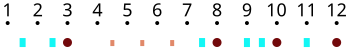Blog
Flamenco Friday presents Soleá.
The metre or “compás” of the soleá is one of the most widely used in Flamenco. Other palos have derived their compás from the soleá, including Bulerías por soleá, the palos in the Cantiñasgroup, like Alegrías, Romeras, Mirabrás, Caracoles or, to a certain extent, Bulerías. It consists of 12 beats, and could be described as a combination of triple and duple beat bars, so it’s a polymetre form, with strong beats at the end of each bar. The basic “skeleton” of the soleá rhythm, thus, follows this pattern:
(Each number represents a beat. Blue squares mean weak beats, while big brown dots are strong beats.)
Nevertheless, this is just an underlying structure, like a foundation, a kind of grid where flamenco artists creatively draw the rhythm by means of subdivisions, articulation, and less commonly, syncopation and accent displacement.
The first example of “palmas” is a very common, simple pattern:
Notice that palmas are often (though by no means always) silent during beats 4 to 6, even if beat number 6 is a “strong one”. This is specially true when no dancing takes place: the main interest there is the singing (or playing) and too much percussion can take attention away from the music. Those beats though are often marked when there is dance, or when performing other palos in the same metre like Alegrías or Bulería por soleá. However, these are not to be taken as hard-and-fast rules, but just as general guidelines.
A more complex example.
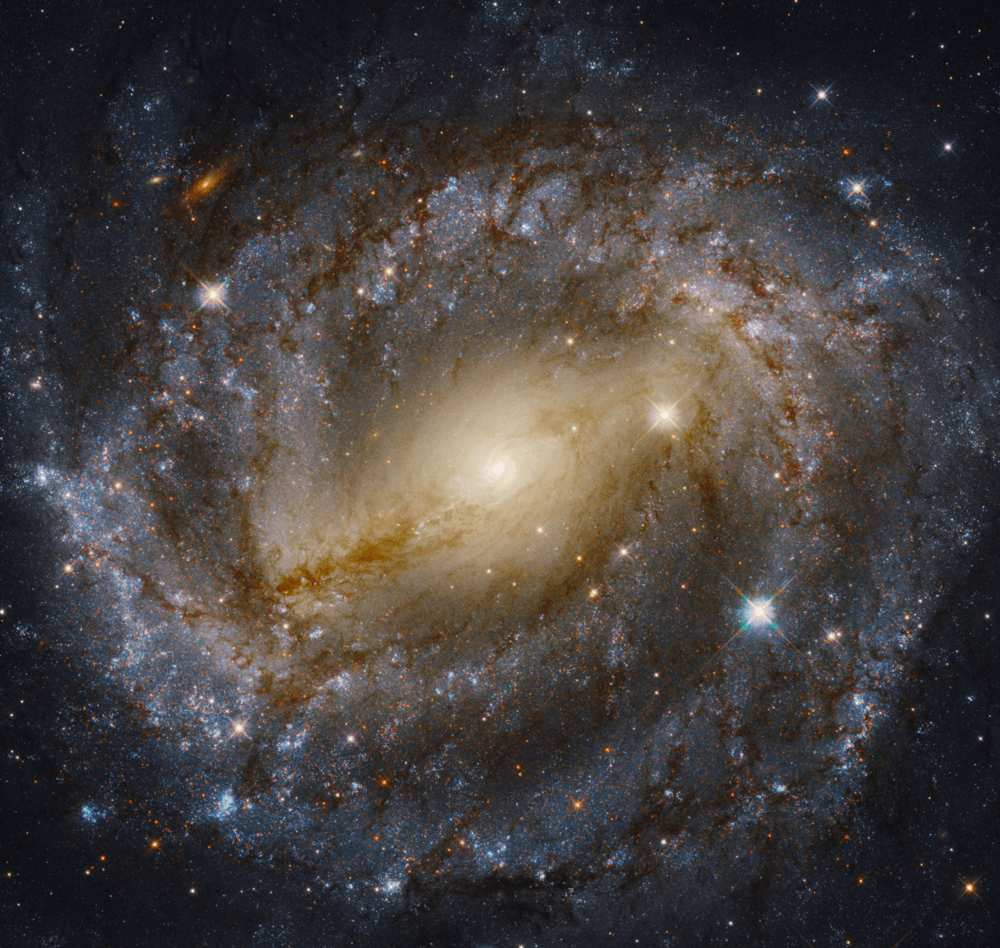
more...NGC 5643 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in constellation Lupus. It is located at a distance of circa 60 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 5643 is about 100,000 light years across. NGC 5643 has an active galactic nucleus and is a type II Seyfert galaxy.
