Blog
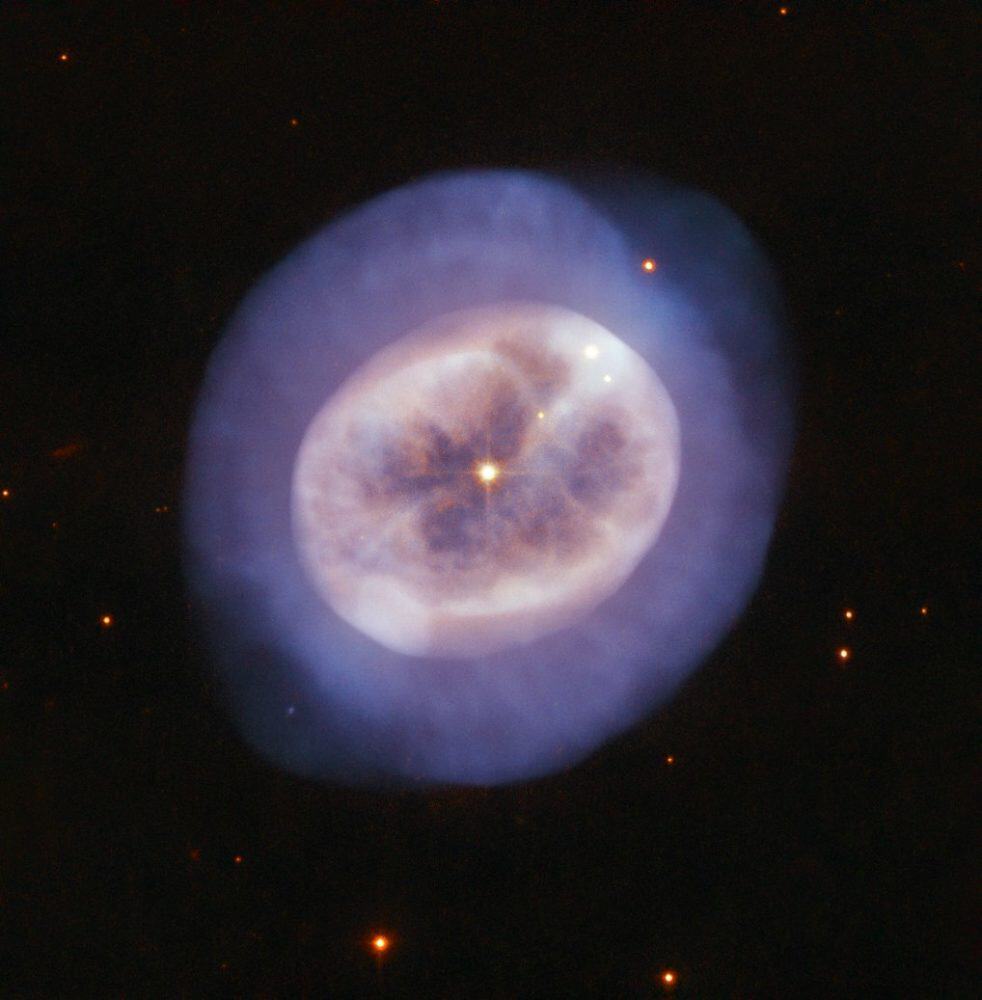
NGC 2022 is a planetary nebula located in the constellation of Orion.Also known as PK 196-10 1 and IRAS 05393+0903, the nebula is 8,213 light-years away from Earth.The object was discovered on December 28, 1785 by the German-born British astronomer William Herschel.“This type of object is called, somewhat confusingly, a planetary nebula, though it has nothing to do with planets,” said members of the Hubble science team.“The name derives from the rounded, planet-like appearance of these objects in early telescopes.”“When stars like the Sun grow advanced in age, they expand and glow red,” they explained.“These so-called red giants then begin to lose their outer layers of material into space.”“More than half of such a star’s mass can be shed in this manner, forming a shell of surrounding gas.”“At the same time, the star’s core shrinks and grows hotter, emitting ultraviolet light that causes the expelled gases to glow.”
more...
