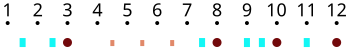Blog
Peter Tosh, OM (born Winston Hubert McIntosh; 19 October 1944 – 11 September 1987) was a Jamaican reggae musician. Along with Bob Marley and Bunny Wailer, he was one of the core members of the band the Wailers (1963–1976), after which he established himself as a successful solo artist and a promoter of Rastafari. He was murdered in 1987 during a home invasion.
Tosh was born in Westmoreland, the westernmost parish of Jamaica. He was abandoned by his parents and “shuffled among relatives”. When McIntosh was fifteen, his aunt died and he moved to Trenchtown in Kingston, Jamaica. He first learned guitar after watching a man in the country play a song that captivated him. He watched the man play the same song for half a day, memorizing everything his fingers were doing. He then picked up the guitar and played the song back to the man. The man then asked McIntosh who had taught him to play; McIntosh told him that he had. During the early 1960s, as an aspiring musician, Tosh went to vocal teacher Joe Higgs, who gave free music lessons to young people. Through his contact with Higgs, Tosh met Robert Nesta Marley (Bob Marley) and Neville O’Reilly Livingston (Bunny Wailer). He then changed his name to Peter Tosh and the trio started singing together in 1962. Higgs taught the trio to harmonize and while developing their music, they would often play on the street corners of Trenchtown.[citation needed]
In 1964 Tosh helped organize the band the Wailing Wailers, with Junior Braithwaite, a falsetto singer, and backup singers Beverley Kelso and Cherry Smith. Initially, Tosh was the only one in the group who could play musical instruments. According to Bunny Wailer, Tosh was critical to the band because he was a self-taught guitarist and keyboardist, and thus became an inspiration for the other band members to learn to play. The Wailing Wailers had a major ska hit with their first single, “Simmer Down”, and recorded several more successful singles before Braithwaite, Kelso and Smith left the band in late 1965. Marley spent much of 1966 in Delaware in the United States with his mother, Cedella (Malcolm) Marley-Booker, and for a brief time was working at a nearby Chrysler factory. He then returned to Jamaica in early 1967 with a renewed interest in music and a new spirituality. Tosh and Bunny were already Rastafarians when Marley returned from the US, and the three became very involved with the Rastafari faith. Soon afterwards, they renamed the musical group the Wailers. Tosh would explain later that they chose the name Wailers because to “wail” means to mourn or to, as he put it, “…express one’s feelings vocally”. He also claims that he was the beginning of the group, and that it was he who first taught Bob Marley the guitar. The latter claim may very well be true, for according to Bunny Wailer, the early Wailers learned to play instruments from Tosh.
more...Farid al-Atrash (Arabic: فريد الأطرش; October 19, 1910 – December 26, 1974), also written Farid El-Atrache, was a Syrian composer, singer, virtuoso oud player, and actor. Having immigrated to Egypt at the age of nine years old with his mother and siblings, Al-Atrash embarked on a highly successful career spanning more than four decades—recording 500 songs and starring in 31 movies. Sometimes referred to as “King of the Oud”, he is one of the most important figures of 20th century Arab music.
Al-Atrash was born in Al-Qurayya, in southern Syria to the Druze al-Atrash family who fought the French colonial army. His father was Syrian and his mother was Lebanese. As a child, al-Atrash emigrated with his mother and siblings to Egypt, escaping the French occupation. Later, they were naturalized by the Egyptian government as citizens. Farid’s mother sang and played the Oud, which spurred his musical interest at an early age.
As a child and young adult, al-Atrash sang in school events. He studied in a music conservatory and became an apprentice of the renowned composer Riad Al Sunbati. In the 1930s, al-Atrash began his professional singing career by working for privately owned Egyptian radio stations. Eventually, he was hired as an oud player for the national radio station and later as a singer. His sister, Asmahan, was also a talented singer, and for a while they worked together. In 1941, they starred in their first successful movie Intisar a l-Shabab (انتصار الشباب – The Triumph of Youth, 1941), in which Farid himself composed all the music.
more...UGC 8335 is a strongly interacting pair of spiral galaxies resembling two ice skaters. The interaction has united the galaxies via a bridge of material and has yanked two strongly curved tails of gas and stars from the outer parts of their “bodies”. Both galaxies show dust lanes in their centres. UGC 8335 is located in the constellation of Ursa Major, the Great Bear, about 400 million light-years from Earth. It is the 238th galaxy in Arp’s Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies.