The galaxy was first reported by James Dunlop on May 10, 1826 with his 9-inch reflector telescope and described it as exceedingly faint. The galaxy was also spotted by John Herschel and added it in the General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters as number 3572. The galaxy is located only 15 degrees from the galactic plane.

Tarkan Tevetoğlu (Turkish pronunciation: [taɾˈkan teveˈtoːɫu]; born 17 October 1972) is a Turkish singer-songwriter. Since the early 1990s, with the successful sales of his albums, he has been a prominent figure of the Turkish pop music, being known in both Turkey and Europe.
Tarkan was born and raised in Alzey, Rhineland-Palatinate. In 1986, he moved to Turkey together with his family. Tarkan, who had been interested in music since his childhood, went to high school at Karamürsel and took music lessons. In the following years, he met the owner of İstanbul Plak, Mehmet Söğütoğlu, and signed a contract to release his own album.
Tarkan released his first album Yine Sensiz in late 1992 with “Kıl Oldum” being chosen as its lead single. His second and third albums, Aacayipsin and Ölürüm Sana, were released in 1994 and 1998 respectively. The song “Şımarık” from Ölürüm Sana became popular in a number of countries. In 1998, he signed a new contract with Universal Music Group. In 1999, his compilation album, Tarkan, received platinum and gold certifications in several countries. In 2001, he made music videos for the songs “Kuzu Kuzu, “Hüp” and “Verme” from his fourth studio album Karma. Two years later, the album Dudu performed well on the sales charts, and in 2006 with the release of his first English album, Come Closer, he became known in Europe. “Bounce” and “Start the Fire” were the lead singles of this album. The lyrics of the songs included in the album Metamorfoz were praised by the Turkish Language Association. In 2010, his seventh studio album, Adımı Kalbine Yaz, became the best-selling album of the year in Turkey. In 2016, his ninth studio album, Ahde Vefa, which has a Classical Turkish theme, was released.
more...William Randolph “Cozy” Cole (October 17, 1909 – January 9, 1981) was an American jazz drummer who had hits with the songs “Topsy I” and “Topsy II“. “Topsy II” peaked at No. 3 on the Billboard Hot 100, and at No. 1 on the R&B chart. It sold over one million copies and was awarded a gold disc. The track peaked at No. 29 in the UK Singles Chart in 1958. The recording contained a long drum solo and was one of the few drum solo recordings to make the charts at Billboard magazine. The single was issued by Love Records, a small record label in Brooklyn, New York. Cole’s song “Turvy II” reached No. 36 in 1959.
William Randolph Cole was born in 1909 in East Orange, New Jersey. His first music job was with Wilbur Sweatman in 1928. In 1930 he played for Jelly Roll Morton‘s Red Hot Peppers, recording an early drum solo on “Load of Cole”. He spent 1931–33 with Blanche Calloway, 1933–34 with Benny Carter, 1935–36 with Willie Bryant, 1936–38 with Stuff Smith‘s small combo, and 1938–42 with Cab Calloway. In 1942, he was hired by CBS Radio music director Raymond Scott as part of network radio’s first mixed-race orchestra. After that he played with Louis Armstrong’s All Stars.
Cole performed with Louis Armstrong and his All Stars with Velma Middleton singing vocals for the famed ninth Cavalcade of Jazz concert held at Wrigley Field in Los Angeles. The concert was produced by Leon Hefflin, Sr. on June 7, 1953. Also featured that day were Roy Brown and his Orchestra, Don Tosti and His Mexican Jazzmen, Earl Bostic, Nat “King” Cole, and Shorty Rogers and his Orchestra.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=THKo3nYZfkM
more...Barney Kessel (October 17, 1923 – May 6, 2004) was an American jazz guitarist born in Muskogee, Oklahoma. Noted in particular for his knowledge of chords and inversions and chord-based melodies, he was a member of many prominent jazz groups as well as a “first call” guitarist for studio, film, and television recording sessions. Kessel was a member of the group of session musicians informally known as the Wrecking Crew.
