 count palos, this one tends to start on 1 rather than the 12 for the letra. Also, the end of the compás is emphasized.
1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 –12
The structure of a dance of Solea is similar to all the others:
- Salida (singer & guitarist start, dancer makes entrance)
- Llamada (rhythmical accent from dancer that “calls” the singer to sing)
- 1st Letra (1st verse)
- Llamada
- 2nd Letra
- Falseta (guitar interlude)
- Escobilla (footwork section)
- Buleria (fast ending letra)
- Estribillo (chorus that the dancer ends with)
Of course, there are many variations to this structure. There can be more letras and falsetas. Or there can be more spots for different escobillas. The dancer could even add a letra of Solea por Bulerias after the letras of Solea and before the Buleria. Options!!! Choices!!!
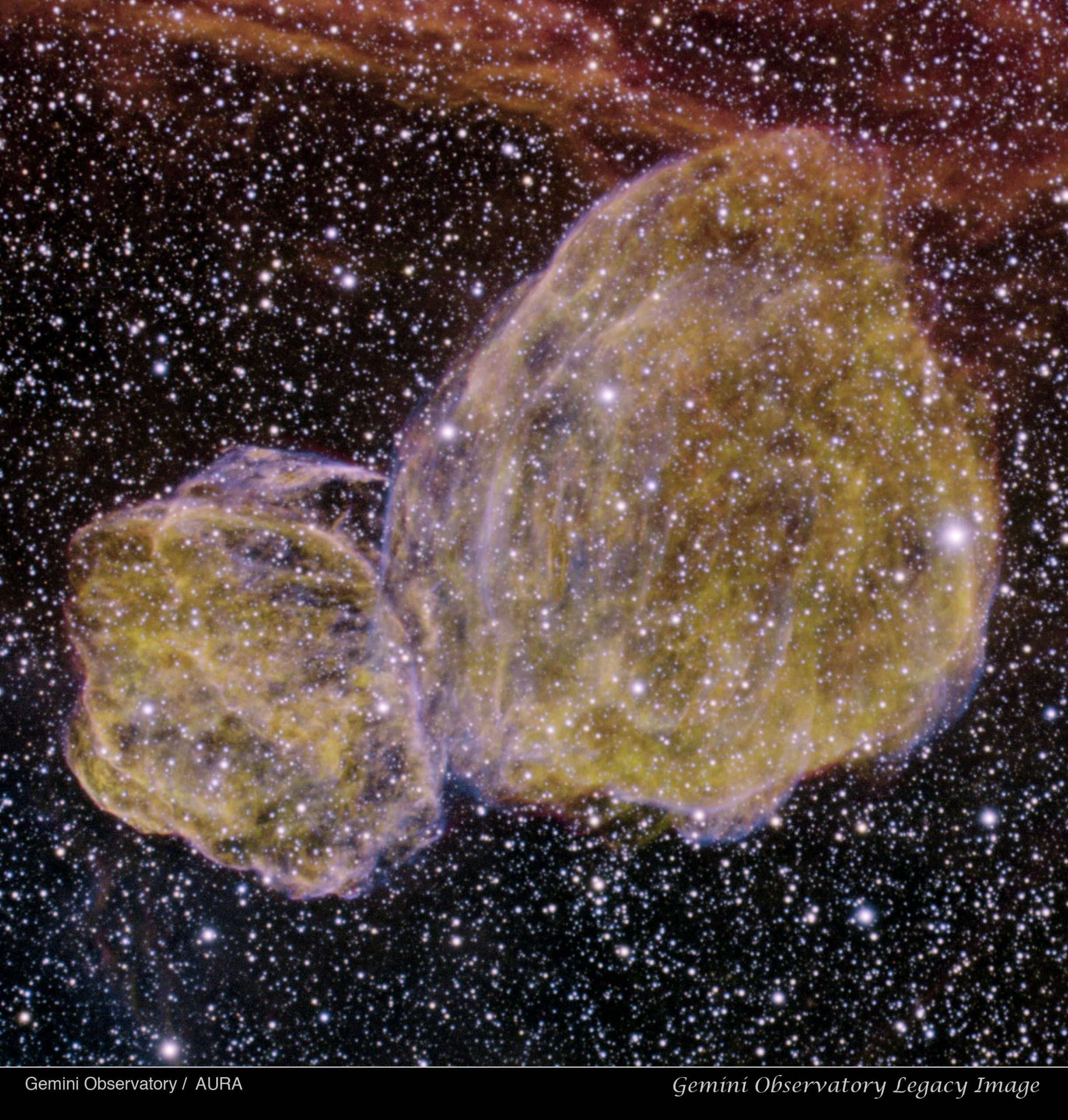
more...The Gemini South Multi-Object Spectograph (GMOS) recently captured a dramatic image of a vast cloud complex named DEM L316 located in the Large Magellanic Cloud. The peanut-shaped nebula appears to be a single object, but the latest research indicates that it is really comprised of two distinct gas and dust clouds formed by different types of supernova explosions.
The new image reveals the intricate tendrils of gas and dust located in the remnants of the stellar explosions that created the still-expanding cloud complex. The object was first recognized in the early 1970s as a supernova remnant, a type of object that is enriched with elements created in stellar explosions. The nebula was likely created a few tens of thousands of years ago by more than one type of supernova exploding in this region of the Large Magellanic Cloud.
“The remarkable clarity of these Gemini-South observations shows the complex shock structure of these two supernova remnants in impressive detail,” said Dr. Rosa Williams of Columbus State University, an astronomer who has studied DEM L316 extensively. “It’s a great step forward in efforts to understand this fascinating pair of remnants – whether they represent only a chance alignment on the sky or some as-yet uncovered physical relationship.”
