Blog
Sir Edward William Elgar, 1st Baronet OM GCVO (/ˈɛlɡɑːr/; 2 June 1857 – 23 February 1934) was an English composer, many of whose works have entered the British and international classical concert repertoire. Among his best-known compositions are orchestral works including the Enigma Variations, the Pomp and Circumstance Marches, concertos for violin and cello, and two symphonies. He also composed choral works, including The Dream of Gerontius, chamber music and songs. He was appointed Master of the King’s Musick in 1924.
Although Elgar is often regarded as a typically English composer, most of his musical influences were not from England but from continental Europe. He felt himself to be an outsider, not only musically, but socially. In musical circles dominated by academics, he was a self-taught composer; in Protestant Britain, his Roman Catholicism was regarded with suspicion in some quarters; and in the class-conscious society of Victorian and Edwardian Britain, he was acutely sensitive about his humble origins even after he achieved recognition. He nevertheless married the daughter of a senior British army officer. She inspired him both musically and socially, but he struggled to achieve success until his forties, when after a series of moderately successful works his Enigma Variations (1899) became immediately popular in Britain and overseas. He followed the Variations with a choral work, The Dream of Gerontius (1900), based on a Roman Catholic text that caused some disquiet in the Anglicanestablishment in Britain, but it became, and has remained, a core repertory work in Britain and elsewhere. His later full-length religious choral works were well received but have not entered the regular repertory.
In his fifties, Elgar composed a symphony and a violin concerto that were immensely successful. His second symphony and his cello concerto did not gain immediate public popularity and took many years to achieve a regular place in the concert repertory of British orchestras. Elgar’s music came, in his later years, to be seen as appealing chiefly to British audiences. His stock remained low for a generation after his death. It began to revive significantly in the 1960s, helped by new recordings of his works. Some of his works have, in recent years, been taken up again internationally, but the music continues to be played more in Britain than elsewhere.
