Blog
Kenny Barron (born June 9, 1943) is an American jazz pianist, who has appeared on hundreds of recordings as leader and sideman and is considered one of the most influential mainstream jazz pianists since the bebop era.
Born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, Kenny Barron is the younger brother of tenor saxophonist Bill Barron (1927–1989). One of his first gigs was as pianist with the Dizzy Gillespie quartet. Barron was briefly a member of the Jazztet around 1962, but did not record with them.
He graduated in 1978 with a BA in arts from Empire State College (Metropolitan Center, New York City).
more...Lester William Polsfuss (June 9, 1915 – August 12, 2009), known as Les Paul, was an American jazz, country, and blues guitarist, songwriter, luthier, and inventor. He was one of the pioneers of the solid-body electric guitar, and his prototype, called the Log, served as inspiration for the Gibson Les Paul. Paul taught himself how to play guitar, and while he is mainly known for jazz and popular music, he had an early career in country music. In the 1950s, he and his wife, singer and guitarist Mary Ford, recorded numerous records, selling millions of copies.
Paul is credited with many recording innovations. His early experiments with overdubbing (also known as sound on sound), delay effects such as tape delay, phasing, and multitrack recording were among the first to attract widespread attention His licks, trills, chording sequences, fretting techniques, and timing set him apart from his contemporaries and inspired many guitarists of the present day.
Among his many honors, Paul is one of a handful of artists with a permanent exhibit in the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame. He is prominently named by the music museum on its website as an “architect” and a “key inductee” with Sam Phillips and Alan Freed. Paul is the only inductee in both the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame and the National Inventors Hall of Fame.
Paul was born Lester William Polsfuss in Waukesha, Wisconsin, to George and Evelyn (Stutz) Polsfuss, both of German ancestry. His only sibling, Ralph, was seven years older. Paul’s mother was related to the founders of Milwaukee’s Valentin Blatz Brewing Company and the makers of the Stutz automobile. His parents divorced when he was a child. His mother simplified their Prussian family name first to Polfuss, then to Polfus, although Les Paul never legally changed his name. Before taking the stage name Les Paul, he performed as Red Hot Red and Rhubarb Red.
more...Nehemiah Curtis “Skip” James (June 9, 1902 – October 3, 1969) was an American Delta blues singer, guitarist, pianist and songwriter.
His guitar playing is noted for its dark, minor-key sound, played in an open D-minor tuning with an intricate fingerpicking technique. James first recorded for Paramount Records in 1931, but these recordings sold poorly, having been released during the Great Depression, and he drifted into obscurity.
After a long absence from the public eye, James was rediscovered in 1964 by blues enthusiasts including John Fahey, helping further the blues and folk music revival of the 1950s and early 1960s. During this period, James appeared at folk and blues festivals, gave concerts around the country, and recorded several albums for various record labels. His songs have influenced generations of musicians and have been adapted by numerous artists. He has been hailed as “one of the seminal figures of the blues”.
James was born near Bentonia, Mississippi. His father was a bootlegger who reformed and became a preacher. As a youth, James heard local musicians, such as Henry Stuckey, from whom he learned to play the guitar, and the brothers Charlie and Jesse Sims. James began playing the organ in his teens. He worked on road construction and levee-building crews in Mississippi in the early 1920s and wrote what is perhaps his earliest song, “Illinois Blues”, about his experiences as a laborer. He began playing the guitar in open D-minor tuning.