William “Billy” Cox (born October 16, 1939) is an American bassist, best known for performing with Jimi Hendrix. Cox is the only surviving musician to have regularly played with Hendrix: first with the experimental group that backed Hendrix at Woodstock (informally referred to as “Gypsy Sun and Rainbows”), followed by the trio with drummer Buddy Miles that recorded the live Band of Gypsys album, and, lastly, The Cry of Love Tour trio with Mitch Mitchell back on drums. Cox continues to perform dates with the Band of Gypsys Experience and the Experience Hendrix Tour.
In addition to Hendrix, he has either been a member of the house or touring band or recorded sessions for Sam Cooke, Slim Harpo, Joe Simon, Charlie Daniels, John McLaughlin, Rufus Thomas, Carla Thomas, Lou Rawls, Etta James, Jackie Wilson and Little Richard. Born in Wheeling, West Virginia, Billy Cox was raised in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, and attended Schenley High School.
more...Esperanza Emily Spalding (born October 18, 1984) is an American jazz bassist and singer. Spalding was raised in Portland, Oregon, and was a musical prodigy, playing violin in the Chamber Music Society of Oregon at five years old. She was later both self-taught and -trained on a number of instruments, including guitar and bass. Her proficiency earned her scholarships to Portland State University and the Berklee College of Music. In 2017, she was appointed Professor of the Practice of Music at Harvard University.
She has won four Grammy Awards, including the Grammy Award for Best New Artist at the 53rd Grammy Awards, making her the first jazz artist to win the award. Spalding was born in Portland, Oregon, to an African-American father and a mother of Welsh, Native American, and Hispanic descent.[8][9] She was raised in the King neighborhood in Northeast Portland, which at that time was at its height of gang violence. Her mother raised her and her brother as a single parent.
more...Wynton Learson Marsalis (born October 18, 1961) is an American virtuoso trumpeter, composer, teacher, and artistic director of Jazz at Lincoln Center. He has promoted classical and jazz music, often to young audiences. Marsalis has been awarded nine Grammy Awards and his Blood on the Fields was the first jazz composition to win the Pulitzer Prize for Music. He is the son of jazz musician Ellis Marsalis Jr. (pianist), grandson of Ellis Marsalis Sr., and brother of Branford (saxophonist), Delfeayo (trombonist), and Jason (drummer). Marsalis is the only musician to win a Grammy Award in jazz and classical during the same year.
Marsalis was born in New Orleans, Louisiana, on October 18, 1961 and grew up in the suburb of Kenner. He is the second of six sons born to Delores Ferdinand and Ellis Marsalis Jr., a pianist and music teacher. He was named for jazz pianist Wynton Kelly.Branford Marsalis is his older brother and Jason Marsalis and Delfeayo Marsalis are younger. All three are jazz musicians. While sitting at a table with trumpeters Al Hirt, Miles Davis, and Clark Terry, his father jokingly suggested that he might as well get Wynton a trumpet, too. Hirt volunteered to give him one, so at the age of six Marsalis received his first trumpet.
more...Laura Nyro (/ˈnɪəroʊ/ NEER-oh; born Laura Nigro, October 18, 1947 – April 8, 1997) was an American songwriter, singer, and pianist. She achieved critical acclaim with her own recordings, particularly the albums Eli and the Thirteenth Confession (1968) and New York Tendaberry(1969), and had commercial success with artists such as Barbra Streisand and The 5th Dimension recording her songs. Her style was a hybrid of Brill Building-style New York pop, jazz, rhythm and blues, show tunes, rock, and soul.
Between 1968 and 1970, a number of artists had hits with her songs: The 5th Dimension with “Blowing Away“, “Wedding Bell Blues“, “Stoned Soul Picnic“, “Sweet Blindness“, and “Save the Country“; Blood, Sweat & Tears and Peter, Paul and Mary, with “And When I Die“; Three Dog Night and Maynard Ferguson, with “Eli’s Comin’“; and Barbra Streisand with “Stoney End“, “Time and Love”, and “Hands off the Man (Flim Flam Man)”. Nyro’s best-selling single was her recording of Carole King‘s and Gerry Goffin‘s “Up on the Roof“.
In 2010, Laura Nyro was posthumously inducted into the Songwriters Hall of Fame, arguably her greatest professional accolade, in the footsteps of composers like George Gershwin, Oscar Hammerstein, and Stephen Sondheim.
