Blog
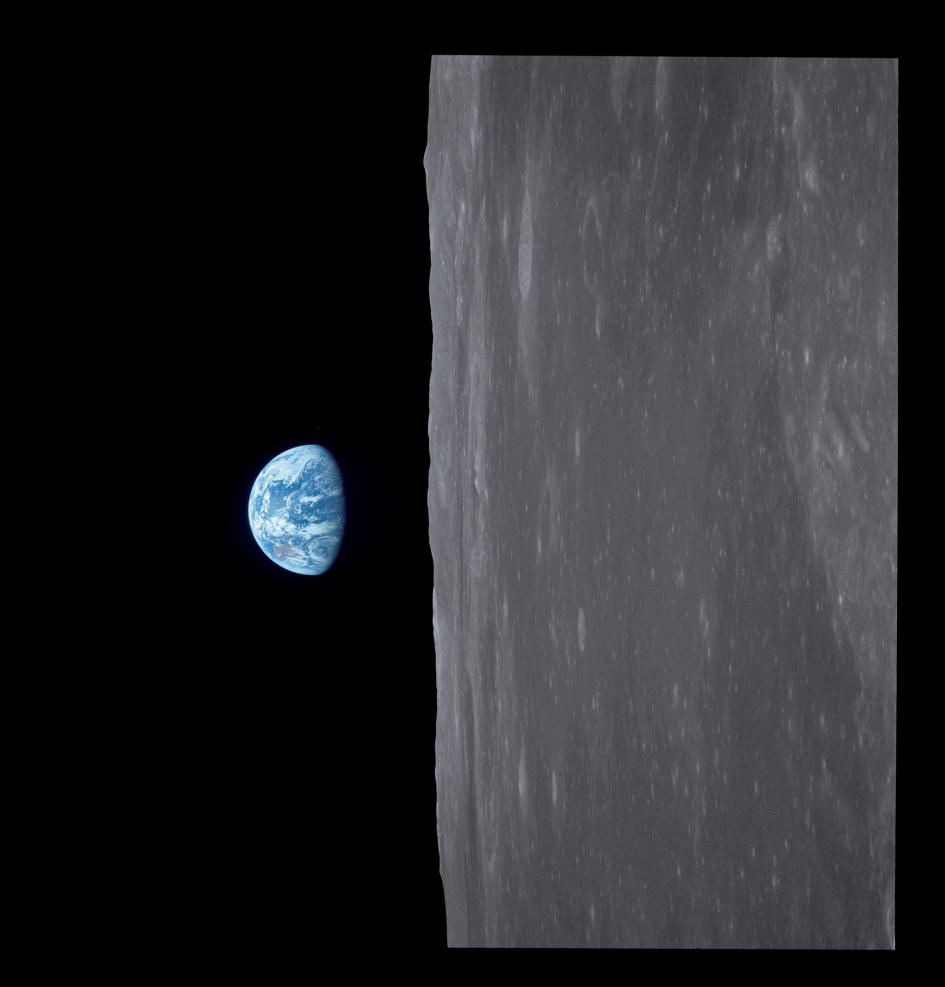
Apollo 11 launched from Cape Kennedy on July 16, 1969, carrying Commander Neil Armstrong, Command Module Pilot Michael Collins and Lunar Module Pilot Edwin “Buzz” Aldrin into an initial Earth-orbit of 114 by 116 miles. An estimated 650 million people watched Armstrong’s televised image and heard his voice describe the event as he took “…one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind” on July 20, 1969.
Two hours, 44 minutes and one-and-a-half revolutions after launch, the S-IVB stage reignited for a second burn of five minutes, 48 seconds, placing Apollo 11 into a translunar orbit. The command and service module, or CSM, Columbia separated from the stage, which included the spacecraft-lunar module adapter, or SLA, containing the lunar module, or LM, Eagle. After transposition and jettisoning of the SLA panels on the S-IVB stage, the CSM docked with the LM. The S-IVB stage separated and injected into heliocentric orbit four hours, 40 minutes into the flight.
The first color TV transmission to Earth from Apollo 11 occurred during the translunar coast of the CSM/LM. Later, on July 17, a three-second burn of the SPS was made to perform the second of four scheduled midcourse corrections programmed for the flight. The launch had been so successful that the other three were not needed.
On July 18, Armstrong and Aldrin put on their spacesuits and climbed through the docking tunnel from Columbia to Eagle to check out the LM, and to make the second TV transmission.
On July 19, after Apollo 11 had flown behind the moon out of contact with Earth, came the first lunar orbit insertion maneuver. At about 75 hours, 50 minutes into the flight, a retrograde firing of the SPS for 357.5 seconds placed the spacecraft into an initial, elliptical-lunar orbit of 69 by 190 miles. Later, a second burn of the SPS for 17 seconds placed the docked vehicles into a lunar orbit of 62 by 70.5 miles, which was calculated to change the orbit of the CSM piloted by Collins. The change happened because of lunar-gravity perturbations to the nominal 69 miles required for subsequent LM rendezvous and docking after completion of the lunar landing. Before this second SPS firing, another TV transmission was made, this time from the surface of the moon.