more...https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-KEiGHfG-m8
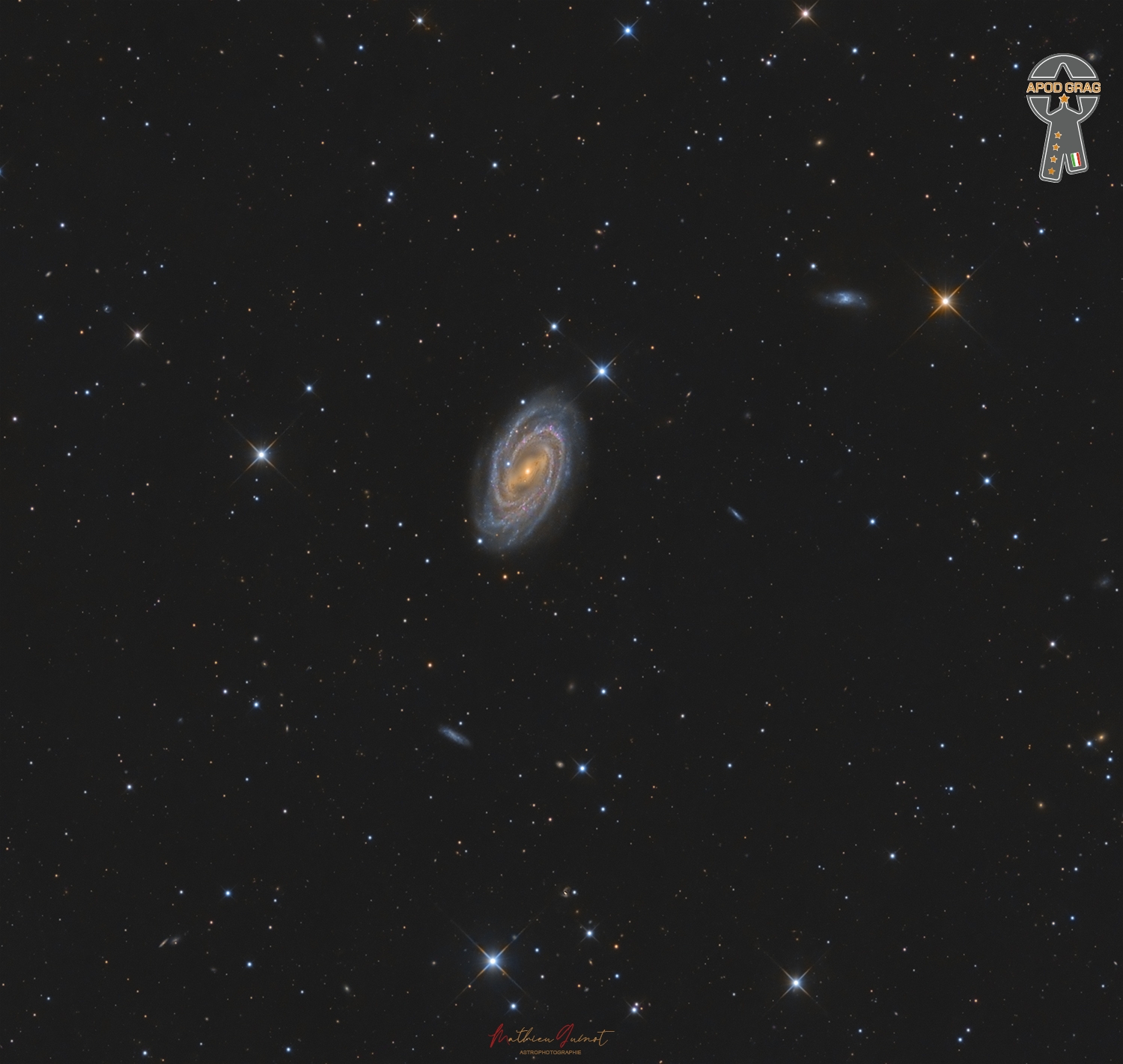
more...Messier 109 (also known as NGC 3992) is a barred spiral galaxy located approximately 83.5 ± 24 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major.
This galaxy is by far the most distant object in the Messier Catalog and one of the faintest, and it is the brightest member of a group of roughly 80 galaxies known as the Ursa Major Galaxy Cluster.
M109 is exhibiting a weak inner ring structure around the central bar and astronomers believe its structure may be influenced by interactions with three satellite galaxies.