Afterwards, in 2012, Nyro was also posthumously inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame. Nyro was born Laura Nigro in the Bronx, the daughter of Gilda (née Mirsky) Nigro, a bookkeeper, and Louis Nigro, a piano tuner and jazz trumpeter. Laura had a younger brother, Jan Nigro, who has become a well-known children’s musician. Laura was of Russian Jewish, Polish Jewish, with Italian ancestry from her paternal grandfather.
Charles Edward Anderson Berry (October 18, 1926 – March 18, 2017) was an American singer and songwriter, and one of the pioneers of rock and roll music. With songs such as “Maybellene” (1955), “Roll Over Beethoven” (1956), “Rock and Roll Music” (1957) and “Johnny B. Goode” (1958), Berry refined and developed rhythm and blues into the major elements that made rock and roll distinctive. Writing lyrics that focused on teen life and consumerism, and developing a music style that included guitar solos and showmanship, Berry was a major influence on subsequent rock music.
Born into a middle-class African-American family in St. Louis, Missouri, Berry had an interest in music from an early age and gave his first public performance at Sumner High School. While still a high school student he was convicted of armed robbery and was sent to a reformatory, where he was held from 1944 to 1947. After his release, Berry settled into married life and worked at an automobile assembly plant. By early 1953, influenced by the guitar riffs and showmanship techniques of the blues musician T-Bone Walker, Berry began performing with the Johnnie Johnson Trio. His break came when he traveled to Chicago in May 1955 and met Muddy Waters, who suggested he contact Leonard Chess, of Chess Records. With Chess, he recorded “Maybellene”—Berry’s adaptation of the country song “Ida Red“—which sold over a million copies, reaching number one on Billboard magazine’s rhythm and blues chart. By the end of the 1950s, Berry was an established star, with several hit records and film appearances and a lucrative touring career. He had also established his own St. Louis nightclub, Berry’s Club Bandstand. However, he was sentenced to three years in prison in January 1962 for offenses under the Mann Act—he had transported a 14-year-old girl across state lines. After his release in 1963, Berry had several more hits, including “No Particular Place to Go“, “You Never Can Tell“, and “Nadine“. But these did not achieve the same success, or lasting impact, of his 1950s songs, and by the 1970s he was more in demand as a nostalgic performer, playing his past hits with local backup bands of variable quality. However, in 1972 he reached a new level of achievement when a rendition of “My Ding-a-Ling” became his only record to top the charts. His insistence on being paid in cash led in 1979 to a four-month jail sentence and community service, for tax evasion. His reputation took a nosedive in the early 1990s, when the FBI seized home videos of him urinating in women’s eyes, farting in their mouths, and having them defecate into his mouth and played them in court.
Berry was among the first musicians to be inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame on its opening in 1986; he was cited for having “laid the groundwork for not only a rock and roll sound but a rock and roll stance.” Berry is included in several of Rolling Stone magazine’s “greatest of all time” lists; he was ranked fifth on its 2004 and 2011 lists of the 100 Greatest Artists of All Time. The Rock and Roll Hall of Fame’s 500 Songs That Shaped Rock and Roll includes three of Berry’s: “Johnny B. Goode”, “Maybellene”, and “Rock and Roll Music”. Berry’s “Johnny B. Goode” is the only rock-and-roll song included on the Voyager Golden Record. He was nicknamed by NBC as the “Father of Rock and Roll”. Born in St. Louis, Missouri, Berry was the fourth child in a family of six. He grew up in the north St. Louis neighborhood known as the Ville, an area where many middle-class people lived. His father, Henry William Berry (1895–1987), was a contractor and deacon of a nearby Baptist church; his mother, Martha Bell (Banks) (1894–1980), was a certified public school principal.
Flamenco Friday presents Soleá.
The metre or “compás” of the soleá is one of the most widely used in Flamenco. Other palos have derived their compás from the soleá, including Bulerías por soleá, the palos in the Cantiñasgroup, like Alegrías, Romeras, Mirabrás, Caracoles or, to a certain extent, Bulerías. It consists of 12 beats, and could be described as a combination of triple and duple beat bars, so it’s a polymetre form, with strong beats at the end of each bar. The basic “skeleton” of the soleá rhythm, thus, follows this pattern:
(Each number represents a beat. Blue squares mean weak beats, while big brown dots are strong beats.)
Nevertheless, this is just an underlying structure, like a foundation, a kind of grid where flamenco artists creatively draw the rhythm by means of subdivisions, articulation, and less commonly, syncopation and accent displacement.
