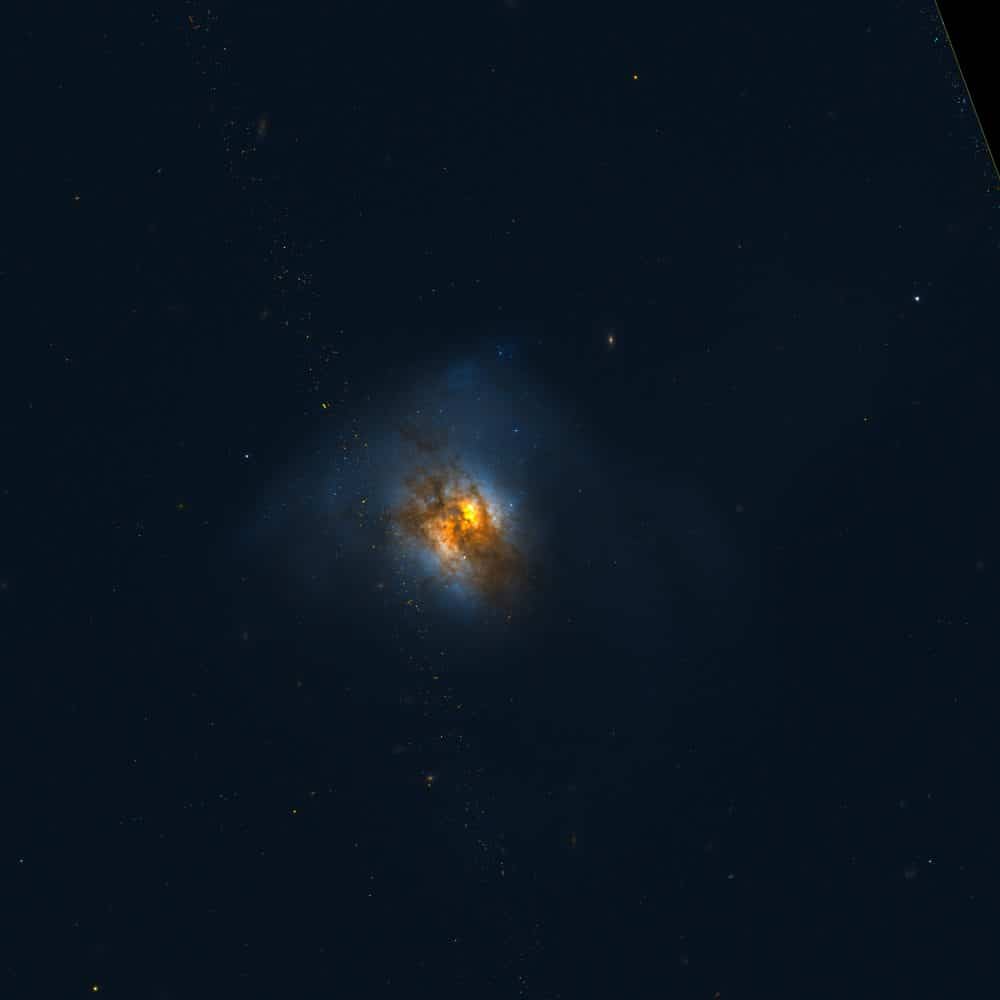
The Cosmos with Arp 220
Arp 220 is the closest Ultraluminous Infrared Galaxy (ULIRG) to Earth. Its energy output was discovered by IRASto be dominated by the far-infrared part of the spectrum. It is often regarded as the prototypical ULIRG and has been the subject of much study as a result. Most of its energy output is thought to be the result of a massive burst of star formation, or starburst, probably triggered by the merging of two smaller galaxies. Recent (2002 and 1997) HST observations of Arp 220, taken in visible light with the ACS, and in infrared light with NICMOS, revealed more than 200 huge star clusters in the central part of the galaxy. The most massive of these clusters contains enough material to equal about 10 million suns. X-ray observations by the Chandra and XMM-Newton satellites have shown that Arp 220 probably includes an active galactic nucleus (AGN) at its core, which raises interesting questions about the link between galaxy mergers and AGN, since it is believed that galactic mergers often trigger starbursts, and may also give rise to the supermassive black holes that appear to power AGN.