Katerina “Katy” Garbi ; born 8 June 1961) is a Greek singer active in Greece and Cyprus, with some popularity in Turkey. Her career has spanned over 30 years with over 1.5 million records sold in Greece and abroad. Garbi’s discography is marked by several multi-platinum releases, including Arhizo Polemo (1996) and Evaisthisies (1997), two of the best-selling albums of the decade. Garbi represented Greece in the annual Eurovision Song Contest in 1993 with the song “Ellada, Hora Tou Fotos“, taking ninth place. She later struck her biggest commercial success with To Kati (2000) in terms of unit sales. Over the years, Garbi has won 11 Pop Corn Music Awards, including three for Album of the Year, and one Arion Music Award. On 14 March 2010, Alpha TV ranked her among the top-certified female artists in Greece’s phonographic era (since 1960), at 8th place.
more...
Derek Trucks (born June 8, 1979) is an American guitarist, songwriter, and founder of The Derek Trucks Band. He became an official member of The Allman Brothers Band in 1999. In 2010, he formed the Tedeschi Trucks Band with his wife, blues singer/guitarist Susan Tedeschi. His musical style encompasses several genres and he has twice appeared on Rolling Stone‘s list of 100 Greatest Guitarists of All Time. He is the nephew of the late Butch Trucks, drummer for the Allman Brothers.
Trucks was born in Jacksonville, Florida. According to Trucks, the name of Eric Clapton‘s band, Derek and the Dominos, had “something to do with the name [Derek] if not the spelling”.
Trucks bought his first guitar at a yard sale for $5 at age nine and became a child prodigy, playing his first paid performance at age 11. Trucks began playing the guitar using a slide because it allowed him to play the guitar despite his small hands as a young guitarist. By his 13th birthday, Trucks had played alongside Buddy Guy and toured with Thunderhawk.
more...Uri Caine (born June 8, 1956, Philadelphia, United States) is an American classical and jazz pianist and composer.
The son of Burton Caine, a professor at Temple Law School, and poet Shulamith Wechter Caine, Caine began playing piano at seven and studied with French jazz pianist Bernard Peiffer at 12. He later studied at the University of Pennsylvania, where he came under the tutelage of George Crumb. He also gained a greater familiarity with classical music in this period and worked at clubs in Philadelphia.
Caine played professionally after 1981, and by 1985 had his recording debut with the Rochester-Gerald Veasley band. In the 1980s, he moved to New York City, where he continues to live. His solo recording debut was in 1992. He also appeared on a klezmer album (Don Byron Plays the Music of Mickey Katz, 1993) and other recordings with modern jazz musicians Don Byron and Dave Douglas, among many others.
more...Willie Jones III (born June 8, 1968 in Los Angeles, California) is a jazz drummer. He has played, toured, and recorded with Horace Silver, Roy Hargrove, Hank Jones, Cedar Walton, and Herbie Hancock. He played on Arturo Sandoval‘s Grammy-winning album Hot House (1998).
Jones’ father, also named Willie Jones, was a pianist, composer and arranger, who moved to Los Angeles from Jacksonville in 1961. By the time Jones was born, his father “was gigging locally and working as a vocal coach for entertainers, including Ann-Margret.” Willie Jones III was born on June 8, 1968, in Los Angeles. Jones reported that he wanted to be a jazz musician from the age of seven.
more...Robert Schumann; 8 June 1810 – 29 July 1856) was a German composer, pianist, and influential music critic. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest composers of the Romantic era. Schumann left the study of law, intending to pursue a career as a virtuosopianist. His teacher, Friedrich Wieck, a German pianist, had assured him that he could become the finest pianist in Europe, but a hand injury ended this dream. Schumann then focused his musical energies on composing.
In 1840, Schumann married Clara Wieck, after a long and acrimonious legal battle with her father, Friedrich, who opposed the marriage. A lifelong partnership in music began, as Clara herself was an established pianist and music prodigy. Clara and Robert also maintained a close relationship with German composer Johannes Brahms.
Until 1840, Schumann wrote exclusively for the piano. Later, he composed piano and orchestral works, and many Lieder (songs for voice and piano). He composed four symphonies, one opera, and other orchestral, choral, and chamber works. His best-known works include Carnaval, Symphonic Studies, Kinderszenen, Kreisleriana, and the Fantasie in C. Schumann was known for infusing his music with characters through motifs, as well as references to works of literature. These characters bled into his editorial writing in the Neue Zeitschrift für Musik (New Journal for Music), a Leipzig-based publication that he co-founded.