On July 20, Armstrong and Aldrin entered the LM again, made a final check, and at 100 hours, 12 minutes into the flight, the Eagle undocked and separated from Columbia for visual inspection. At 101 hours, 36 minutes, when the LM was behind the moon on its 13th orbit, the LM descent engine fired for 30 seconds to provide retrograde thrust and commence descent orbit insertion, changing to an orbit of 9 by 67 miles, on a trajectory that was virtually identical to that flown by Apollo 10. At 102 hours, 33 minutes, after Columbia and Eagle had reappeared from behind the moon and when the LM was about 300 miles uprange, powered descent initiation was performed with the descent engine firing for 756.3 seconds. After eight minutes, the LM was at “high gate” about 26,000 feet above the surface and about five miles from the landing site.
The descent engine continued to provide braking thrust until about 102 hours, 45 minutes into the mission. Partially piloted manually by Armstrong, the Eagle landed in the Sea of Tranquility in Site 2 at 0 degrees, 41 minutes, 15 seconds north latitude and 23 degrees, 26 minutes east longitude. This was about four miles downrange from the predicted touchdown point and occurred almost one-and-a-half minutes earlier than scheduled. It included a powered descent that ran a mere nominal 40 seconds longer than preflight planning due to translation maneuvers to avoid a crater during the final phase of landing. Attached to the descent stage was a commemorative plaque signed by President Richard M. Nixon and the three astronauts.
The flight plan called for the first EVA to begin after a four-hour rest period, but it was advanced to begin as soon as possible. Nonetheless, it was almost four hours later that Armstrong emerged from the Eagle and deployed the TV camera for the transmission of the event to Earth. At about 109 hours, 42 minutes after launch, Armstrong stepped onto the moon. About 20 minutes later, Aldrin followed him. The camera was then positioned on a tripod about 30 feet from the LM. Half an hour later, President Nixon spoke by telephone link with the astronauts.
Commemorative medallions bearing the names of the three Apollo 1 astronauts who lost their lives in a launch pad fire, and two cosmonauts who also died in accidents, were left on the moon’s surface. A one-and-a-half inch silicon disk, containing micro miniaturized goodwill messages from 73 countries, and the names of congressional and NASA leaders, also stayed behind.
During the EVA, in which they both ranged up to 300 feet from the Eagle, Aldrin deployed the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package, or EASEP, experiments, and Armstrong and Aldrin gathered and verbally reported on the lunar surface samples. After Aldrin had spent one hour, 33 minutes on the surface, he re-entered the LM, followed 41 minutes later by Armstrong. The entire EVA phase lasted more than two-and-a-half hours, ending at 111 hours, 39 minutes into the mission.
Armstrong and Aldrin spent 21 hours, 36 minutes on the moon’s surface. After a rest period that included seven hours of sleep, the ascent stage engine fired at 124 hours, 22 minutes. It was shut down 435 seconds later when the Eagle reached an initial orbit of 11 by 55 miles above the moon, and when Columbia was on its 25th revolution. As the ascent stage reached apolune at 125 hours, 19 minutes, the reaction control system, or RCS, fired so as to nearly circularize the Eagle orbit at about 56 miles, some 13 miles below and slightly behind Columbia. Subsequent firings of the LM RCS changed the orbit to 57 by 72 miles. Docking with Columbia occurred on the CSM’s 27th revolution at 128 hours, three minutes into the mission. Armstrong and Aldrin returned to the CSM with Collins. Four hours later, the LM jettisoned and remained in lunar orbit.
Trans-Earth injection of the CSM began July 21 as the SPS fired for two-and-a-half minutes when Columbia was behind the moon in its 59th hour of lunar orbit. Following this, the astronauts slept for about 10 hours. An 11.2 second firing of the SPS accomplished the only midcourse correction required on the return flight. The correction was made July 22 at about 150 hours, 30 minutes into the mission. Two more television transmissions were made during the trans-Earth coast.
Re-entry procedures were initiated July 24, 44 hours after leaving lunar orbit. The SM separated from the CM, which was re-oriented to a heat-shield-forward position. Parachute deployment occurred at 195 hours, 13 minutes. After a flight of 195 hours, 18 minutes, 35 seconds – about 36 minutes longer than planned – Apollo 11 splashed down in the Pacific Ocean, 13 miles from the recovery ship USS Hornet. Because of bad weather in the target area, the landing point was changed by about 250 miles. Apollo 11 landed 13 degrees, 19 minutes north latitude and 169 degrees, nine minutes west longitude July 24, 1969.
more...
Yusuf Islam (born Steven Demetre Georgiou; 21 July 1948), commonly known by his stage name Cat Stevens, and later Yusuf, is a British singer-songwriter and multi-instrumentalist. His 1967 debut album reached the top 10 in the UK, and its title song “Matthew and Son” reached number 2 on the UK Singles Chart. Stevens’ albums Tea for the Tillerman (1970) and Teaser and the Firecat (1971) were certified triple platinum in the US by the RIAA.[2] His musical style consists of folk, pop, rock, and, in his later career, Islamic music.
His 1972 album Catch Bull at Four spent three weeks at number one on the Billboard 200, and fifteen weeks at number one in the Australian ARIA Charts. He earned two ASCAP songwriting awards in 2005 and 2006 for “The First Cut Is the Deepest“, and the song has been a hit for four artists. His other hit songs include “Father and Son“, “Wild World“, “Moonshadow“, “Peace Train“, and “Morning Has Broken“. In 2007, he received the Ivor Novello Award for Outstanding Song Collection from the British Academy of Songwriters, Composers and Authors.