Elgar has been described as the first composer to take the gramophone seriously. Between 1914 and 1925, he conducted a series of acoustic recordings of his works. The introduction of the moving-coil microphone in 1923 made far more accurate sound reproduction possible, and Elgar made new recordings of most of his major orchestral works and excerpts from The Dream of Gerontius.
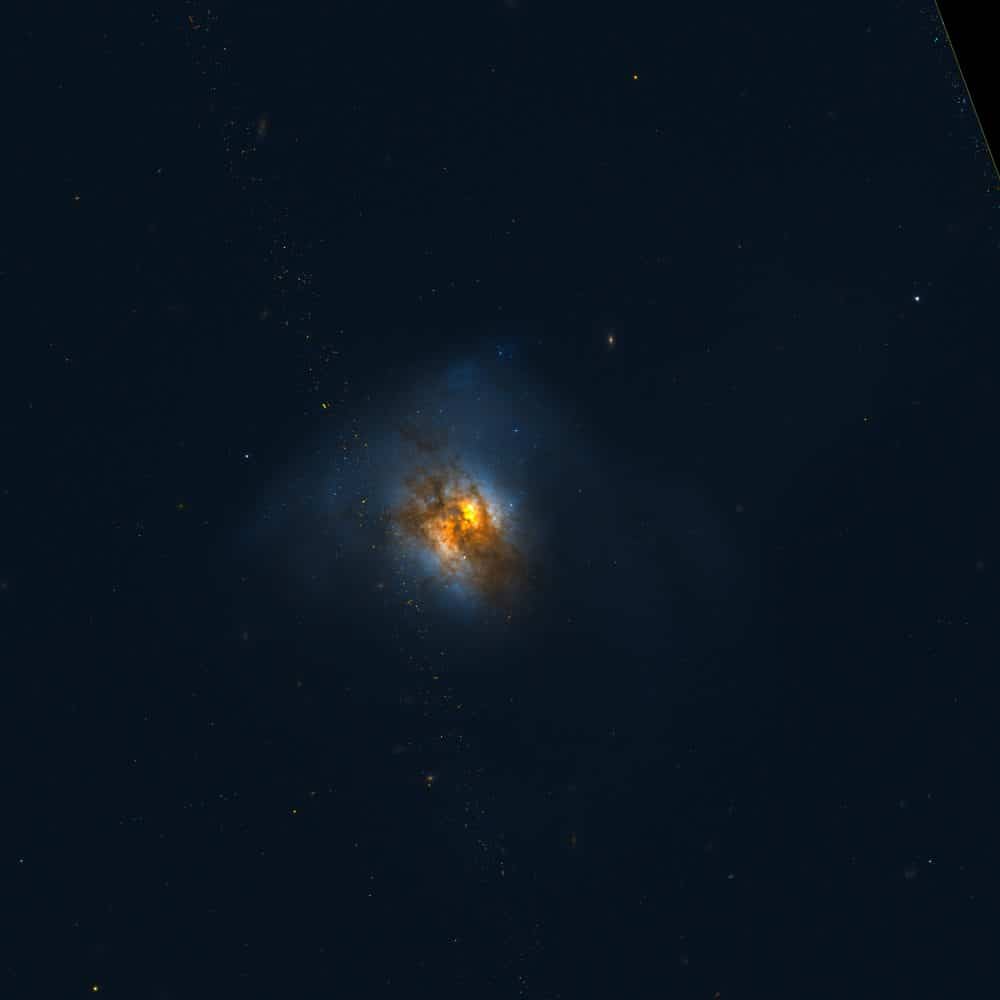
more...Arp 220 is the closest Ultraluminous Infrared Galaxy (ULIRG) to Earth. Its energy output was discovered by IRASto be dominated by the far-infrared part of the spectrum. It is often regarded as the prototypical ULIRG and has been the subject of much study as a result. Most of its energy output is thought to be the result of a massive burst of star formation, or starburst, probably triggered by the merging of two smaller galaxies. Recent (2002 and 1997) HST observations of Arp 220, taken in visible light with the ACS, and in infrared light with NICMOS, revealed more than 200 huge star clusters in the central part of the galaxy. The most massive of these clusters contains enough material to equal about 10 million suns. X-ray observations by the Chandra and XMM-Newton satellites have shown that Arp 220 probably includes an active galactic nucleus (AGN) at its core, which raises interesting questions about the link between galaxy mergers and AGN, since it is believed that galactic mergers often trigger starbursts, and may also give rise to the supermassive black holes that appear to power AGN.
more...
Herbie Lovelle (1 June 1924 – April 8, 2009) was an American drummer, who played jazz, R&B, rock, and folk. He was also a studio musician and an actor.
Lovelle’s uncle was the drummer Arthur Herbert. Lovelle began his career with the trumpeter, singer and band leader Hot Lips Page in the late 1940s, then played in the 1950s with the saxophonist Hal Singer, Johnny Moore‘s Three Blazers and the pianist Earl Hines. Through working for both Lucky Thompson and Jimmy Rushing of Count Basie’s Orchestra, he became house drummer at the Savoy Ballroom in New York City for much of the 1950s. He toured with the tenor saxophonist Arnett Cobb and the pianist Teddy Wilson in 1954. In 1959 he contributed to the pianist Paul Curry’s album Paul Curry Presents the Friends of Fats, released on the Golden Crest label.
In the early years of television, he performed with the King Guion Orchestra on the Jerry Lester Show and the Ed Sullivan Show. In 1966, he was the lead drummer for the Sammy Davis, Jr. TV show.