Schumann had a mental disorder that first manifested in 1833 as a severe melancholic depressive episode—which recurred several times alternating with phases of “exaltation” and increasingly also delusional ideas of being poisoned or threatened with metallic items. What is now thought to have been a combination of bipolar disorder and perhaps mercury poisoning led to “manic” and “depressive” periods in Schumann’s compositional productivity. After a suicide attempt in 1854, Schumann was admitted at his own request to a mental asylum in Endenich (now in Bonn). Diagnosed with psychotic melancholia, he died of pneumonia two years later at the age of 46, without recovering from his mental illness.
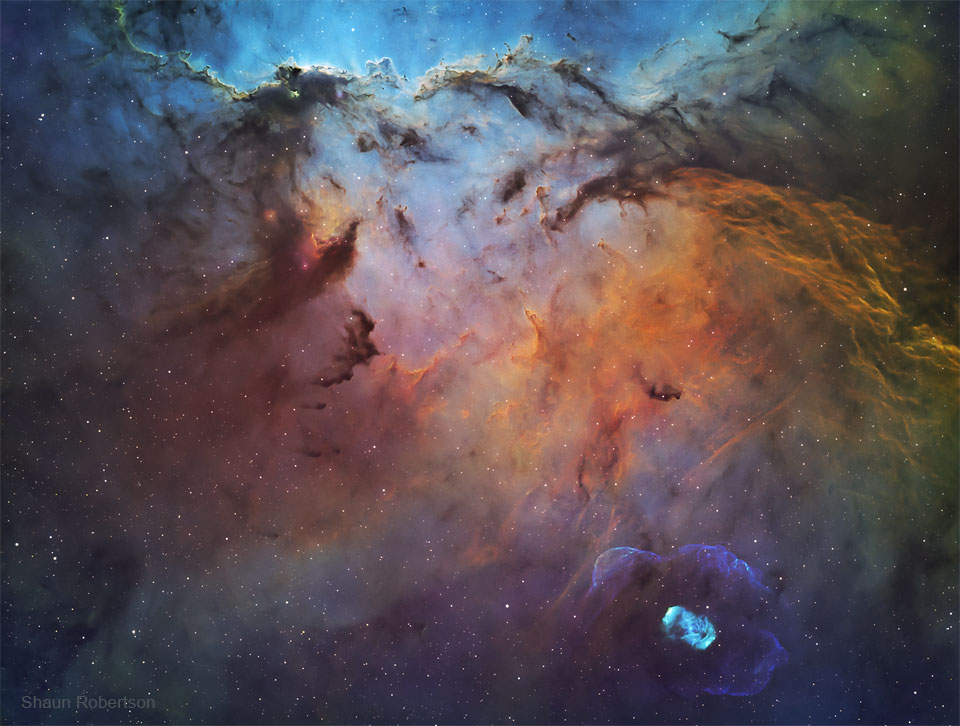
more...The emission nebula NGC 6188, home to the glowing clouds, is found about 4,000 light years away near the edge of a large molecular cloud unseen at visible wavelengths, in the southern constellation Ara (the Altar). Massive, young stars of the embedded Ara OB1 association were formed in that region only a few million years ago, sculpting the dark shapes and powering the nebular glow with stellar winds and intense ultraviolet radiation. The recent star formation itself was likely triggered by winds and supernova explosions, from previous generations of massive stars, that swept up and compressed the molecular gas. Joining NGC 6188 on this cosmic canvas, visible toward the lower right, is rare emission nebula NGC 6164, also created by one of the region’s massive O-type stars. Similar in appearance to many planetary nebulae, NGC 6164’s striking, symmetric gaseous shroud and faint halo surround its bright central star near the bottom edge. This impressively wide field of view spans over 2 degrees (four full Moons), corresponding to over 150 light years at the estimated distance of NGC 6188.