The first example of “palmas” is a very common, simple pattern:
Notice that palmas are often (though by no means always) silent during beats 4 to 6, even if beat number 6 is a “strong one”. This is specially true when no dancing takes place: the main interest there is the singing (or playing) and too much percussion can take attention away from the music. Those beats though are often marked when there is dance, or when performing other palos in the same metre like Alegrías or Bulería por soleá. However, these are not to be taken as hard-and-fast rules, but just as general guidelines.
A more complex example.
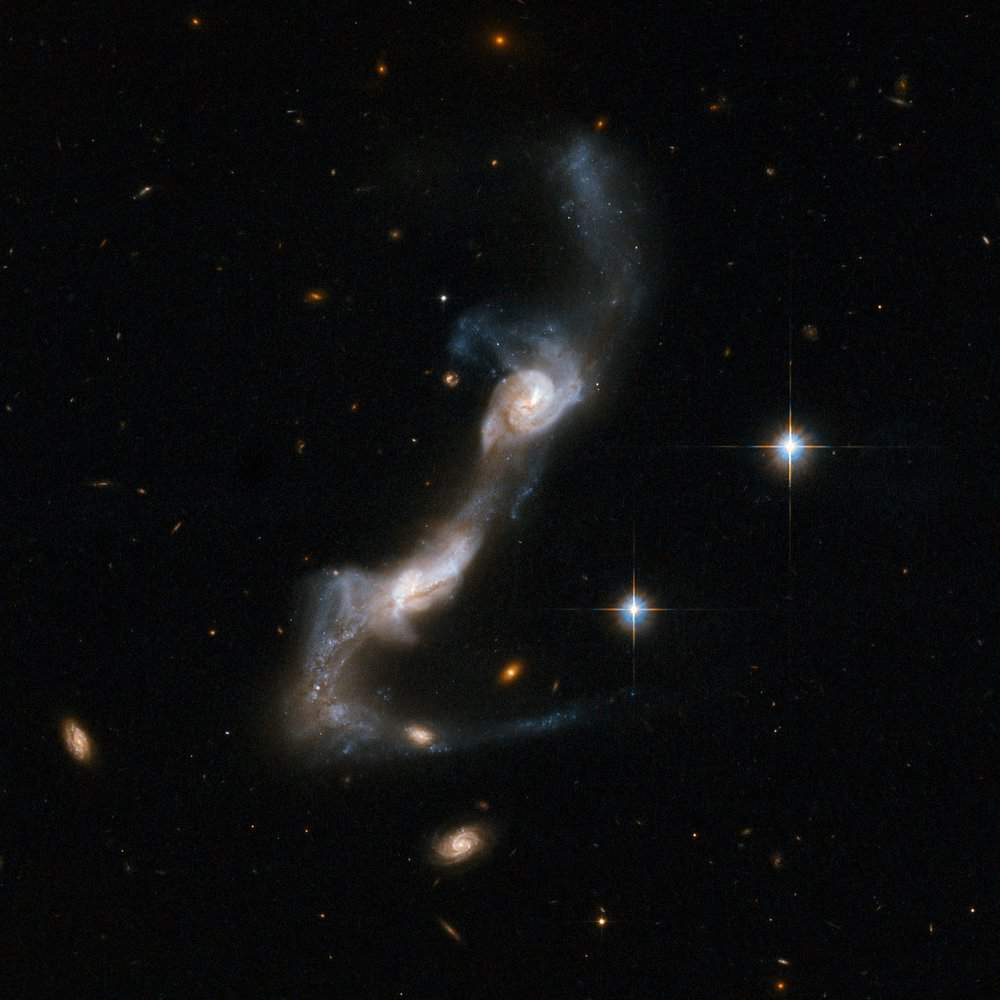
more...NGC 5643 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in constellation Lupus. It is located at a distance of circa 60 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 5643 is about 100,000 light years across. NGC 5643 has an active galactic nucleus and is a type II Seyfert galaxy.
The galaxy was first reported by James Dunlop on May 10, 1826 with his 9-inch reflector telescope and described it as exceedingly faint. The galaxy was also spotted by John Herschel and added it in the General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters as number 3572. The galaxy is located only 15 degrees from the galactic plane.

Tarkan Tevetoğlu (Turkish pronunciation: [taɾˈkan teveˈtoːɫu]; born 17 October 1972) is a Turkish singer-songwriter. Since the early 1990s, with the successful sales of his albums, he has been a prominent figure of the Turkish pop music, being known in both Turkey and Europe.