Lovelle began playing more R&B in the 1950s and worked as a studio musician, often with Sam Taylor. He played on albums by Bob Dylan (The Freewheelin’ Bob Dylan), Pearls Before Swine, Eric Andersen, David Blue, John Denver, Tom Rush, B. B. King, John Martyn (Stormbringer!), the Strangeloves, the McCoys, and the Monkees. He continued working as a studio musician well into the 1980s.
more...Nelson Smock Riddle Jr. (June 1, 1921 – October 6, 1985 Oradell, NJ) was an American arranger, composer, bandleader and orchestrator whose career stretched from the late 1940s to the mid-1980s. His work for Capitol Records kept such vocalists as Frank Sinatra, Ella Fitzgerald, Nat King Cole, Judy Garland, Dean Martin, Peggy Lee, Johnny Mathis, Rosemary Clooney and Keely Smith household names. He found commercial and critical success again in the 1980s with a trio of Platinum albums with Linda Ronstadt. His orchestrations earned an Academy Award and three Grammy Awards.
more...Lafayette Leake (June 1, 1919 – August 14, 1990) was a blues and jazz pianist, organist, vocalist and composer who played for Chess Records as a session musician, and as a member of the Big Three Trio, during the formative years of Chicago blues. He played piano on many of Chuck Berry‘s recordings. Leake was born in Winona, Missouri, in 1919. Information about his early years is sparse, but in the early 1950s he joined the Big Three Trio (replacing Leonard Caston) and began his association with Chess Records, where he worked closely with bassist, producer, and songwriter Willie Dixon.
Leake played piano on One Dozen Berrys, Chuck Berry’s second album, released in 1958 by Chess. He was then on Chuck Berry Is on Top; Leake (not Berry’s longtime bandmate Johnnie Johnson) played the prominent piano on the classic original rendition of “Johnny B. Goode“, as well as “Rock and Roll Music“. Leake played on numerous other Chess sessions from the ’50s through the ’70s, backing many of the Chess greats, including Sonny Boy Williamson, Otis Rush, Junior Wells, and Little Walter. Leake gave Chicago blues musician Harmonica Hinds his first harmonica lesson on the street in Toronto, Ontario.
During the 1960s Willie Dixon formed the Chicago Blues All-Stars, with Leake as resident pianist. Leake toured and recorded with this group until the mid-1970s. After that he did little recording or touring, although he appeared with Chuck Berry at the Chicago Blues Festival in 1986 and recorded “Hidden Charms” with Willie Dixon in 1988.
more...Local harmonica legend departs planet Earth.
Tony Glover
Born: October 7, 1939, Minneapolis, MN
Died: May 29, 2019
I didn’t know Tony well but he was always a pleasure and kind guy. Very supportive of other musicians like myself.
Have a great new adventure Tony.
https://www.mprnews.org/story/2019/05/30/minnesota-music-legend-tony-little-sun-glover-dies-at-79
more...Stars are forming in Lynds Dark Nebula (LDN) 1251. About 1,000 light-years away and drifting above the plane of our Milky Way galaxy, the dusty molecular cloud is part of a complex of dark nebulae mapped toward the Cepheus flare region. Across the spectrum, astronomical explorations of the obscuring interstellar clouds reveal energetic shocks and outflows associated with newborn stars, including the telltale reddish glow from scattered Herbig-Haro objects seen in this sharp image. Distant background galaxies also lurk on the scene, visually buried behind the dusty expanse. The deep telescopic field of view imaged with broadband filters spans about two full moons on the sky, or 17 light-years at the estimated distance of LDN 1251.
more...John Henry Bonham (31 May 1948 – 25 September 1980) was an English musician and songwriter, best known as the drummer for the British rock band Led Zeppelin. Esteemed for his speed, power, fast bass drumming, distinctive sound, and “feel” for the groove, he is regarded by many as the greatest and most influential rock drummer in history. In 2016, Rolling Stone magazine ranked him number one in their list of the “100 Greatest Drummers of All Time”. John Henry Bonham was born on 31 May 1948, in Redditch, Worcestershire, England, to Joan and Jack Bonham. He began learning to play drums at five, making a kit of containers and coffee tins, imitating his idols Max Roach, Gene Krupa and Buddy Rich. His mother gave him a snare drum when he was 10. He received his first drum kit from his father at age 15, a Premier Percussion set. Bonham never took formal drum lessons, though as a teen he had advice from other Redditch drummers. Between 1962 and 1963, still at school, Bonham joined the Blue Star Trio, and Gerry Levene & the Avengers.