Jonathan Paul Clegg, OBE, OIS (7 June 1953 – 16 July 2019) was a South African musician, singer-songwriter, dancer, anthropologist and anti-apartheid activist, some of whose work was in musicology focused on the music of indigenous South African peoples. His band Juluka began as a duo with Sipho Mchunu, and was the first group in the South African apartheid-era with a white man and a black man. The pair performed and recorded, later with an expanded lineup.
In 1986 Clegg founded the band Savuka, and also recorded as a solo act, occasionally reuniting with his earlier band partners. Sometimes called Le Zoulou Blanc (French: [lə zulu blɑ̃], for “The White Zulu“), he was an important figure in South African popular music and a prominent white figure in the resistance to apartheid, becoming for a period the subject of investigation by the security branch of the South African Police. His songs mixed English with Zulu lyrics, and also combined idioms of traditional African music with those of modern Western styles.
more...Harold Floyd “Tina” Brooks (June 7, 1932 – August 13, 1974) was an American jazz tenor saxophonist and composer best remembered for his work in the hard bop style.
Harold Floyd Brooks was born in Fayetteville, North Carolina, and was the brother of David “Bubba” Brooks. The nickname “Tina”, pronounced Teena, was a variation of “Teeny”, a childhood moniker. His favourite tune was “My Devotion”. He studied harmony and theory with Herbert Bourne.
Initially, he studied the C-melody saxophone, which he began playing shortly after he moved to New York with his family in 1944. Brooks’ first professional work came in 1951 with rhythm and blues pianist Sonny Thompson, and in 1955 Brooks played with vibraphonist Lionel Hampton.Brooks also received less formal guidance from trumpeter and composer “Little” Benny Harris, who led the saxophonist to his first recording as a leader. Harris recommended Brooks to Blue Note producer Alfred Lion in 1958. Brooks did not record after 1961. Plagued by heroin dependency, and gradually deteriorating health, he died of liver failure aged 42.
more...Talmage Holt Farlow (June 7, 1921 – July 25, 1998) was an American jazz guitarist. He was nicknamed “Octopus” because of how his large, quick hands spread over the fretboard. As Steve Rochinski notes, “Of all the guitarists to emerge in the first generation after Charlie Christian, Tal Farlow, more than any other, has been able to move beyond the rhythmic, melodic, and harmonic vocabulary associated with the early electric guitar master. Tal’s incredible speed, long, weaving lines, rhythmic excitement, highly developed harmonic sense, and enormous reach (both physical and musical) have enabled him to create a style that clearly stands apart from the rest.” Where guitarists of his day combined rhythmic chords with linear melodies, Farlow placed single notes together in clusters, varying between harmonically enriched tones. As music critic Stuart Nicholson put it, “In terms of guitar prowess, it was the equivalent of Roger Bannister breaking the four-minute mile.” Talmage Holt Farlow was born in Greensboro, North Carolina, United States. He taught himself how to play guitar, which he started when he was 22 years old. He learned chord melodies by playing a mandolin tuned like a ukulele. He said playing the ukulele was the reason he used the higher four strings on the guitar for the melody and chord structure, with the two bottom strings for bass counterpoint, which he played with his thumb. His only professional training was as an apprentice sign painter. He requested the night shift so he could listen to big band standards on the shop radio. He listened to Bix Beiderbecke, Louis Armstrong, and Eddie Lang. His career was influenced by hearing Charlie Christian playing electric guitar with the Benny Goodman band. He said he made his own electric guitar because he could not afford to purchase one.
