The Cosmos with M57
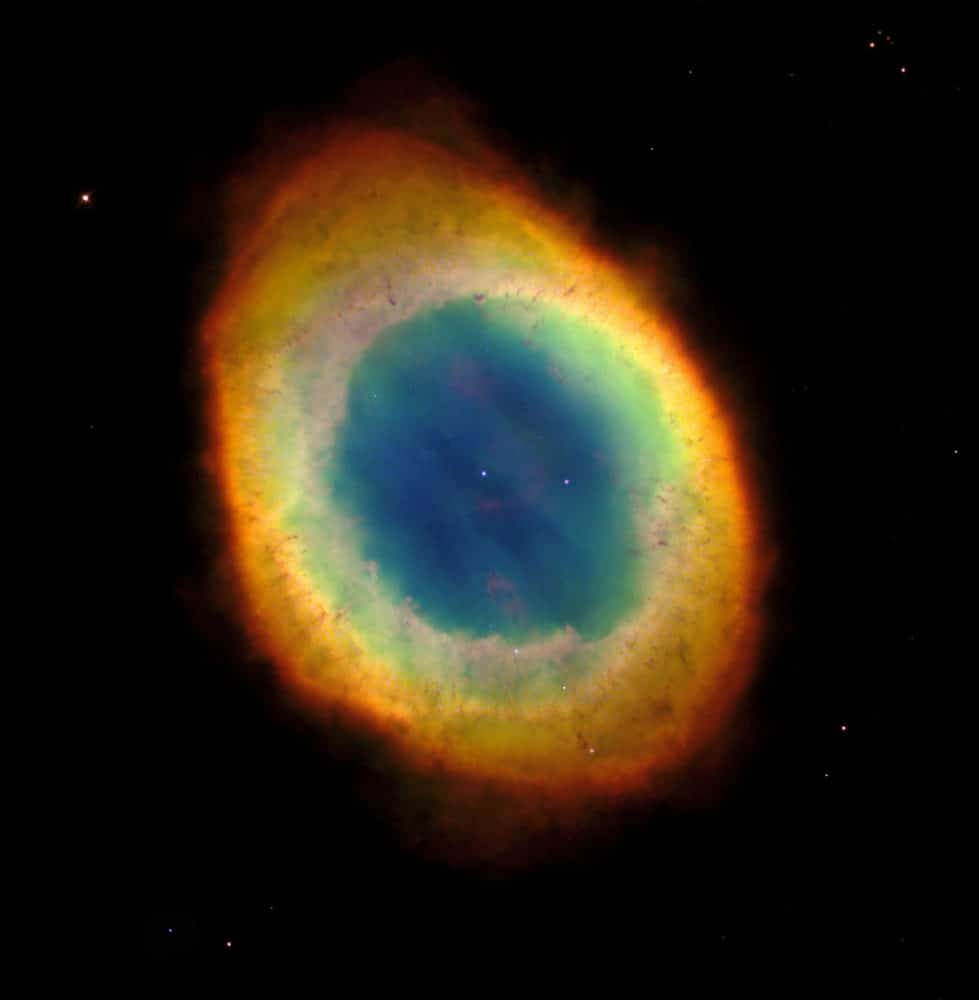
The Ring Nebula (also catalogued as Messier 57, M57 or NGC 6720) is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation of Lyra. Such objects are formed when a shell of ionized gas is expelled into the surrounding interstellar medium by a star at the end of its asymptotic giant branch phase, in the last stages of its evolution before becoming a white dwarf. This nebula was discovered by the French astronomer Charles Messier while searching for comets in late January 1779. Messier’s report of his independent discovery of Comet Bode reached fellow French astronomer Antoine Darquier de Pellepoix two weeks later, who then independently rediscovered the nebula while following the comet. Darquier later reported that it was “…as large as Jupiter and resembles a planet which is fading” (which may have contributed to the use of the “planetary nebula” terminology). It would be entered into Messier’s catalogue as the 57th object. Messier and German-born astronomer William Herschel speculated that the nebula was formed by multiple faint stars that were unresolvable with his telescope.
M57 is 0.787 kpc (2,570 light-years) from Earth. It has a visual magnitude of 8.8v and photographic magnitude of 9.7p. Photographs taken over a period of 50 years show the rate of nebula expansion is roughly 1 arcsecond per century, which corresponds to spectroscopic observations as 20–30 km s−1. M57 is illuminated by a central white dwarf or planetary nebula nucleus (PNN) of 15.75v visual magnitude.