Bonham attended Lodge Farm Secondary Modern School, where his headmaster wrote in his report that “He will either end up a dustman or a millionaire.” After leaving school in 1964, he worked for his father as an apprentice carpenter between drumming for local bands. In 1964, Bonham joined his first semi-professional band, Terry Webb and the Spiders, and met his future wife Pat Phillips around the same time. He played in other Birminghambands such as The Nicky James Movement and The Senators, who made a single, “She’s a Mod“, in 1964. Bonham took up drumming full-time. Two years later, he joined A Way of Life, but the band folded. Needing a regular income, he joined a blues group called Crawling King Snakes, whose lead singer was Robert Plant.
In 1967, A Way of Life asked Bonham to return to the group, and he agreed, while keeping in touch with Plant. Plant formed Band of Joy and chose Bonham as the drummer. The band recorded demos but no album. In 1968, American singer Tim Rose toured Britain and asked Band of Joy to open his concerts. When Rose returned months later, Bonham was invited by the singer to drum for Rose’s band, which gave him a regular income. After the breakup of the The Yardbirds in July of 1968, guitarist Jimmy Page formed another band and recruited Plant, who in turn suggested Bonham. Page’s choices for drummer included Procol Harum‘s B.J. Wilson and Paul Francis. However, on seeing Bonham drum for Tim Rose at a club in Hampstead, north London, in July 1968, Page and manager Peter Grant were convinced he was perfect for the project, first known as the New Yardbirds and later as Led Zeppelin. Bonham was reluctant. Plant sent eight telegrams to Bonham’s pub, the “Three Men in a Boat”, in Bloxwich, which were followed by 40 telegrams from Grant. Bonham was also receiving offers from Joe Cocker and Chris Farlowe but he accepted Grant’s offer. He recalled, “I decided I liked their music better than Cocker’s or Farlowe’s.
more...Louis Hayes (born May 31, 1937) is an American jazz drummer. His father played drums and piano and his mother played the piano. Hayes refers to the early influence of hearing jazz, especially hearing big bandson the radio. His main influence was Philly Joe Jones and he was mentored by Jo Jones. His three main associations were with Horace Silver‘s Quintet (1956–59), the Cannonball Adderley Quintet (1959–65), and the Oscar Peterson Trio (1965–67). Hayes often joined Sam Jones, both with Adderley and Peterson, and in freelance settings.
When he was a teenager, he led a band in Detroit clubs before he was 16. He worked with Yusef Lateef and Curtis Fuller from 1955 to 1956. He moved to New York in August 1956 to replace Art Taylor in the Horace Silver Quintet and in 1959 joined the Cannonball Adderley Quintet, with which he remained until mid-1965, when he succeeded Ed Thigpen in the Oscar Peterson Trio. He left Peterson in 1967, and formed a series of groups, which he led alone or with others; among his sidemen were Freddie Hubbard, Joe Henderson, Kenny Barron, and James Spaulding. He returned to Peterson in 1971.
more...Albert “Tootie” Heath (born May 31, 1935) is an American jazz hard bop drummer, the brother of tenor saxophonist Jimmy Heath and the double-bassist Percy Heath.
He first recorded in 1957 with John Coltrane. From 1958 to 1974 he worked with, among others, J. J. Johnson, Wes Montgomery, Art Farmer and Benny Golson‘s Jazztet, Cedar Walton, Bobby Timmons, Kenny Drew, Sonny Rollins, Dexter Gordon, Johnny Griffin, Herbie Hancock, Friedrich Gulda, Nina Simone, and Yusef Lateef. In 1975, he, Jimmy and Percy formed the Heath Brothers. He remained with the group until 1978, then left to freelance. He has recorded extensively throughout his career.