Joseph Armand “Joe” Castro (August 15, 1927 – December 13, 2009) was an American bebop jazz pianist, based primarily on the West Coast of the United States. Castro was born in Miami, Arizona on August 15, 1927 to John L. Castro and Lucy Sanchez. Castro went to school in Pittsburg, California in the San Francisco Bay area, north of Oakland, where he began playing professionally at the age of 15. His enrollment at San Jose State University was interrupted twice—first by a stint in the army from 1946 to 1947 and then when he formed his first jazz trio working on both the West Coast and in Hawaii. In 1956 Castro moved to New York City, where his trio successfully appeared in the city’s top jazz clubs—Basin Street, The Embers, The Hickory House and Birdland. He was critically lauded by the likes of Leonard Feather who described his style as “assertively swinging,” and Dave Brubeck, who had known Castro since the early 1950s, as “an extremely talented individual, a fine musician, an excellent pianist and a tasteful performer.” In 1958, he moved to Los Angeles to be associated almost exclusively with Teddy Edwards, Billy Higgins and Leroy Vinnegar. “The group has been very important to me,” Castro says. “I had been working so long with piano trios, I had to learn how to play less and say more. Actually I have more freedom in this group without having to carry the load.” Castro recorded and performed extensively with The Teddy Edwards Quartet while also making two of his own recordings as a leader for Atlantic Records.
Oscar Emmanuel Peterson, CC CQ OOnt (August 15, 1925 – December 23, 2007) was a Canadian jazz pianist and composer. He was called the “Maharaja of the keyboard” by Duke Ellington, but simply “O.P.” by his friends. He released over 200 recordings, won eight Grammy Awards, and received numerous other awards and honours. He is considered one of the greatest jazz pianists, and played thousands of concerts worldwide in a career lasting more than 60 years. Peterson was born in Montreal, Quebec, to immigrants from the West Indies; his father worked as a porter for Canadian Pacific Railway. Peterson grew up in the neighbourhood of Little Burgundy in Montreal. It was in this predominantly black neighborhood that he encountered the jazz culture. At the age of five, Peterson began honing his skills on trumpet and piano, but a bout of tuberculosis when he was seven prevented him from playing the trumpet again, so he directed all his attention to the piano. His father, Daniel Peterson, an amateur trumpeter and pianist, was one of his first music teachers, and his sister Daisy taught him classical piano. Peterson was persistent at practising scales and classical études.
more...Buster Brown (August 15, 1911 – January 31, 1976) was an American blues and R&B singer best known for his hit, “Fannie Mae“.
Brown was born in Cordele, Georgia. In the 1930s and 1940s he played harmonica at local clubs and made a few non-commercial recordings. These included “War Song” and “I’m Gonna Make You Happy” (1943), which were recorded when he played at the folk festival at Fort Valley (GA) State Teachers College, for the Library of Congress’ Folk Music Archive.