Tarkan was born and raised in Alzey, Rhineland-Palatinate. In 1986, he moved to Turkey together with his family. Tarkan, who had been interested in music since his childhood, went to high school at Karamürsel and took music lessons. In the following years, he met the owner of İstanbul Plak, Mehmet Söğütoğlu, and signed a contract to release his own album.
Tarkan released his first album Yine Sensiz in late 1992 with “Kıl Oldum” being chosen as its lead single. His second and third albums, Aacayipsin and Ölürüm Sana, were released in 1994 and 1998 respectively. The song “Şımarık” from Ölürüm Sana became popular in a number of countries. In 1998, he signed a new contract with Universal Music Group. In 1999, his compilation album, Tarkan, received platinum and gold certifications in several countries. In 2001, he made music videos for the songs “Kuzu Kuzu, “Hüp” and “Verme” from his fourth studio album Karma. Two years later, the album Dudu performed well on the sales charts, and in 2006 with the release of his first English album, Come Closer, he became known in Europe. “Bounce” and “Start the Fire” were the lead singles of this album. The lyrics of the songs included in the album Metamorfoz were praised by the Turkish Language Association. In 2010, his seventh studio album, Adımı Kalbine Yaz, became the best-selling album of the year in Turkey. In 2016, his ninth studio album, Ahde Vefa, which has a Classical Turkish theme, was released.
more...William Randolph “Cozy” Cole (October 17, 1909 – January 9, 1981) was an American jazz drummer who had hits with the songs “Topsy I” and “Topsy II“. “Topsy II” peaked at No. 3 on the Billboard Hot 100, and at No. 1 on the R&B chart. It sold over one million copies and was awarded a gold disc. The track peaked at No. 29 in the UK Singles Chart in 1958. The recording contained a long drum solo and was one of the few drum solo recordings to make the charts at Billboard magazine. The single was issued by Love Records, a small record label in Brooklyn, New York. Cole’s song “Turvy II” reached No. 36 in 1959.
William Randolph Cole was born in 1909 in East Orange, New Jersey. His first music job was with Wilbur Sweatman in 1928. In 1930 he played for Jelly Roll Morton‘s Red Hot Peppers, recording an early drum solo on “Load of Cole”. He spent 1931–33 with Blanche Calloway, 1933–34 with Benny Carter, 1935–36 with Willie Bryant, 1936–38 with Stuff Smith‘s small combo, and 1938–42 with Cab Calloway. In 1942, he was hired by CBS Radio music director Raymond Scott as part of network radio’s first mixed-race orchestra. After that he played with Louis Armstrong’s All Stars.
Cole performed with Louis Armstrong and his All Stars with Velma Middleton singing vocals for the famed ninth Cavalcade of Jazz concert held at Wrigley Field in Los Angeles. The concert was produced by Leon Hefflin, Sr. on June 7, 1953. Also featured that day were Roy Brown and his Orchestra, Don Tosti and His Mexican Jazzmen, Earl Bostic, Nat “King” Cole, and Shorty Rogers and his Orchestra.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=THKo3nYZfkM
more...Barney Kessel (October 17, 1923 – May 6, 2004) was an American jazz guitarist born in Muskogee, Oklahoma. Noted in particular for his knowledge of chords and inversions and chord-based melodies, he was a member of many prominent jazz groups as well as a “first call” guitarist for studio, film, and television recording sessions. Kessel was a member of the group of session musicians informally known as the Wrecking Crew.
Kessel began his career as a teenager touring with local dance bands. When he was 16, he started playing with the Oklahoma A&M band, Hal Price & the Varsitonians. The band members nicknamed him “Fruitcake” because he practiced up to 16 hours a day.
In the early 1940s he moved to Los Angeles, where for one year he was a member of the Chico Marx big band. He appeared in the film Jammin’ the Blues, which featured Lester Young. Soon after, he played in the bands of Charlie Barnet and Artie Shaw. During the day, he worked as a studio musician and at night played jazz in clubs. In 1947 he recorded with Charlie Parker. He worked in Jazz at the Philharmonic and for one year in the early 1950s he was a member of the Oscar Peterson trio.[1][2] After leaving the trio, he recorded several solo albums for Contemporary. He recorded a series of albums with Ray Brown and Shelly Manne The Poll Winners because the three of them often won polls conducted by Metronome and DownBeat magazines. He was the guitarist on the album Julie Is Her Name (1955) by Julie London, which includes the standard “Cry Me a River, which sold a million copies and demonstrated Kessel’s chordal approach to guitar.