Among his many workshop and classroom teaching assignments, Tootie Heath is a regular instructor at the Stanford Jazz Workshop.
Tootie Heath is now the producer and leader of The Whole Drum Truth, a jazz drum ensemble featuring Ben Riley, Ed Thigpen, Jackie Williams, Billy Hart, Charlie Persip, Leroy Williams and Louis Hayes.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lLIpEO27APM
more...Flamenco Fridays featuring Tientos y Tangos
Tientos is a flamenco Andalusian palo which has a rhythm consisting of 4 beats. It is in the same family as the Tangos, but slower and with different topics, lyrics and mood. Every Tientos becomes a Tangos at the end of the song/dance.[1] Traditionally, cantaor El Marrurro (1848 -1906) has been considered one of the creators of this style. Enrique el Mellizo gave it the modern form by which we know it today. Other famous cantaores who interpreted this style were Antonio Chacón and Pastora Pavón.
Like many Cante Jondo, traditional Tientos lyrics (letras) tend to be pathetic, sentimental, and speak about the lack of love, disillusionment and revenge. Dancers strive to capture this mood in their solos. It can be danced by a man or a woman.
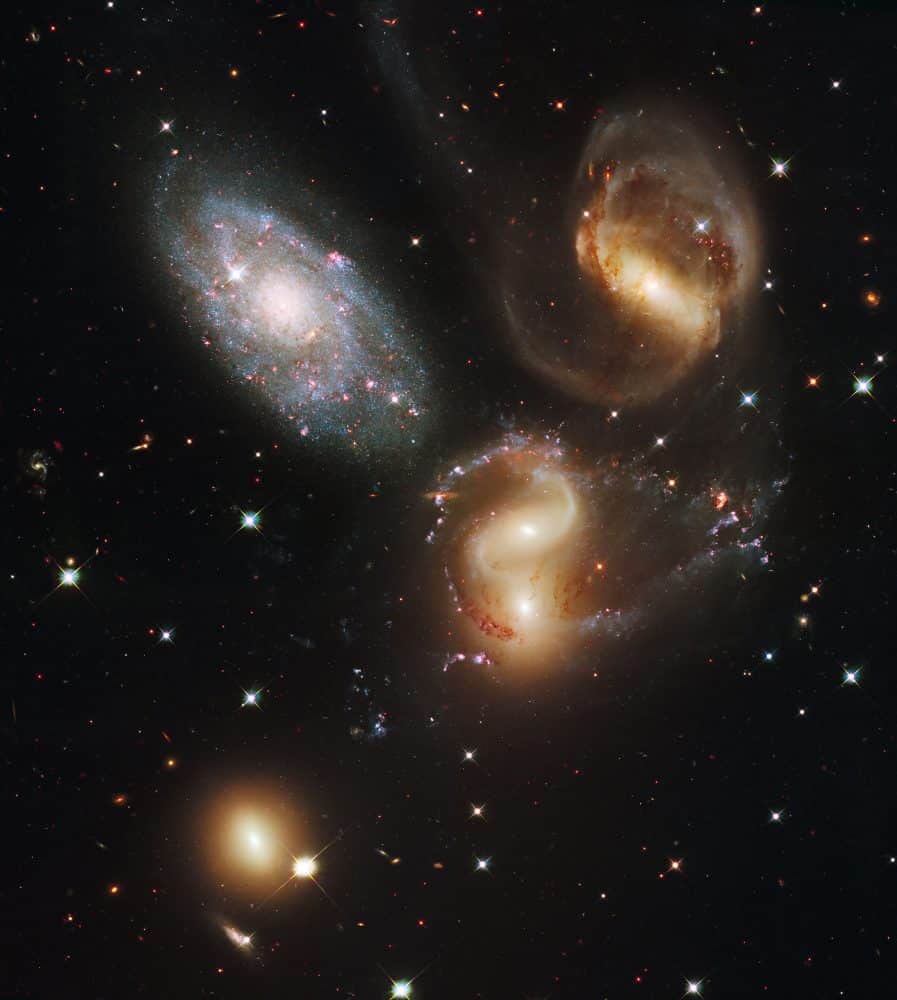
more...Stephan’s Quintet is a visual grouping of five galaxies of which four form the first compact galaxy group ever discovered. The group, visible in the constellation Pegasus, was discovered by Édouard Stephan in 1877 at the Marseille Observatory. The group is the most studied of all the compact galaxy groups. The brightest member of the visual grouping is NGC 7320 that is shown to have extensive H II regions, identified as red blobs, where active star formation is occurring.