In December 1977, Stevens converted to Islam and adopted the name Yusuf Islam the following year. In 1979, he auctioned all of his guitars for charity and left his musical career to devote himself to educational and philanthropic causes in the Muslim community. He was embroiled in a long-running controversy regarding comments he made in 1989 about the death fatwa on author Salman Rushdie. He has received two honorary doctorates and awards for promoting peace from two organisations founded by Mikhail Gorbachev.
In 2006, he returned to pop music – releasing his first new studio album of new pop songs in 28 years, titled An Other Cup. With that release and subsequent ones, he dropped the surname “Islam” from the album cover art – using the stage name Yusuf as a mononym. In 2009, he released the album Roadsinger, and in 2014, he released the album Tell ‘Em I’m Gone, and began his first US tour since 1978. He was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 2014. His second North American tour since his resurgence, featuring 12 shows in intimate venues, ran from 12 September to 7 October 2016. In 2017, he released the album The Laughing Apple.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d34f0ts2PGs
more...Conrad Yeatis “Sonny” Clark (July 21, 1931 – January 13, 1963) was an American jazz pianist who mainly worked in the hard bop idiom. Clark was born and raised in Herminie, Pennsylvania, a coal mining town east of Pittsburgh. His parents were originally from Stone Mountain, Georgia. His miner father, Emery Clark, died of a lung disease two weeks after Sonny was born. Sonny was the youngest of eight children. At age 12, he moved to Pittsburgh.
When visiting an aunt in California at age 20, Clark decided to stay and began working with saxophonist Wardell Gray. Clark went to San Franciscowith Oscar Pettiford and after a couple months, was working with clarinetist Buddy DeFranco in 1953. Clark toured the United States and Europe with DeFranco until January 1956, when he joined The Lighthouse All-Stars, led by bassist Howard Rumsey.
Wishing to return to the east coast, Clark served as accompanist for singer Dinah Washington in February 1957 in order to relocate to New York City. In New York, Clark was often requested as a sideman by many musicians, partly because of his rhythmic comping. He frequently recorded for Blue Note Records, playing as a sideman with many hard bop players, including Kenny Burrell, Donald Byrd, Paul Chambers, John Coltrane, Dexter Gordon, Art Farmer, Curtis Fuller, Grant Green, Philly Joe Jones, Clifford Jordan, Jackie McLean, Hank Mobley, Art Taylor, and Wilbur Ware. He also recorded sessions with Charles Mingus, Sonny Rollins, Billie Holiday, Stanley Turrentine, and Lee Morgan.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W3FLd1eBmTU&t=21s
more...Isaac Stern (21 July 1920 – 22 September 2001) was an American violinist. The son of Solomon and Clara Stern, Isaac Stern was born in Kremenets, Poland (now Ukraine), into a Jewish family. He was 14 months old when his family moved to San Francisco in 1921. He received his first music lessons from his mother. In 1928, he enrolled at the San Francisco Conservatory of Music, where he studied until 1931 before going on to study privately with Louis Persinger. He returned to the San Francisco Conservatory to study for five years with Naoum Blinder, to whom he said he owed the most. At his public début on 18 February 1936, aged 15, he played Saint-Saëns’ Violin Concerto No. 3 in B minor with the San Francisco Symphony under the direction of Pierre Monteux. Reflecting on his background, Stern once memorably quipped that cultural exchanges between the U.S. and Soviet Russia were simple affairs:
-
- “They send us their Jews from Odessa, and we send them our Jews from Odessa.”
Stern toured the Soviet Union in 1951, the first American violinist to do so. In 1967, Stern stated his refusal to return to the USSR until the Soviet regime allowed artists to enter and leave the country freely. His only visit to Germany was in 1999, for a series of master classes, but he never performed publicly in Germany.
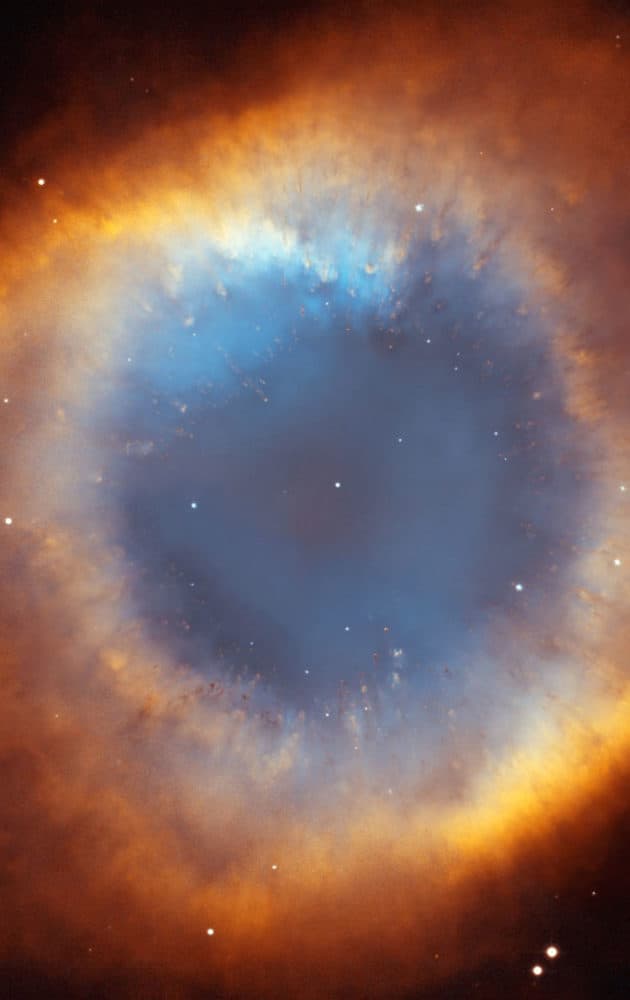
more...The Helix Nebula, also known as The Helix, NGC 7293, is a large planetary nebula (PN) located in the constellation Aquarius. Discovered by Karl Ludwig Harding, probably before 1824, this object is one of the closest to the Earth of all the bright planetary nebulae. The distance, having now been measured by GAIA, is 655±13 light-years. It is similar in appearance to the Cat’s Eye Nebula and the Ring Nebula, whose size, age, and physical characteristics are similar to the Dumbbell Nebula, varying only in its relative proximity and the appearance from the equatorial viewing angle. The Helix Nebula has sometimes been referred to as the “Eye of God” in pop culture, as well as the “Eye of Sauron.
