Blog
Niels-Henning Ørsted Pedersen (Danish pronunciation: [nelsˈhɛneŋ ˈɶɐ̯sdəð ˈpɛðɐsn̩], 27 May 1946 – 19 April 2005), often known as NHØP, was a Danish jazz upright bassist known for his technique and musical approach.
Ørsted Pedersen was born in Osted, near Roskilde, on the Danish island of Zealand, the son of a church organist. As a child, Ørsted Pedersen played piano, but from the age of 13, he started learning to play upright bass and at the age of 14, while studying, he began his professional jazz career in Denmark with his first band, Jazzkvintet 60 (Danish for ‘Jazz Quintet 60’). By the age of fifteen, he had the ability to accompany leading musicians at nightclubs, working regularly at Copenhagen’s Jazzhus Montmartre, after his debut there on New Year’s Eve 1961, when he was only 15. When seventeen, he had already turned down an offer to join the Count Basie orchestra, mainly because he was too young to get legal permission to live and work as a musician in the United States.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n-F-agyY3dc
more...Ramsey Emmanuel Lewis Jr. (born May 27, 1935) is an American jazz composer, pianist and radio personality. Ramsey Lewis has recorded over 80 albums and has received seven gold records and three Grammy Awards so far in his career.
Ramsey Lewis was born in Chicago, Illinois, to Ramsey Lewis Sr. and Pauline Lewis. Lewis began taking piano lessons at the age of four. At 15 he joined his first jazz band, the Cleffs. The seven-piece group provided Lewis his first involvement with jazz; he would later join Cleffs drummer Isaac “Red” Holt and bassist Eldee Young to form the Ramsey Lewis Trio.
The trio started as primarily a jazz unit and released their first album, Ramsey Lewis and the Gentlemen of Swing, in 1956. Following their 1965 hit “The In Crowd” (the single reached No. 5 on the pop charts, and the album No. 2) they concentrated more on pop material. Young and Holt left in 1966 to form Young-Holt Unlimited and were replaced by Cleveland Eaton and Maurice White. White left to form Earth, Wind & Fire and was replaced by Morris Jennings in 1970. Later, Frankie Donaldson and Bill Dickens replaced Jennings and Eaton; Felton Crews also appeared on many 1980’s releases.
By 1966, Lewis was one of the nation’s most successful jazz pianists, topping the charts with “The In Crowd“, “Hang On Sloopy“, and “Wade in the Water“. All three singles each sold over one million copies, and were awarded gold discs. Many of his recordings attracted a large non-jazz audience. In the 1970s, Lewis often played electric piano, although by later in the decade he was sticking to acoustic and using an additional keyboardist in his groups.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9scvvfCsvaA
more...
Clifford Everett “Bud” Shank, Jr. (May 27, 1926 – April 2, 2009) was an American alto saxophonist and flautist. He rose to prominence in the early 1950s playing lead alto and flute in Stan Kenton‘s Innovations in Modern Music Orchestra and throughout the decade worked in various small jazz combos. He spent the 1960s as a first-call studio musician in Hollywood. In the 1970s and 1980s, he performed regularly with the L. A. Four. Shank ultimately abandoned the flute to focus exclusively on playing jazz on the alto saxophone. He also recorded on tenor and baritone sax. He is also well known for the alto flute solo on the song “California Dreamin’” recorded by The Mamas & the Papas in 1965.
Bud Shank was born in Dayton, Ohio. He began with clarinet in Vandalia, Ohio, but had switched to saxophone before attending the University of North Carolina. While at UNC, Shank was initiated into the Pi Kappa Alpha Fraternity. In 1946 he worked with Charlie Barnet before moving on to Kenton and the West coast jazz scene.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5tzXHm-Fn4I
more...Super Uba, a skilled vocalist from Santiago in the Dominican Republic, performs music that represents the island’s diverse musical culture. The band combines modern bachata guitar styles with classic son, bolero and merengue rhythms.