Four of the five galaxies in Stephan’s Quintet form a physical association, Hickson Compact Group 92, and will likely merge with each other. Radio observations in the early 1970s revealed a mysterious filament of emission which lies in inter-galactic space between the galaxies in the group. This same region is also detected in the faint glow of ionized atomic hydrogen seen in the visible part of the spectrum as a green arc.
Two space telescopes have recently provided new insight into the nature of the filament, which is now believed to be a giant intergalactic shock-wave (similar to a sonic boom but traveling in intergalactic gas rather than air) caused by one galaxy (NGC 7318B) falling into the center of the group at several millions of kilometers per hour.
more...5-30-62
Central to Darrell Grant’s music is a sense of purpose, agency, and connection to community.
Through eight albums as a bandleader, numerous recordings as a sideman, a growing body of compositions, and two decades of service as an educator and leader in the arts, Grant’s multi-faceted creative projects and innovative initiatives reflect a belief in the extraordinary power of art to communicate, inspire, provoke, inform, and move others to transform society and themselves.
“Darrell Grant is a musician worthy of some serious listening. He is a very fine pianist and composer.”
Speaking to Nat Hentoff for the liner notes to his debut CD Black Art, Grant told the renowned jazz critic that “the longer I play, the clearer it becomes that, at least for me, the goal is to give voice to the meanings behind the music. I have a deep desire to reach people, to communicate something of the things that I am finding to be true, with humor, with love, with silence, with swing, and with passion.” Telling those truths has been the driving force in Darrell Grant’s musical career.
DARRELL GRANT was introduced to international audiences in 1988 as the pianist with the legendary vocalist Betty Carter. He has performed and recorded with such notable musicians as Branford Marsalis, David Sanborn, Esperanza Spalding, John Clayton, Nicholas Payton, James Moody, Kevin Eubanks, Lenny White, Jane Bunnett, Somi, Tom Harrell, Jack Dejohnette, Terence Blanchard, and Art Farmer. He has performed extensively as a bandleader and solo artist throughout the U.S., Canada, and Europe in venues ranging from clubs to major jazz festivals, and been featured on Marian McPartland’s “Piano Jazz” on National Public Radio.
Born May 30, 1962 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, Grant grew up in Denver, Colorado in a musical family. He began classical lessons at age seven and quickly received honors for his prowess on piano. He discovered jazz in school band programs and played family concerts and talent shows. At 15, he joined the Pearl Street Jazz Band, a precocious ensemble of teenaged musicians playing traditional New Orleans-style jazz. The group held down regular professional gigs, recorded two albums, and appeared at regional jazz festivals.
Harold Winston “Harry” Beckett (30 May 1935 – 22 July 2010) was a British trumpeter and flugelhorn player of Barbadian origin.
Born in Bridgetown, Saint Michael, Barbados, Harry Beckett learned to play music in a Salvation Army band. A resident in the UK since 1954, he had an international reputation. In 1961, he played with Charles Mingus in the film All Night Long. In the 1960s he worked and recorded within the band of bass player and composer Graham Collier. Beginning in 1970, he led groups of his own, recording for Philips, RCA and Ogun Recordsamong other labels.