Kessel began his career as a teenager touring with local dance bands. When he was 16, he started playing with the Oklahoma A&M band, Hal Price & the Varsitonians. The band members nicknamed him “Fruitcake” because he practiced up to 16 hours a day.
In the early 1940s he moved to Los Angeles, where for one year he was a member of the Chico Marx big band. He appeared in the film Jammin’ the Blues, which featured Lester Young. Soon after, he played in the bands of Charlie Barnet and Artie Shaw. During the day, he worked as a studio musician and at night played jazz in clubs. In 1947 he recorded with Charlie Parker. He worked in Jazz at the Philharmonic and for one year in the early 1950s he was a member of the Oscar Peterson trio.[1][2] After leaving the trio, he recorded several solo albums for Contemporary. He recorded a series of albums with Ray Brown and Shelly Manne The Poll Winners because the three of them often won polls conducted by Metronome and DownBeat magazines. He was the guitarist on the album Julie Is Her Name (1955) by Julie London, which includes the standard “Cry Me a River, which sold a million copies and demonstrated Kessel’s chordal approach to guitar.
more...https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cRCXQKWmesY
more...NGC 6670 are a pair of interacting galaxies within the Draco constellation, which lie around 401 million light-years from Earth. Its shape resembles a Leaping Dolphin. NGC 6670 was discovered by Lewis A. Swift on July 31, 1886. NGC 6670 is a combination of two colliding disc galaxies which are known as NGC 6670E and NGC 6670W. The galaxy is 100 billion times brighter than our Sun. The galaxies have already collided once before and they are now moving towards each other again nearing a second collision. Its apparent magnitude is 14.3, its size is 1.0 arc minutes.

Roy Anthony Hargrove (October 16, 1969 – November 2, 2018) was an American jazz trumpeter. He won worldwide notice after winning two Grammy Awards for differing types of music in 1997 and in 2002. Hargrove primarily played in the hard bop style for the majority of his albums, especially performing jazz standards on his 1990s albums.
Hargrove was the bandleader of the progressive group the RH Factor, which combined elements of jazz, funk, hip-hop, soul, and gospel music. Its members have included Chalmers “Spanky” Alford, Pino Palladino, James Poyser, Jonathan Batiste, and Bernard Wright. His longtime manager was Larry Clothier. Hargrove was born in Waco, Texas, to Roy Allan Hargrove and Jacklyn Hargrove. When he was 9, his family moved to Dallas, Texas. He took lessons on trumpet and was discovered by Wynton Marsalis when Marsalis visited the Booker T. Washington High School for the Performing and Visual Arts in Dallas. One of his most profound early influences was a visit to his junior high school by saxophonist David “Fathead” Newman, who performed as a sideman in Ray Charles‘s Band.
Hargrove spent one year (1988–1989) studying at Boston’s Berklee College of Music but could more often be found in New York City jam sessions. He transferred to the New School in New York. His first recording there was with the saxophonist Bobby Watson. Shortly afterwards he made a recording with Superblue featuring Watson, Mulgrew Miller, Frank Lacy, and Kenny Washington. In 1990 he released his first solo album, Diamond in the Rough, on the Novus/RCA label. He was commissioned by the Lincoln Center Jazz Orchestra and wrote The Love Suite: In Mahogany which premiered in 1993.
more...María del Carmen García Galisteo MML (born 16 October 1930) known professionally as Carmen Sevilla is a Spanish actress, singer and television presenter. Her film roles include Academy Award nominee Vengeance, Searching for Monica (1962) and the 1956 French film Don Juan. Carmen Sevilla was born in Seville. Sevilla made her film début in 1948 in Jalisco Sings in Seville, She joy great famous in the make The Troublemaker with Tony Leblanc. She played Mary Magdalene in Nicholas Ray‘s King of Kings.