Brown moved to New York in 1956, where he was discovered by Fire Records owner Bobby Robinson. In 1959, at almost fifty years of age, Brown recorded the rustic blues, “Fannie Mae“, which featured Brown’s harmonica playing and whoops, which went to # 38 in the U.S. Top 40, and to #1 on the R&B chart in April 1960. His remake of Louis Jordan‘s “Is You Is or Is You Ain’t My Baby” reached # 81 on the pop charts later in 1960, but did not make the R&B chart.“Sugar Babe” was his only other hit, in 1962, reaching # 19 on the R&B chart and # 99 on the pop chart.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-M7CZBtkvws
more...Finland
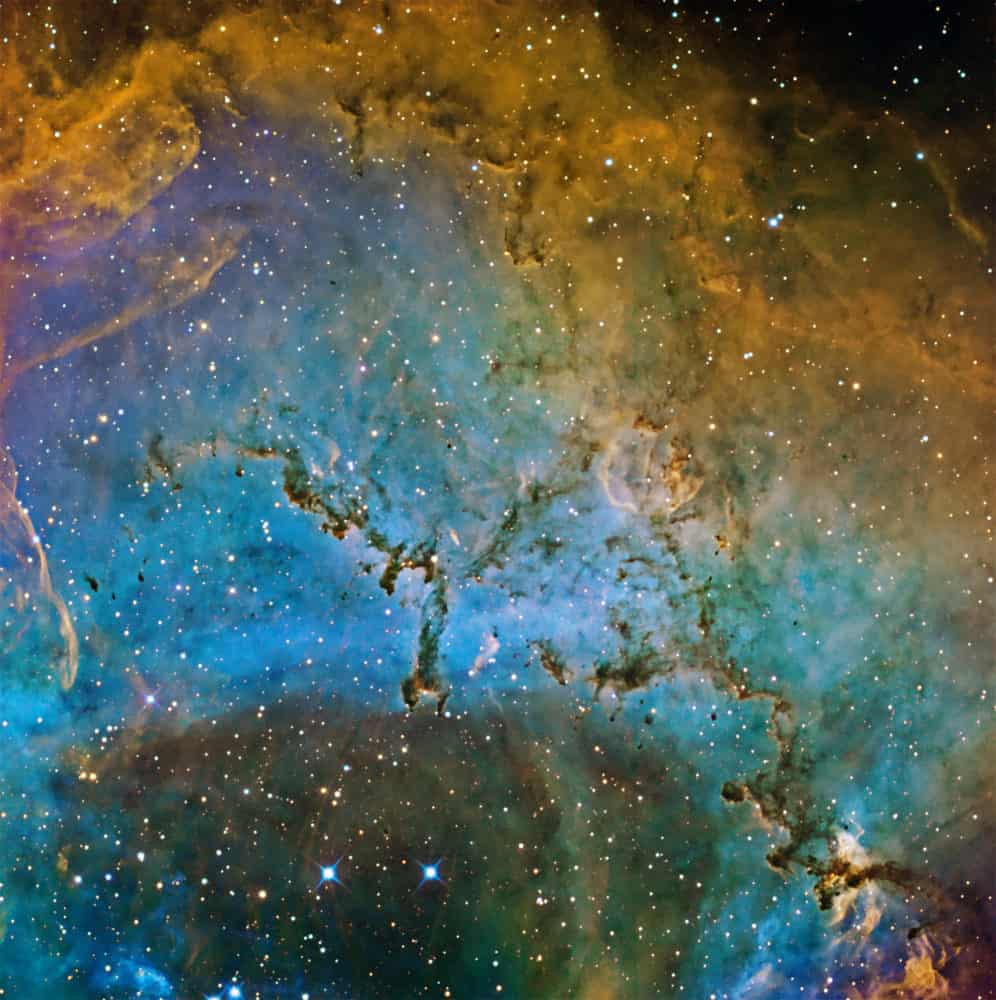
more...The Rosette Nebula (also known as Caldwell 49) is a large spherical H II region (circular in appearance) located near one end of a giant molecular cloud in the Monoceros region of the Milky Way Galaxy. The open cluster NGC 2244(Caldwell 50) is closely associated with the nebulosity, the stars of the cluster having been formed from the nebula’s matter.
The complex has the following NGC designations:
- NGC 2237 – Part of the nebulous region (Also used to denote whole nebula)
- NGC 2238 – Part of the nebulous region
- NGC 2239 – Part of the nebulous region (Discovered by John Herschel)
- NGC 2244 – The open cluster within the nebula (Discovered by John Flamsteed in 1690)
- NGC 2246 – Part of the nebulous region
The cluster and nebula lie at a distance of some 5,000 light-years from Earth) and measure roughly 130 light years in diameter. The radiation from the young stars excites the atoms in the nebula, causing them to emit radiation themselves producing the emission nebula we see. The mass of the nebula is estimated to be around 10,000 solar masses.
A survey of the nebula with the Chandra X-ray Observatory has revealed the presence of numerous new-born stars inside optical Rosette Nebula and studded within a dense molecular cloud. Altogether, approximately 2500 young stars lie in this star-forming complex, including the massive O-type stars HD 46223 and HD 46150, which are primarily responsible for blowing the ionized bubble.
more...Frank “Son” Seals (August 13, 1942 – December 20, 2004) was an American electric blues guitarist and singer. In 2009, Seals was inducted into the Blues Hall of Fame. Seals was born in Osceola, Arkansas, where his father, Jim “Son” Seals, owned a small juke joint, called the Dipsy Doodle Club. He began performing professionally by the age of 13, first as a drummer with Robert Nighthawk and later as a guitarist. At age 16, he began to play at the T-99, a local upper-echelon club, with his brother-in-law Walter “Little Walter” Jefferson. He played there with prominent blues musicians, including Albert King, Rufus Thomas, Bobby Bland, Junior Parker, and Rosco Gordon. Their varying styles contributed to the development of Seals’s own playing techniques. While playing at the T-99, he was also introduced to country–western music by Jimmy Grubbs, who occasionally asked Seals to play the drums or guitar with his group. At the age of 19, Seals formed his own band, Son Seals and the Upsetters, to fill in at the Rebel Club, in Osceola.The band members were Johnny Moore (“Old Man Horse”) on piano; Alvin Goodberry on drums, guitar, bass, or piano; Little Bob Robinson on vocals; and Walter Lee “Skinny Dynamo” Harris on piano. Shortly thereafter, a man from Little Rock, Arkansas, came to find “Little Walter” for a gig at his club, but when Walter turned it down the offer went to Seals.