He was a key figure of important groups in the British free jazz/improvised music scene, including Ian Carr‘s Nucleus, the Brotherhood of Breath and The Dedication Orchestra, London Jazz Composers Orchestra, London Improvisers Orchestra, John Surman‘s Octet, Django Bates, Ronnie Scott‘s Quintet, Kathy Stobart, Charlie Watts, Stan Tracey‘s Big Band and Octet; Elton Dean‘s Ninesense. He has also recorded with Keef Hartley, Jah Wobble, David Sylvian and worked with David Murray. He toured abroad with Johnny Dyani, Chris McGregor, Keith Tippett, John Tchicai, Joachim Kühn, Dudu Pukwana‘s Zila, George Gruntz‘s Bands, Belgian quintet The Wrong Object, Pierre Dørge‘s New Jungle Band and Annie Whitehead‘s Robert Wyatt project, Soupsongs, which also featured Phil Manzanera and Julie Tippetts, among other jazz and rock luminaries.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xgio9T2K5LM
more...Armando Peraza (May 30, 1924 – April 14, 2014) was a Latin jazz percussionist and a member of the rock band Santana. Peraza played congas, bongos, and timbales. Born in Lawton Batista, Havana, Cuba in 1924 (although the birth year is uncertain),he was orphaned by age 7 and lived on the streets. When he was twelve, he supported himself by selling vegetables, coaching boxing, playing semi-pro baseball, and becoming a loan shark. His music career began at seventeen when he heard at a baseball game that bandleader Alberto Ruiz was looking for a conga player. Ruiz’s brother was on the same baseball team as Peraza. Despite the absence of experience in music, he practiced and won the audition.
In 1954, while in San Francisco with pianist Dave Brubeck, Peraza met Cal Tjader, Brubeck’s drummer at the time. Jazz critic Leonard Feather recommended Peraza to Fantasy Records with Tjader to record an Afro-Cuban album. The result was Ritmo Caliente, which combined Afro-Cuban rhythms with a jazz sensibility. He was introduced to British pianist George Shearing by bassist Al McKibbon. He spent the next twelve years with Shearing, a collaboration that put Peraza at the front of Afro-Cuban music. He emerged as a composer, writing and recording twenty-one songs for Shearing, such as “Mambo in Chimes”, “Mambo in Miami”, “Ritmo Africano”, “Armando’s Hideaway”, “This is Africa”, and “Estampa Cubana”. These recordings were during the mambo craze in the U.S. and the world. Peraza’s technique and power as a hand drummer became a feature of Shearing’s performances.
He toured all over the world with Shearing, but it was in America that he experienced persistent and institutionalized racism. In Miami during dates with Shearing and Peggy Lee in 1959, Peraza and black members of the band were prohibited from staying at the same hotel as the white musicians. Shearing and Lee resolved the situation by threatening to quit the performance unless Peraza and the others were allowed to stay at their hotel. Shearing’s was one of the first racially integrated jazz groups. While with Shearing, Peraza had opportunity to play with the classical symphonies of Boston, Philadelphia, New York, and Oklahoma City.
In 1959, Peraza joined Mongo Santamaría for the Mongo album with conga drummer Francisco Aguabella, another contemporary and friend of Peraza. “Afro-Blue” became a jazz standard after John Coltrane recorded it. The album combined with Yambo in the compilation Afro Roots in 1972.
More Posts
- Cees See
- Elizabeth Cotten
- World Music with Terakaft
- Daily Roots with Sofie Stevenson
- The Dragon Who Liked to Spit Fire 2022
- Rocky Horror Picture Show 2022
- Cosmos M81
- Tito Rodriguez
- John Mclaughlin
- Frank Wess
- World Music with Riya Volkova
- Daily Roots with the Shades
- Cosmos NGC 105
- James Carter
- John Jenkins
- Herbie Nichols
- World Music with Benedito Luiz Amauro Lumumba
- Daily Roots with Skin, Flesh & Bones Feat. Ranchie
- Cosmos M31
- Trombone Shorty