In 1972, she played Octavia in the English-language film Antony and Cleopatra, She also appeared in La Cera Virgen (1972), Nadie oyó gritar (1973), and Beatriz (1976). She received a Círculo de Escritores Cinematográficos (Cinema Writers Circle) lifetime award in 2004.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R13nv0c5q3w
more...Joseph Lee “Big Joe” Williams (October 16, 1903 – December 17, 1982) was an American Delta blues guitarist, singer and songwriter, notable for the distinctive sound of his nine-string guitar. Performing over four decades, he recorded the songs “Baby Please Don’t Go”, “Crawlin’ King Snake” and “Peach Orchard Mama”, among many others, for various record labels, including Bluebird, Delmark, Okeh, Prestige and Vocalion. He was inducted into the Blues Hall of Fame on October 4, 1992.
The blues historian Barry Lee Pearson (Sounds Good to Me: The Bluesman’s Story, Virginia Piedmont Blues) described Williams’s performance:
- When I saw him playing at Mike Bloomfield’s “blues night” at the Fickle Pickle, Williams was playing an electric nine-string guitar through a small ramshackle amp with a pie plate nailed to it and a beer can dangling against that. When he played, everything rattled but Big Joe himself. The total effect of this incredible apparatus produced the most buzzing, sizzling, African-sounding music I have ever heard.
- Born in Oktibbeha County, a few miles west of Crawford, Mississippi, Williams as a youth began wandering across the United States busking and playing in stores, bars, alleys and work camps. In the early 1920s he worked in the Rabbit Foot Minstrels revue. He recorded with the Birmingham Jug Band in 1930 for Okeh Records.
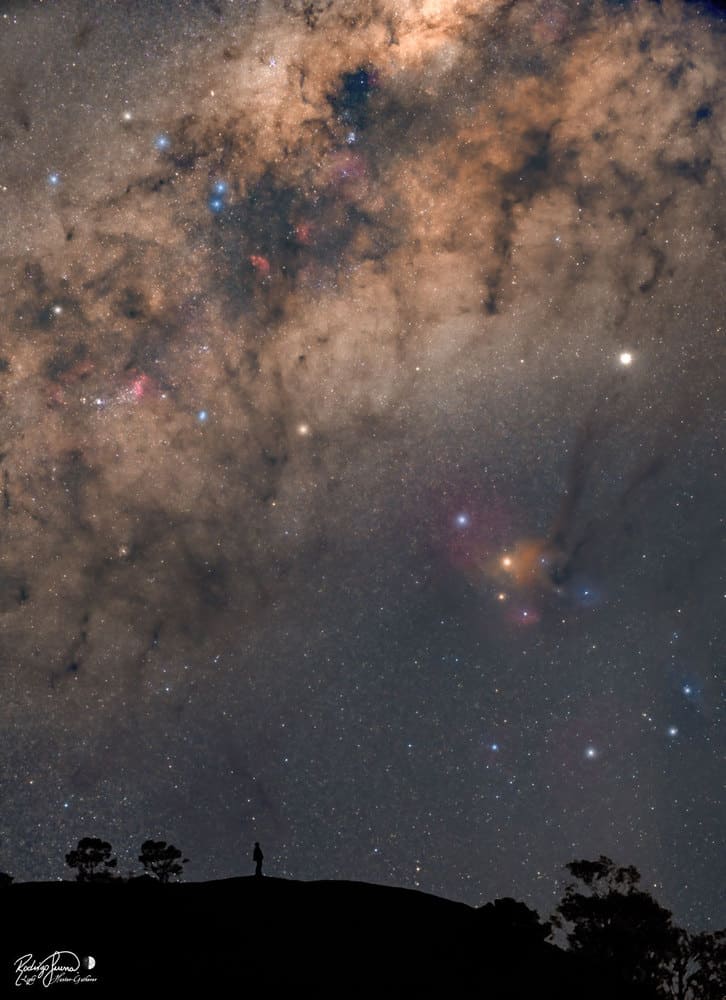
The featured picture is actually a composite of two images taken last month from the same location in south Brazil and with the same camera — but a few hours apart. The person in the image — also the astrophotographer — has much to see in the Milky Way Galaxy above. The central band of our home Galaxy stretches diagonally up from the lower left. This band is dotted with spectacular sights including dark nebular filaments, bright blue stars, and red nebulas. Millions of fainter and redder stars fill in the deep Galactic background. To the lower right of the Milky Way are the colorful gas and dust clouds of Rho Ophiuchi, featuring the bright orange star Antares. On this night, just above and to the right of Antares was the bright planetJupiter. The sky is so old and so familiar that humanity has formulated many stories about it, some of which inspired this very picture.