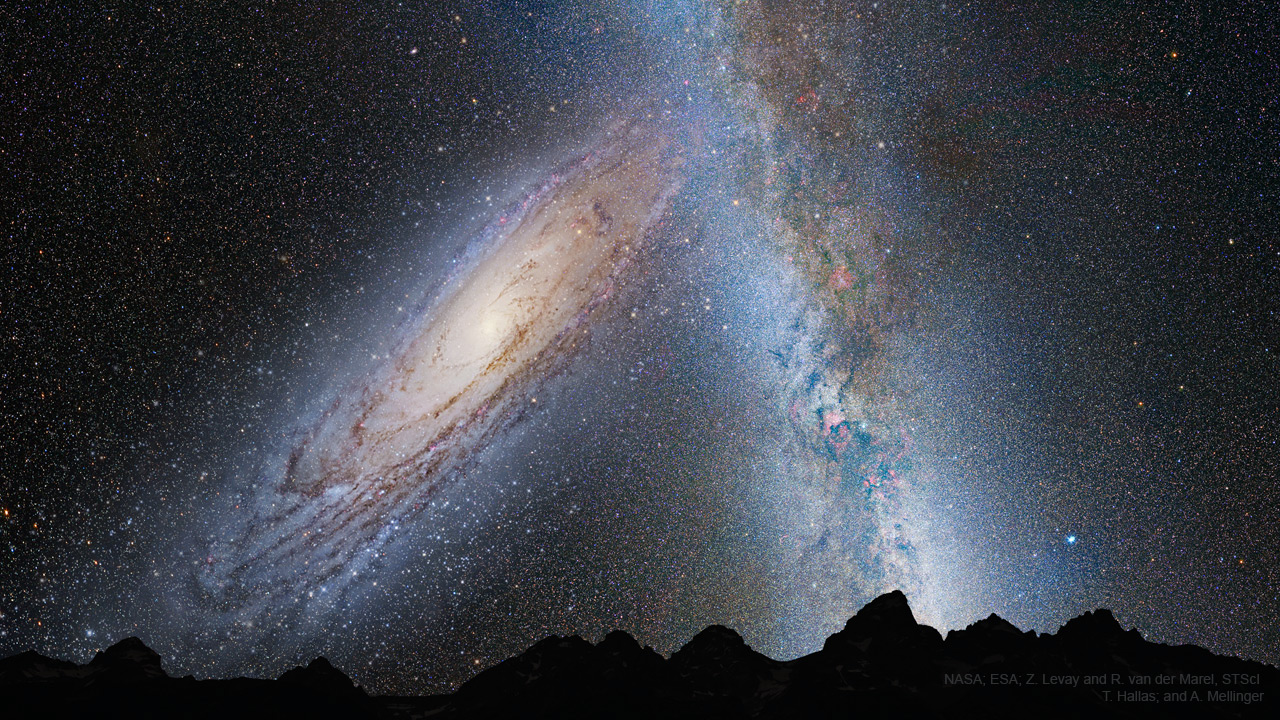
more...Will our Milky Way Galaxy collide one day with its larger neighbor, the Andromeda Galaxy? Most likely, yes. Careful plotting of slight displacements of M31’s stars relative to background galaxies on recent Hubble Space Telescope images indicate that the center of M31 could be on a direct collision course with the center of our home galaxy. Still, the errors in sideways velocity appear sufficiently large to admit a good chance that the central parts of the two galaxies will miss, slightly, but will become close enough for their outer halos to become gravitationally entangled. Once that happens, the two galaxies will become bound, dance around, and eventually merge to become one large elliptical galaxy — over the next few billion years. Pictured here is a combination of images depicting the sky of a world (Earth?) in the distant future when the outer parts of each galaxy begin to collide. The exact future of our Milky Way and the entire surrounding Local Group of Galaxies is likely to remain an active topic of research for years to come.

More Posts
- Cosmos NGC 5643
- Larry Fast
- Bob Cranshaw
- Guitar Slim
- Ray Nance
- World Music Refugees for Refugees
- Daily Roots Viceroys
- Little Shop of Horrors 2025
- Baba Hari Dass Pockets
- One Toke Over the Line Sweet Jesus
- Lennon God
- Alto Cumulous Clouds 2024
- Cosmos IC 2872/Gum 40
- Joan Armatrading
- Dan Hicks
- Jessie Hill
- Donald Byrd
- Junior Wells
- World Music Ruşan Filiztek
- Daily Roots Prince Jammy & Scientist