The Helix Nebula is an example of a planetary nebula, formed by an intermediate to low-mass star, which sheds its outer layers near the end of its evolution. Gases from the star in the surrounding space appear, from our vantage point, as if we are looking down a helix structure. The remnant central stellar core, known as a planetary nebula nucleus or PNN, is destined to become a white dwarf star. The observed glow of the central star is so energetic that it causes the previously expelled gases to brightly fluoresce. The Helix Nebula in the constellation of Aquarius lies about 700 light-years away, spanning about 0.8 parsecs (2.5 light-years).
more...Carlos Santana (born July 20, 1947) is a Mexican and American guitarist who rose to fame in the late 1960s and early 1970s with his band, Santana, which pioneered a fusion of rock and roll and Latin American jazz. Its sound featured his melodic, blues-based lines set against Latin and African rhythms played on percussion instruments such as timbales and congas not generally heard in rock. Santana continued to work in these forms over the following decades. He experienced a resurgence of popularity and critical acclaim in the late 1990s. In 2015, Rolling Stone magazine listed Santana at number 20 on their list of the 100 Greatest Guitarists. He has won 10 Grammy Awards and three Latin Grammy Awards. Santana was born in Autlán de Navarro, Jalisco, Mexico. He learned to play the violin at age five and the guitar at age eight under the tutelage of his father, a mariachimusician. His younger brother, Jorge Santana, would also become a professional guitarist. Young Carlos was heavily influenced by Ritchie Valens at a time when there were very few Mexicans in American rock and pop music. The family moved from Autlán de Navarro to Tijuana, the city on Mexico’s border with California, and then San Francisco. Santana moved to San Francisco and, in October 1966, started the Santana Blues Band. By 1968, the band had begun to incorporate different types of influences into their electric blues. “If I would go to some cat’s room,” remembered the guitarist of the band, “he’d be listening to Sly [Stone] and Jimi Hendrix; another guy to the Stones and the Beatles. Another guy’d be listening to Tito Puente and Mongo Santamaría. Another guy’d be listening to Miles [Davis] and [John] Coltrane… . To me it was like being at a university.” Around the age of eight, Santana “fell under the influence” of blues performers like B.B. King, Javier Bátiz, Mike Bloomfield, and John Lee Hooker. Gábor Szabó‘s mid-1960s jazz/gypsy guitar work also strongly influenced Santana’s playing. Indeed, Szabó’s composition “Gypsy Queen” was used as the second part of Santana’s 1970 treatment of Peter Green’s composition “Black Magic Woman“, almost down to identical guitar licks. Santana’s 2012 instrumental album Shape Shifter includes a song called “Mr. Szabo”, played in tribute in the style of Gábor Szabó. Santana also credits Jimi Hendrix, Mike Bloomfield, Hank Marvin and Peter Green as important influences; he considered Bloomfield a direct mentor, writing of a key meeting with Bloomfield in San Francisco in the foreword he wrote to a biography of Bloomfield, Michael Bloomfield: If You Love These Blues – An Oral History in 2000. Between the age of 10–12 he was sexually molested by an American man who brought him across the border. Santana lived in the Mission District, graduated from James Lick Middle School, and in 1965 from Mission High School. He was accepted at California State University Northridge and Humboldt State University, but chose not to attend college. “The ’60s were a leap in human consciousness. Mahatma Gandhi, Malcolm X, Martin Luther King, Che Guevara, Mother Teresa, they led a revolution of conscience. The Beatles, the Doors, Jimi Hendrixcreated revolution and evolution themes. The music was like Dalí, with many colors and revolutionary ways. The youth of today must go there to find themselves.” Santana was influenced by popular artists of the 1950s such as B.B. King, T-Bone Walker, Javier Batiz, and John Lee Hooker. Soon after he began playing guitar, he joined local bands along the “Tijuana Strip” where he was able to begin developing his own sound. He was also introduced to a variety of new musical influences, including jazz and folk music, and witnessed the growing hippie movement centered in San Francisco in the 1960s. After several years spent working as a dishwasher in a diner and busking for spare change, Santana decided to become a full-time musician. In 1966 he was chosen along with other musicians to form an ad hoc band to substitute for that of an intoxicated Paul Butterfield set to play a Sunday matinee at Bill Graham‘s Fillmore West. Graham selected the substitutes from musicians he knew primarily through his connections with the Butterfield Blues Band, Grateful Dead, and Jefferson Airplane. Santana’s guitar playing caught the attention of both the audience and Graham. During the same year he and fellow street musicians David Brown (bass guitar), Marcus Malone (percussion) and Gregg Rolie (lead vocals, Hammond Organ B3), formed the Santana Blues Band.[12] Playing a highly original blend of Latin-infused rock, jazz, blues, salsa, and African rhythms, the band gained an immediate following on the San Francisco club circuit. Santana’s band was signed by Columbia Records, which shortened its name to simply “Santana“. It went into the studio to record its first album in January 1969, finally laying down tracks in May that became its first album. Members were not satisfied with the release, dismissed drummer Bob Livingston, and added Mike Shrieve, who had a strong background in both jazz and rock. The band then lost percussionist Marcus Malone, who was charged with involuntary manslaughter. Michael Carabello was re-enlisted in his place, bringing with him experienced Nicaraguan percussionist Jose Chepito Areas.