Other recent observations of DEM L316 by the Chandra and XMM-Newton X-ray space telescopes have strengthened the idea that the cloud is actually two supernova remnants that are aligned in the sky by chance and not a single remnant with a distorted bi-polar shape. The Chandra observations reveal that the chemical compositions of the two shells are very different. This is a strong hint that they were created in very different types of supernova outbursts. The data show that the smaller shell (lower left in the GMOS image) contains significantly more iron than the larger one. The high abundance of iron in the small bubble indicates that the gas is the product of a Type Ia supernova. This type of explosion is triggered by the infall of matter from a star onto a white dwarf. Since white dwarf stars are extremely old objects, the system must have been a few billion years old when this supernova explosion took place.
Charles Robert Watts (born 2 June 1941) is an English drummer, best known as a member of the Rolling Stones since 1963. Originally trained as a graphic artist, he started playing drums in London’s rhythm and blues clubs, where he met Brian Jones, Mick Jagger, and Keith Richards. In January 1963, he joined their fledgling group, the Rolling Stones, as drummer, while doubling as designer of their record sleeves and tour stages. Watts cites jazz as a major influence on his drumming style. He has toured with his own group, the Charlie Watts Quintet, and appeared in London at Ronnie Scott’s Jazz Club with the Charlie Watts Tentet.
In 2006, Watts was elected into the Modern Drummer Hall of Fame; in the same year, Vanity Fair elected him into the International Best Dressed List Hall of Fame. In the estimation of noted music critic Robert Christgau, Watts is “rock’s greatest drummer.” In 2016, he was ranked 12th on Rolling Stone‘s “100 Greatest Drummers of All Time” list.
more...Ahmad Jamal (born Frederick Russell Jones, July 2, 1930) is an American jazz pianist, composer, bandleader, and educator. For five decades, he has been one of the most successful small-group leaders in jazz. Jamal was born in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. He began playing piano at the age of three, when his uncle Lawrence challenged him to duplicate what he was doing on the piano. Jamal began formal piano training at the age of seven with Mary Cardwell Dawson, whom he describes as greatly influencing him. His Pittsburgh roots have remained an important part of his identity (“Pittsburgh meant everything to me and it still does,” he said in 2001) and it was there that he was immersed in the influence of jazz artists such as Earl Hines, Billy Strayhorn, Mary Lou Williams, and Erroll Garner. Jamal also studied with pianist James Miller and began playing piano professionally at the age of fourteen, at which point he was recognized as a “coming great” by the pianist Art Tatum. When asked about his practice habits by a critic from The New York Times, Jamal commented that, “I used to practice and practice with the door open, hoping someone would come by and discover me. I was never the practitioner in the sense of twelve hours a day, but I always thought about music. I think about music all the time.”Jamal began touring with George Hudson’s Orchestra after graduating from George Westinghouse High School in 1948. He joined another touring group known as The Four Strings, which disbanded when violinist Joe Kennedy Jr. left. In 1950 he moved to Chicago and performed intermittently with local musicians Von Freeman and Claude McLin, and solo at the Palm Tavern, occasionally joined by drummer Ike Day.
more...b. Angelo Chambers, 2 July 1924, Denton, Texas, USA, d. 7 June 1993, St. Paul, Minnesota, USA. While living in Dallas, Chambers worked for a while as a waiter at a blues club where he also acted as emcee and developed an engaging stage presence. Later, he appeared regularly at blues clubs in many Midwestern cities. His day job was a bus driver but whenever the opportunity arose he would be on stage, singing, occasionally playing drums, and introducing other acts with considerable panache. Although he lived in several other cities, he eventually settled in St. Paul, Minnesota. There, he led his own band, the Blue Birds, and also worked with a band led by Harmonica Tom Schafer. In 1991 he recorded the single, ‘Mean And Evil Woman’, which became a local hit, as did the b-side, ‘Cleo’. These tracks appeared on his sole album, which was completed not long before his death. A cassette was prepared for a launch, which Milwaukee Slim was able to attend even though he was failing in health. The album itself was released two years later and included ‘Standing On The Outside Crying’, ‘Sweet Little Angel’, ‘You Got Me Thinkin’’, ‘I’m A Legend’, ‘Double Trouble Blues’, ‘Mean And Evil Woman’, and ‘Mean Old World’, as well as his hit singles.
more...FIRE EXTINGUISHER ALERT
I had a small stove fire in one of my rentals this morning. The tenant rushed down to tell me THERES A FIRE IN APARTMENT! I rushed in couldn’t breath got a N95 it turned black, I grabbed a fire extinguisher and put it out. Then extinguisher emptied out in apt. Just a big mess no one hurt and minimal damages. I did call Farmers Ins and made a claim just in case. So my friends & family please make certain you have a good solid fire extinguisher in your home. I’m buying new units today for all apts! Even called neighbors!

more...
More Posts
- The Cosmos with Comet Iwamoto
- Ralph Towner Day
- Benny Powell Day
- World Music with María Terremoto
- Daily Roots with Big Youth
- The Cosmos with UGC 6093
- Brian Jones Day
- John Fahey Day
- Willie Bobo Day
- World Music with Houssam Gania
- Daily Roots with Winston Groovy
- The Cosmos with Arp 194
- Dexter Gordon Day
- Chuck Wayne Day
- World Music with Urna Chahar-Tugchi
- Daily Roots with Lloyd & Claudette
- The Cosmos with the Milky Way New Star Stream
- Najwa Karam Day
- Johnny Cash Day
- Fats Domino Day