David Van Cortlandt Crosby (born August 14, 1941) is an American singer-songwriter and musician. In addition to his solo career, he was a founding member of both the Byrds and Crosby, Stills & Nash.
Crosby joined the Byrds in 1964. The band gave Bob Dylan his first number one hit in April 1965 with “Mr. Tambourine Man.” Crosby appeared on the Byrds’ first five albums, and produced the original lineup’s 1973 reunion album. In 1967 he joined Buffalo Springfield on stage at the Monterey Pop Festival, which contributed to his dismissal from the Byrds. He subsequently formed Crosby, Stills & Nash in 1968 with Stephen Stills (of Buffalo Springfield) and Graham Nash of the Hollies. After the release of their debut album CSN won the Grammy Award for Best New Artist of 1969. Neil Young joined the group for live appearances, their second concert being Woodstock, before recording their second album Déjà Vu. Meant to be a group that could collaborate freely, Crosby and Nash recorded three gold albums in the 1970s, while the core trio of CSN remained active from 1976 until 2016. CSNY reunions took place in each decade from the 1970s through the 2000s.
Songs Crosby wrote or co-wrote include “Lady Friend“, “Why“, and “Eight Miles High” with the Byrds and “Guinnevere“, “Wooden Ships“, “Shadow Captain”, and “In My Dreams” with Crosby, Stills & Nash. He wrote “Almost Cut My Hair” and the title track “Déjà Vu” for Crosby, Stills, Nash & Young‘s 1970 album. He is known for his use of alternate guitar tunings and jazz influences. He has released six solo albums, five of which have charted. Additionally he formed a jazz influenced trio with his son James Raymond and guitarist Jeff Pevar in CPR. Crosby’s work with the Byrds and CSN(Y) has sold over 35 million albums.
Crosby has been inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame twice: once for his work in the Byrds and again for his work with CSN. Five albums he contributed to are included in Rolling Stone‘s 500 Greatest Albums of All Time, three with the Byrds and two with CSN(Y). He is outspoken politically and has been depicted as emblematic of the 1960s’ counterculture.
more...Edwin James Costa (August 14, 1930 – July 28, 1962) was an American jazz pianist, vibraphonist, composer and arranger. In 1957 he was chosen as Down Beat jazz critics’ new star on piano and vibes – the first time that one artist won two categories in the same year. He became known for his percussive, driving piano style that concentrated on the lower octaves of the keyboard.
Costa had an eight-year recording career, during which he appeared on more than 100 albums; five of these were under his own leadership. As a sideman he appeared in orchestras led by Manny Albam, Gil Evans, Woody Herman and others; played in smaller groups led by musicians including Tal Farlow, Coleman Hawkins, Gunther Schuller, and Phil Woods; and accompanied vocalists including Tony Bennett and Chris Connor. Costa died, aged 31, in a car accident in New York City.
Eddie Costa was born in Atlas, Pennsylvania, near Mount Carmel, in Northumberland County. He was taught and influenced on piano by his older, musically trained brother, Bill, and a local piano teacher. Eddie took paid jobs as a pianist from the age of 15. In contrast to his piano training, he was self-taught on vibes. In 1949 Costa played and toured for a few months with violinist Joe Venuti. He then worked for his brother in New York until, in 1951, Eddie was drafted into the army. During his time in the armed forces, Costa performed in Japan and Korea. Upon release after two years, Costa again worked around the New York area, including for bands led by Kai Winding, Johnny Smith, and Don Elliott.