Major rock music promoter Bill Graham, a Latin Music aficionado who had been a fan of Santana from its inception, arranged for the band to appear at the Woodstock Music and Art Festival before its debut album was even released. Its set was one of the surprises of the festival, highlighted by an eleven-minute performance of a throbbing instrumental, “Soul Sacrifice“. Its inclusion in the Woodstock film and soundtrack album vastly increased the band’s popularity. Graham also suggested Santana record the Willie Bobo song “Evil Ways“, as he felt it would get radio airplay. The band’s first album, Santana, was released in August 1969 and became a huge hit, reaching #4 on the U.S. album charts.
more...Charles Lacy Tyler (July 20, 1941 – June 27, 1992) was an American jazz baritone saxophonist. He also played alto saxophone and clarinet. Tyler was born in Cadiz, Kentucky, and spent his childhood years in Indianapolis. He played piano as a child and clarinetat 7, before switching to alto in his early teens, and finally baritone saxophone. During the summers, he visited Chicago, New York City and Cleveland, Ohio, where he met the young tenor saxophonist Albert Ayler at age 14. After serving in the army from 1957–1959, Tyler relocated to Cleveland in 1960 and began playing with Ayler, commuting between New York and Cleveland. During that period played with Ornette Coleman and Sunny Murray.
In 1965 Tyler recorded Bells and Spirits Rejoice with Alyer’s group. He recorded his first album as leader the following year for ESP-Disk. He returned to Indianapolis to study with David Baker at Indiana University between 1967 and 1968, recording a second album for ESP, Eastern Man Alone. In 1968, he transferred to the University of California, Berkeley to study and teach. In Los Angeles, he worked with Arthur Blythe, Bobby Bradford, and David Murray. He moved back to New York in 1974, leading his own groups with Blythe, trumpeter Earl Cross, drummer Steve Reid and others, recording the album Voyage from Jericho on Tyler’s own Akba label. In 1975, Tyler enrolled at Columbia University and made an extensive tour of Scandinavia, releasing his second Akba album Live in Europe. In 1976, he performed the piece “Saga of the Outlaws” at Sam Rivers‘s Studio Rivbea, released two years later on Nessa Records.During that period he played as a sideman or co-leader with Steve Reid, Cecil Taylor and Billy Bang.
more...Ernest Brooks Wilkins Jr. (July 20, 1919 – June 5, 1999) was an American jazz saxophonist, conductor and arranger who spent several years with Count Basie. He also wrote for Tommy Dorsey, Harry James, and Dizzy Gillespie. He was musical director for albums by Cannonball Adderley, Dinah Washington, Oscar Peterson, and Buddy Rich. Wilkins was born in St. Louis, Missouri. In his early career he played in a military band, before joining Earl Hines‘s last big band. He worked with Count Basie from 1951 to 1955, eventually leaving to work free-lance as a jazz arranger and songwriter. His success declined in the 1960s, but revived after work with Clark Terry, leading to a tour of Europe. Eventually Wilkins settled in Copenhagen, Denmark, where he would live for the rest of his life. There he formed the Almost Big Band so he could write for a band of his own formation. The idea was partly inspired by his wife Jenny. Copenhagen had a thriving jazz scene with several promising jazz musicians as well as a well-established community of expatriate American jazz musicians which had formed in the 1950s and now included representatives like Kenny Drewand Ed Thigpen who joined the band along with Danish saxophonist Jesper Thilo. The band released four albums, but after 1991 he became too ill to do much with it.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hjs_Tj5yUdE
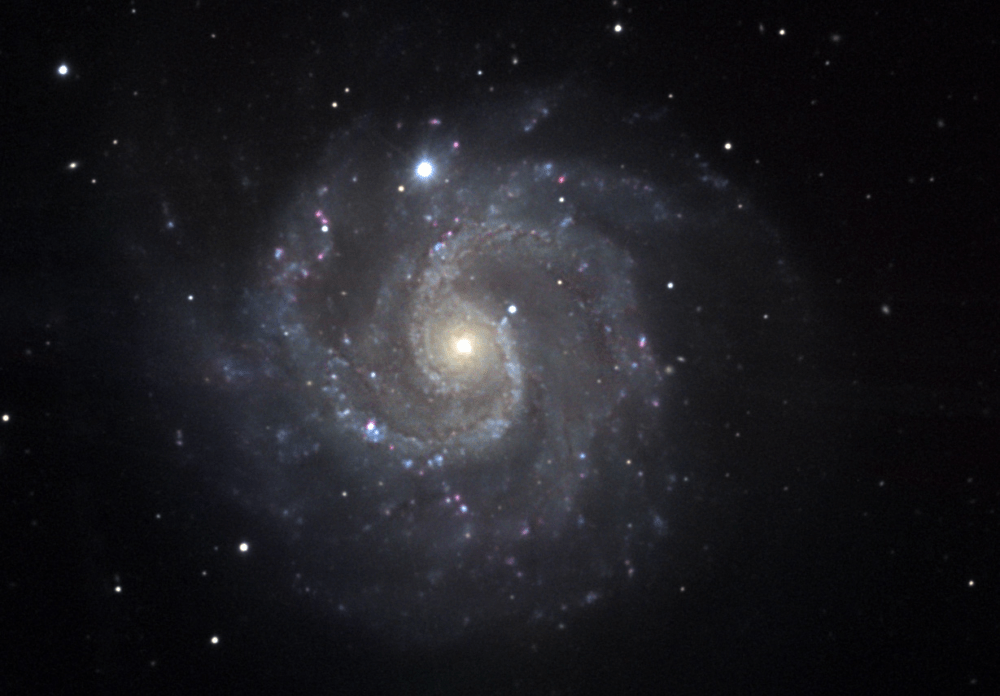
NGC 3184 is a spiral galaxy approximately 40 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major. It has two HII regions named NGC 3180 and NGC 3181.
NGC 3184 houses a high abundance of heavy elements and (SN 1999gi) that was a magnitude 14 Type II supernova detected on December 9, 1999.