Fela Anikulapo Kuti (15 October 1938 – 2 August 1997), also professionally known as Fela Kuti, or simply Fela, was a Nigerian multi-instrumentalist, musician, composer, pioneer of the Afrobeat music genre and human rights activist. At the height of his popularity, he was referred to as one of Africa’s most “challenging and charismatic music performers”. Fela was born Olufela Olusegun Oludotun Ransome-Kuti on 15 October 1938 in Abeokuta, the modern-day capital of Ogun State in the Federal Republic of Nigeria, then a city in the British Colony of Nigeria,into an upper-middle-class family. His mother, Chief Funmilayo Ransome-Kuti, was a feminist activist in the anti-colonial movement; his father, Reverend Israel Oludotun Ransome-Kuti, an Anglican minister and school principal, was the first president of the Nigeria Union of Teachers. His brothers Beko Ransome-Kuti and Olikoye Ransome-Kuti, both medical doctors, are well-known in Nigeria. Fela is a first cousin to the Nigerian writer and Nobel laureate Wole Soyinka, the first African to win the Nobel Prize for Literature.
Fela attended Abeokuta Grammar School. Later he was sent to London in 1958 to study medicine, but decided to study music instead at the Trinity College of Music, the trumpet being his preferred instrument.While there, he formed the band Koola Lobitos, playing a fusion of jazz and highlife. In 1960, Fela married his first wife, Remilekun (Remi) Taylor, with whom he would have three children (Femi, Yeni, and Sola). In 1963, Fela moved back to the newly independent Federation of Nigeria, re-formed Koola Lobitos and trained as a radio producer for the Nigerian Broadcasting Corporation. He played for some time with Victor Olaiya and his All Stars.
In 1967, Fela went to Ghana to think up a new musical direction. That was when Kuti first called his music Afrobeat a combination of funk, jazz, salsa, Calypso and traditional Nigerian Yoruba music. In 1969, Fela took the band to the United States where they spent 10 months in Los Angeles. While there, Fela discovered the Black Power movement through Sandra Smith (now Sandra Izsadore), a partisan of the Black Panther Party. The experience would heavily influence his music and political views. He renamed the band Nigeria ’70. Soon afterwards, the Immigration and Naturalization Service was tipped off by a promoter that Fela and his band were in the US without work permits. The band performed a quick recording session in Los Angeles that would later be released as The ’69 Los Angeles Sessions. After Fela and his band returned to Nigeria, the group was renamed The Afrika ’70, as lyrical themes changed from love to social issues. He formed the Kalakuta Republic, a commune, a recording studio, and a home for the many people connected to the band that he later declared independent from the Nigerian state. According to Lindsay Barrett, the name “Kalakuta” derived from the infamous Black Hole of Calcutta dungeon in India. Fela set up a nightclub in the Empire Hotel, first named the Afro-Spot and later the Afrika Shrine, where he both performed regularly and officiated at personalized Yoruba traditional ceremonies in honour of his nation’s ancestral faith. He also changed his name to Anikulapo (meaning “He who carries death in his pouch”, with the interpretation: “I will be the master of my own destiny and will decide when it is time for death to take me”). He stopped using the hyphenated surname “Ransome” because it was a slave name.