more...Hezekiah Leroy Gordon Smith (August 14, 1909 – September 25, 1967), better known as Stuff Smith, was an American jazz violinist. He is well known for the song “If You’re a Viper” (the original title was “You’se a Viper”). Smith was, along with Stéphane Grappelli, Michel Warlop, Svend Asmussen and Joe Venuti, one of jazz music’s preeminent violinists of the swing era. He was born in Portsmouth, Ohio, in 1909 and studied violin with his father. Smith cited Louis Armstrong as his primary influence and inspiration to play jazz, and like Armstrong, was a vocalist as well as instrumentalist. In the 1920s, he played in Texas as a member of Alphonse Trent‘s band. After moving to New York City he performed regularly with his sextet at the Onyx Club starting in 1935 and also with Coleman Hawkins, Charlie Parker, Dizzy Gillespie, and later, Sun Ra.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AJN7H7_b34c
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0Og7Ie1awNE
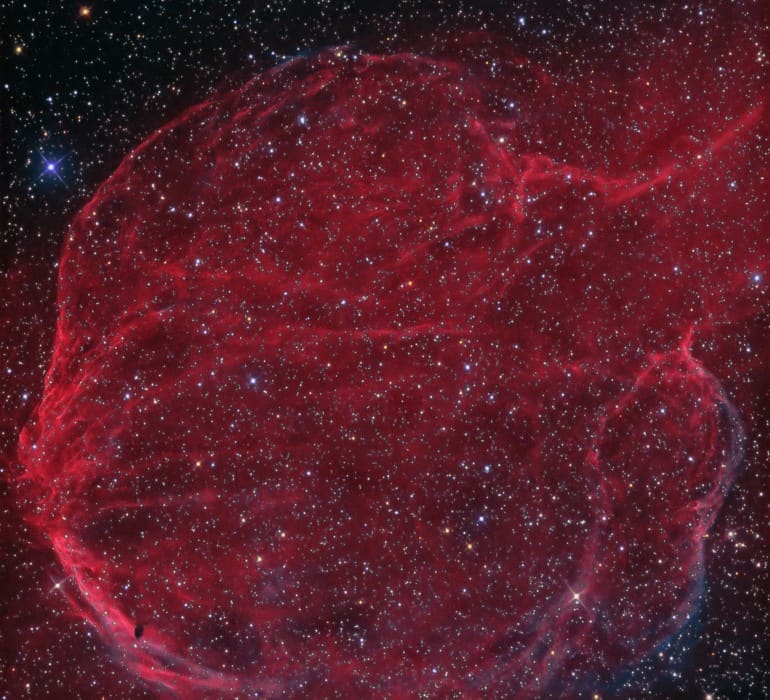
more...Spanning an area of 35 arcminutes on the sky towards the constellation of Cassiopeia, this enigmatic loop of ionized nebulosity is a supernova remnant catalogued as CTB 1. This name denotes it as a radio source compiled in the Caltech Observatory list B catalogue of 110 radio sources discovered in a radio survey in 1960. A few other CTB sources also correspond with a supernova remnant such as CTB 80.
The radio source CTB 1 was suspected to be a supernova remnant in 1960 and confirmed as a supernova remnant in 1971. Optical emission associated with it was discovered by Sidney van den Bergh in 1973. The optical structure consists of a roughly circular shell with a breakout rupture towards the north, which also coincides with a break in the radio shell at this location. This is likely to be the result of the supernova remnant’s interaction with a nearby cavity of neutral hydrogen gas. The Ha shell is composed of multiple interlocking limb brightened filaments with faint emission also extending beyond the main shell towards the south. The OIII structure consists of a series of filaments forming a curved arc towards one side. Close inspection also reveals a small dark globule silhouetted against the southern part.
CTB 1 belongs to the morphological class of mixed-morphology supernova remnants, which consist of a radio shell with central x-ray emission. Other prominent examples of this class include IC 443 and W28. At a distance of 10,000 light years, the diameter of CTB 1 is 100 light years. The expansion of the shell in a highly dynamic environment suggests that the progenitor star that exploded to form the supernova remnant might have been a B or O-type supergiant star. The age of CTB 1 has many estimates but the most commonly accepted one is 10,000 years.
Interestingly this object has been considered erroneously as a planetary nebula and is catalogued as Abell 85 in George Abell’s second version of the Abell planetary nebula catalogue published in 1966 and was also included in the first version published in 1955. It is also wrongly catalogued as a HII region in Beverley Lynd’s amusingly named 1965 catalogue of bright nebulae as LBN 576.