more...Keith Richard Godchaux (July 19, 1948 – July 23, 1980) was a pianist best known for his tenure in the rock group the Grateful Dead from 1971 to 1979. Godchaux was born in Seattle, Washington, and grew up in Concord, California, a regional suburban center within the East Bay of the San Francisco Bay Area. He began piano lessons at age five at the instigation of his father (a semi-professional musician) and subsequently played Dixieland and cocktail jazz in professional ensembles as a teenager. According to Godchaux, “I spent two years wearing dinner jackets and playing acoustic piano in country club bands and Dixieland groups…I also did piano bar gigs and put trios together to back singers in various places around the Bay Area…[playing] cocktail standards like ‘Misty’ the way jazz musicians resentfully play a song that’s popular – that frustrated space… I just wasn’t into it… I was looking for something real to get involved with – which wouldn’t necessarily be music”. He met and married former FAME Studios session vocalist Donna Jean Thatcher in November 1970; their son Zion, of the band BoomBox, was born in 1974.
The couple introduced themselves to Jerry Garcia at a concert in August 1971; coincidentally, ailing keyboardist/vocalist Ron “Pigpen” McKernan (who would go on to play alongside Godchaux from December 1971 to June 1972) was unable to handle the rigors of the band’s next tour. At the time, Godchaux was largely supported by his wife and irregularly employed as a lounge pianist in Walnut Creek, California. While he was largely uninterested in the popular music of the era and eschewed au courant jazz rock in favor of modal jazz, bebop, and swing, several sources claim that he collaborated with such rock acts as Dave Mason and James and the Good Brothers, a Canadian trio acquainted with the Grateful Dead.
Although the band had employed several other keyboardists (including Howard Wales, Merl Saunders and Ned Lagin) as session musicians to augment McKernan’s limited instrumental contributions following the departure of Tom Constanten in January 1970, Godchaux was invited to join the group as a permanent member in September 1971. He first performed publicly with the Dead on October 19, 1971 at the University of Minnesota‘s Northrup Auditorium.
After playing an upright piano and increasingly sporadic Hammond organ on the fall 1971 tour, Godchaux primarily played acoustic grand piano (including nine-foot Yamaha and Steinwayinstruments) at concerts from 1972 to 1974. Throughout this period, Godchaux’s rented pianos were outfitted with a state-of-the-art pickup system designed by Carl Countryman. According to sound engineer Owsley Stanley, “The Countryman pickup worked by an electrostatic principle similar to the way a condenser mic works. It was charged with a very high voltage, and thus was very cantankerous to set up and use. It had a way of crackling in humid conditions and making other rather unmusical sounds if not set up just right, but when it worked it was truly brilliant.” The control box also enabled Godchaux to use a wah-wah pedal with the instrument. He added a Fender Rhodes electric piano in mid-1973 and briefly experimented with the Hammond organ again on the band’s fall 1973 tour; the Rhodes piano would remain in his setup through 1976. Following the group’s extended touring hiatus, he continued to use contractually-stipulated nine-foot Steinways furnished by the band’s venues in 1976 and early 1977 before switching exclusively to the Yamaha CP-70 electric grand piano in September 1977. The instrument’s unwieldy tuning partially contributed to the shelving of the band’s recordings of their 1978 engagement at the Giza Plateau for a planned live album.
more...Born in Boise, Idaho on July 19, 1944, George William Frayne IV grew up in Brooklyn, Queens and Long Island. He graduated from Bay Shore High in 1962 and the University of Michigan in 1966 with a BS degree in design. In 1968, he graduated from the University of Michigan with an MFA degree in sculpture and painting. He was a teaching assistant at the University of Michigan for four semesters and was an instructor of Art at the University of Wisconsin in Oshkosh for two semesters in 1968-69.