more...Nellie Rose Lutcher (October 15, 1912 – June 8, 2007) was an African-American R&B and jazz singer and pianist, who gained prominence in the late 1940s and early 1950s. Lutcher was most recognizable for her diction and exaggerated pronunciation and was credited as an influence by Nina Simone among others. Lutcher was born in Lake Charles, Louisiana, the eldest daughter of the 15 children of Isaac and Suzie Lutcher. She was the sister of saxophonistJoe Lutcher. Her father was a bass player and her mother a church organist. She received piano lessons, and her father formed a family band with her playing piano. At age 12, she played with Ma Rainey, when Rainey’s regular pianist fell ill and had to be left behind in the previous town. Searching for a temporary replacement in Lake Charles, one of the neighbors told Rainey that there was a little girl who played in church who might be able to do it. Aged 15, Lutcher joined her father in Clarence Hart‘s Imperial Jazz Band, and in her mid-teens also briefly married the band’s trumpet player. In 1933, she joined the Southern Rhythm Boys, writing their arrangements and touring widely. In 1935, she moved to Los Angeles, where she married Leonel Lewis and had a son. She began to play swing piano, and also to sing, in small combos throughout the area, and began developing her own style, influenced by Earl Hines, Duke Ellington and her friend Nat “King” Cole.
She was not widely known until 1947 when she learned of the March of Dimes talent show at Hollywood High School, and performed. The show was broadcast on the radio and her performance caught the ear of Dave Dexter, a scout for Capitol Records. She was signed by Capitol and made several records, including “The One I Love (Belongs to Somebody Else)” and her first hit single, the risqué “Hurry On Down”, which went to # 2 on the rhythm and blues chart. This was followed by her equally successful composition “He’s A Real Gone Guy”, which also made # 2 on the R&B chart and crossed over to the pop charts where it reached # 15.
more...MacHouston Baker (October 15, 1925 – November 27, 2012), known professionally as Mickey Baker and Mickey “Guitar” Baker, was an American guitarist. Baker was born in Louisville, Kentucky. His mother was black, and his father, whom he never met, was believed to be white.
In 1936, at the age of 11, Baker was put into an orphanage. He ran away frequently, and had to be retrieved by the staff from St. Louis, New York City, Chicago, and Pittsburgh. Eventually the orphanage quit looking for him, and at the age of 16 he stayed in New York City. He found work as a laborer and then a dishwasher. But after hanging out in the pool halls of 26th Street, he gave up work to become a full-time pool shark.
By 1949, Baker had his own combo, and a few paying jobs. He decided to move west, but found that audiences there were not receptive to progressive jazz music. Baker was stranded without work in California when he saw a show by blues guitarist Pee Wee Crayton.[5] Baker said of the encounter:
“I asked Pee Wee, ‘You mean you can make money playing that stuff on guitar?’ Here he was driving a big white Eldorado and had a huge bus for his band. So I started bending strings. I was starving to death, and the blues was just a financial thing for me then.”
He found a few jobs in Richmond, California, and made enough money to return to New York.
After returning east, Baker began recording for Savoy, King and Atlantic Records. He did sessions with Doc Pomus, The Drifters, Ray Charles, Ivory Joe Hunter, Ruth Brown, Big Joe Turner, Louis Jordan, Coleman Hawkins, and numerous other artists.[6]
Inspired by the success of Les Paul & Mary Ford, he formed the pop duo Mickey & Sylvia (with Sylvia Robinson, one of his guitar students) in the mid-1950s. Together, they had a hit single with “Love Is Strange” in 1956. The duo split up in the late 1950s, but sporadically worked together on additional tracks until the mid-1960s. It was around this time that he moved to France, where he worked with Ronnie Bird and Chantal Goya and made a few solo records. He would remain in France for the rest of his life. Up until the end of his life, Baker was rarely without work.
more...More Posts
- Jesse Fuller
- Don Drummond
- Sir Charles Thompson
- Flamenco Fridays with Camerón y Tomatito
- Daily Roots with the Symbals
- The Cosmos with NGC 602
- Harvey Mandel
- Bobby McFerrin
- Leroy Jenkins
- Astor Piazzolla
- Sonny Boy Williamson II
- World Music with Oberon
- Daily Roots with General Echo
- The Cosmos with NGC 1499
- Norman Blake
- Bix Beiderbecke
- World Music with Electric Jalaba
- Daily Roots with Barrington Levy
- The Cosmos with AFGL 5180
- Zakir Hussain