Taken with a Planewave 17″ f6.7 on a Planewave HD Mount and a SBIG 16803 camera. Imaged from “Dark Sky New Mexico” in Animas.
LRGB- 225 each, HA- 780m, O3- 780m 41 Total Hours total.
more...Daniel Grayling Fogelberg (August 13, 1951 – December 16, 2007) was an American musician, songwriter, composer, and multi-instrumentalist. He is known for his 1980s songs, including “Longer” (1979), “Same Old Lang Syne” (1980), and “Leader of the Band” (1982). Dan Fogelberg was born in Peoria, Illinois. He was the youngest of three sons born to Margaret (née Irvine), a classically trained pianist, and Lawrence Peter Fogelberg, a high school band director who spent most of his career at Peoria’s Woodruff High School and Pekin High School.Dan’s mother was a Scottish immigrant, and his father was of Swedish descent. His father would later be the inspiration for the song “Leader of the Band“. Dan often related his memory of his father allowing him to “conduct” the school band when he was only four years old. At the time, Fogelberg senior was band director at Bradley University in Peoria.
Using a Mel Bay course book, Dan taught himself to play a Hawaiian slide guitar that his grandfather gave him. He also learned to play the piano. At age 14, he joined a band, The Clan, which covered The Beatles. His second band was another cover band, The Coachmen, who, in 1967, released two singles written by Fogelberg. They were cut at Golden Voice Recording studio in South Pekin, Illinois, and released on Ledger Record’s label: “Maybe Time Will Let Me Forget” and “Don’t Want to Lose Her”.
more...Ernest Harold “Benny” Bailey (13 August 1925 – 14 April 2005) was an American jazz trumpeter.
A native of Cleveland, Ohio, Bailey briefly studied flute and piano before turning to trumpet. He attended the Cleveland Conservatory of Music. He was influenced by Cleveland native Tadd Dameron and had a significant influence on other Cleveland musicians, such as Albert Ayler, Bob Cunningham, Bobby Few, Bill Hardman, and Frank Wright. Bailey played with Tony Lovano, father of Joe Lovano.
In the early 1940s he worked with Bull Moose Jackson and Scatman Crothers. He later worked with Dizzy Gillespie and toured with Lionel Hampton. During a European tour with Hampton he remained in Europe and spent time in Sweden, where he worked with Harry Arnold‘s big band.He preferred big bands over small groups, and he became associated with several big bands in Europe, including the Kenny Clarke/Francy Boland Big Band. His time with Quincy Jones led to a brief return to the United States in 1960. He was invited to the studio as part of Freddie Redd‘s sextet to record Redd’s Blues after meeting the pianist during a tour in Sweden. He returned to Europe, first to Germany, then the Netherlands, where he settled permanently.
In 1969 he played on Eddie Harris and Les McCann‘s album Swiss Movement, recorded live at the Montreux Jazz Festival, although it was not his usual style of music. In 1988 he worked with British clarinetist Tony Coe and recorded albums until 2000 when he was in his mid-70s. Bailey died at home in Amsterdam on April 14, 2005.
more...Sir George Albert Shearing, OBE (13 August 1919 – 14 February 2011) was a British jazz pianist who for many years led a popular jazz group that recorded for Discovery Records, MGM Records and Capitol Records. The composer of over 300 titles, including the jazz standards “Lullaby of Birdland” and “Conception“, and had multiple albums on the Billboard charts during the 1950s, 1960s, 1980s and 1990s. He died of heart failure in New York City, at the age of 91.
Born in Battersea, London, Shearing was the youngest of nine children. He was born blind to working class parents: his father delivered coal and his mother cleaned trains in the evening. He started to learn piano at the age of three and began formal training at Linden Lodge School for the Blind, where he spent four years.
more...More Posts
- Bud Shank
- Niels-Henning Ørsted Pedersen
- Ramsey Lewis
- SAVE UKRAINE World Music ONUKA
- Daily Roots The Crystalites
- The Defeat of Jesse James Musical
- Cosmos Virgo Cluster
- Stevie Nicks
- Rubén González
- Miles Davis
- Isadora Duncan
- Flamenco Fridays Camarón, Tomatito, Paco de lucia
- Daily Roots Skin, Flesh & Bones
- Tina Turner Memorial
- The Defeat of Jesse James Musical
- Cosmos NGC 6543
- Wallace Roney
- Sugar Minott
- Gary Foster
- Marshall Allen