more...https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cRCXQKWmesY
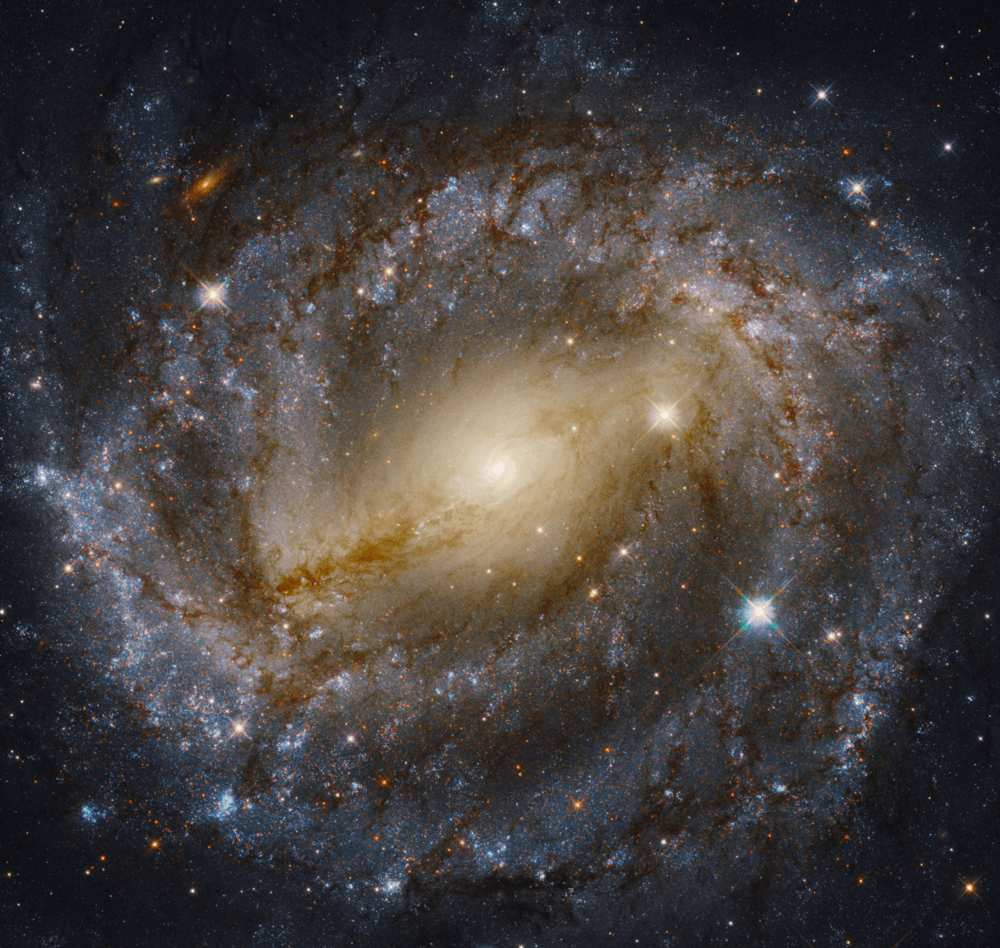
more...NGC 6670 are a pair of interacting galaxies within the Draco constellation, which lie around 401 million light-years from Earth. Its shape resembles a Leaping Dolphin. NGC 6670 was discovered by Lewis A. Swift on July 31, 1886. NGC 6670 is a combination of two colliding disc galaxies which are known as NGC 6670E and NGC 6670W. The galaxy is 100 billion times brighter than our Sun. The galaxies have already collided once before and they are now moving towards each other again nearing a second collision. Its apparent magnitude is 14.3, its size is 1.0 arc minutes.

More Posts
- Cosmos NGC 1499
- Jaime Valle
- David Amram
- Jack Owens
- World Music Sonia Timofeeva
- Daily Roots Lion Youth
- Cosmos NGG 1097
- Diana Krall
- Hubert Sumlin
- Eddie Condon
- W.C. Handy
- World Music Jaganath Hajra
- Daily Roots Pablo Gad
- Cosmos VdB 152
- Clyde McPhatter
- Jerome Richardson
- Little Willie John
- FREE UKRAINE World Music HAYDAMAKY
- Daily Roots Aswad
- Cosmos CB130-3