He moved to San Francisco 1969 and started his career as Commander Cody and the band Lost Planet Airmen. Frayne had many art shows over the years and published two books, Starart, 1978, and Art Music and Life, 2009. He moved to Saratoga Springs, New York in 1997.
more...
Philip Upchurch (born July 19, 1941, Chicago, Illinois) is an American blues, jazz and R&B guitarist and bassist. Upchurch started his career working with the Kool Gents, the Dells, and the Spaniels before going on to work with Curtis Mayfield, Otis Rush, and Jimmy Reed. (His association with Kool Gents member Dee Clark would continue, including playing guitar on Clark’s 1961 solo hit “Raindrops“.) He then returned to Chicago to play and record with Woody Herman, Stan Getz, Groove Holmes, B.B. King, and Dizzy Gillespie.
In 1961, his record “You Can’t Sit Down” by the Philip Upchurch Combo sold over one million copies and was awarded a gold disc. “You Can’t Sit Down, Part 2” peaked at No. 29 on the Billboardcharts in the US. And he released first album. In the 1960s he toured with Oscar Brown, appearing on the 1965 live album, Mr. Oscar Brown, Jr. Goes to Washington. In the mid-’60s he was house guitarist of Chess Records and he played with The Dells, Howlin’ Wolf, Muddy Waters and Gene Chandler. He also played with John Lee Hooker, Grover Washington, Jr. and Cannonball Adderley. Upchurch was part of a group called the Soulful Strings during the 1960s, prior to working with Rotary Connection on Chess’s Cadet label.
In the 1970s he worked with Donny Hathaway, Harvey Mason, Ramsey Lewis, Quincy Jones and led his own quartet with Tennyson Stephens. He met Bob Krasnow and Tommy LiPuma, the founders of Blue Thumb Records, and he released “Darkness Darkness”. Upchurch played on Donny Hathaway’s “This Christmas” and “The Ghetto”. He also played guitar on Hathaway’s “Live” album (1972). In the mid 1970s and 1980s, he performed with George Benson, Mose Allison, Gary Burton, Lenny Breau,[6] Joe Williams, Chaka Khan, Natalie Cole, Carmen McRae, Cat Stevens, David Sanborn, and Michael Jackson. In the 1990s he worked with Jimmy Smith and Jack McDuff.
more...Carmell Jones (July 19, 1936 – November 7, 1996) was an American jazz trumpet player. Jones was born in Kansas City, Kansas. He started piano lessons at age five, and trumpet lessons at age seven. His first professional work was with Kansas City greats Nathan Davis, Cleanhead Vinson and Frank Smith. He moved to California in 1960 and worked as a studio musician for several years, including in the orchestras for two movie soundtracks, ‘The Seven Days In May‘ and ‘The Manchurian Candidate‘, the latter starring Frank Sinatra. He released two albums as a leader for Pacific Jazz at this time, while recording as a sideman with Bud Shank, Onzy Matthews, Curtis Amy, Harold Land, and Gerald Wilson. He toured with Horace Silver in 1964-65, and was on Silver’s seminal 1965 Blue Note album Song for My Father. In 1965 he moved to Germany where he lived for 15 years, working with Paul Kuhn and the SFB Big Band (Sender Freies Berlin) from 1968 to 1980. There he worked with musicians such as Milo Pavlovic, Herb Geller, Leo Wright, Rudi Wilfer and Eugen Cicero. Jones returned to the US in 1980, working as a teacher and appearing at local clubs in Kansas City. He released one additional album as a leader in 1982 entitled “Carmell Jones Returns,” on the Revelation label. Jones died on November 7, 1996 in Kansas City at the age of 60.
In 2003, Mosaic Records released a three-CD set of Jones material in their Mosaic Select series.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RskBrHXMLbw
more...Flamenco Fridays por Alegrias.
Alegrías de Cádiz is a palo with a more defined structure which makes it a bit easier to describe.
The basic structure of alegrías is as follows:
- Salida
- Letras
- Silencio
- Castellana
- Escobilla
- Bulería de Cádiz
Salida
The salida (entrance) includes the presentation of the 3 elements: guitar, song and dance. The salida usually starts with a falseta on the guitar as an introduction to the entrance of the song and llamada (call) by the dancer.
Letras
In developing the letra (verse), remates are often sought to strengthen the line of song, this is optional. Quite often, the letra is concluded with a coletilla (postscript – chorus of 4 bars in length), which can be topped with a cierre (closing) of the feet to call back the song and continue with a 2nd letra, or with a falseta between the letras. A practical way to finish the 2nd letra is to use a subida (rise in pace) with a final cierre (closing).
Silencio
Literally meaning silence, this is the melodic part which highlights the role of the guitar, it is also where the dancer can give more importance to body movements and play of the upper body.
Castellana
The silencio is linked to a chorus of singing of 4 bars where the pace is accelerating and ends with a cierre (closing) that gives way to the escobilla (footwork) for alegrías.
Escobilla
The escobilla is the part devoted to footwork in which the interpreter develops his or her rhythmic virtuosity. To end the escobilla you can do a subida (rise in pace) to a close and make way for the bulería, or raise the speed up and call to enter the bulería directly.
Bulería de Cadiz.
You dance and play with the song of bulería de cádiz and may end with a subida (rise in pace), chorus (tirititran) and cierre (close).
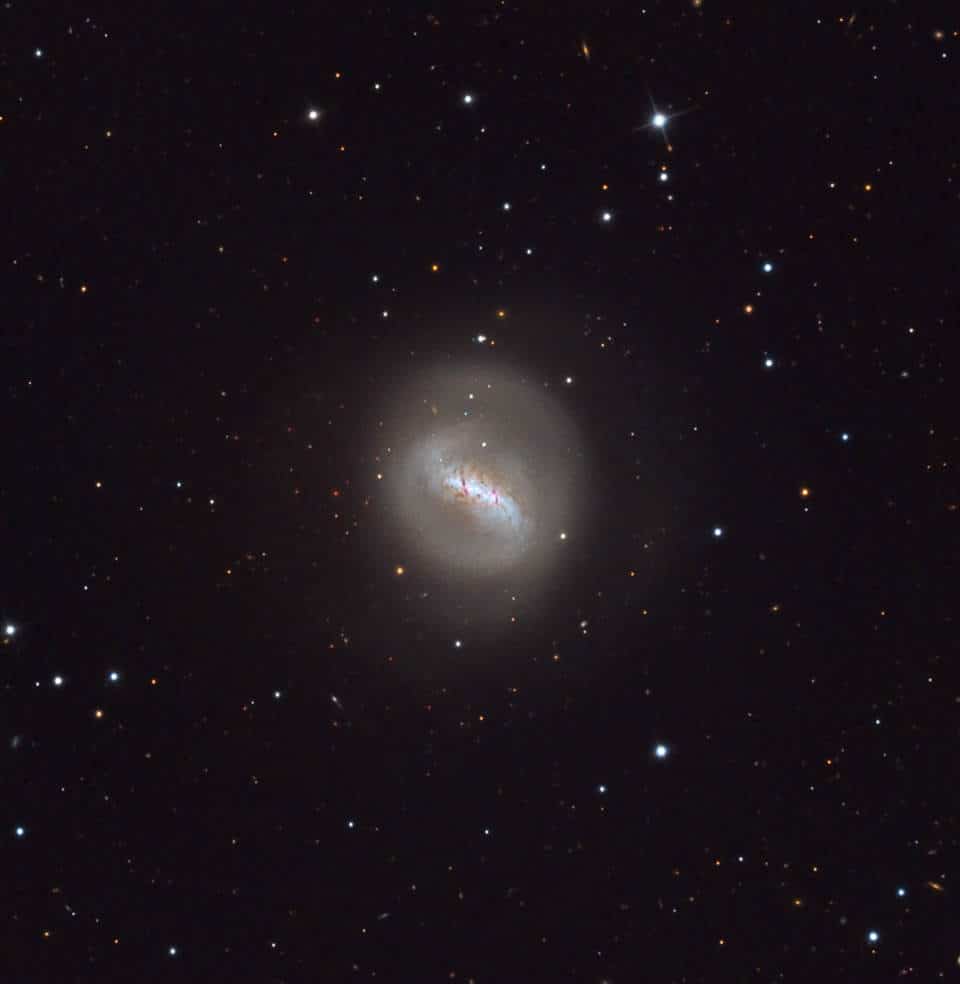
NGC 4691 is a lenticular galaxy in the New General Catalog . Sailing in the sky is in the direction of the constellation. 47.5 in 1784 by British astronomer William Herschel cm (18.7 inches) in diameter.
The entire spiral pattern of NGC 4691 is extremely fuzzy and devoid of any signs of youth. It looks like it is billions of years old. The bar, by contrast, is bursting with ongoing star formation. This is very unusual!
According to Principal Galaxy Catalog, the distance to NGC 4691 is about 47 million light-years, which would make it a little closer than the Virgo Cluster, and its true brightness would be 6 billion stars like the Sun, or 0.3 times the brightness of the Milky Way. But according to this page, NGC 4691 is located some 73 million light-years away, and its true brightness would be much higher.
more...More Posts
- The Cosmos with NGC 317
- Carly Simon Day
- Joe Chambers Day
- Clifton Chenier Day
- Johnny Smith Day
- World Music with Moonlight Benjamin
- Daily Roots with Admiral Tibet
- UFO Sighting June 24th 1947
- Music for Surviving the Pandemic and Realizing Racial Justice
- The Cosmos with NGC 4100
- Derrick “Duckie” Simpson Day
- Mick Fleetwood Day
- Jeff Beck Day
- Terry Riley Day
- Lester Williams Day
- World Music with Jaliba Kuyateh
- Daily Roots with Marlon Asher
- Music for Surviving the Pandemic and Realizing Racial Justice
- The Cosmos with the Milky Way from eROSITA
- June Carter Day