Ubaldo Cabrera was born to a farming family in the rural town of Guateque de la Isabela, near Puerto Plata. At age 19 he was drawn by his love for music to the city of Santiago, where he lived with an uncle who taught him to sing and play the guitar. Santiago is the heart of the Cibao, the northern region of the Dominican Republic which is the cradle of merengue. When Uba talks about the city as it was in the 1970s, he describes a culture where music thrived. “At that time, someone could go to an open air bar, or to a night club, and start playing, and if he was good, crowds would gather to listen to him.”
more...https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X5UZChH_OTI
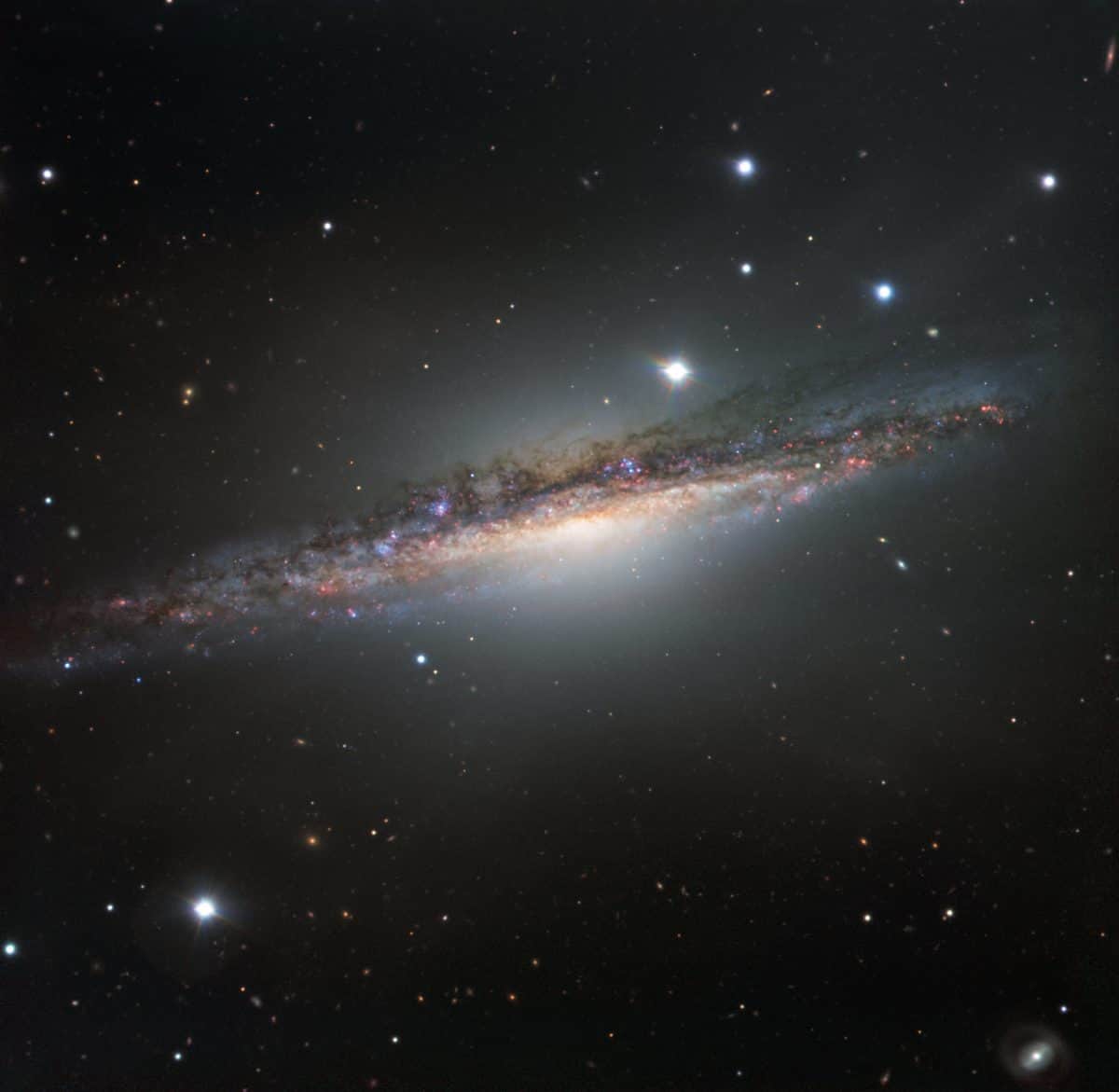
more...This colourful image from ESO’s Very Large Telescope shows NGC 1055 in the constellation of Cetus (The Sea Monster). This large galaxy is thought to be up to 15 percent larger in diameter than the Milky Way. NGC 1055 appears to lack the whirling arms characteristic of a spiral, as it is seen edge-on. However, it displays odd twists in its structure that were probably caused by an interaction with a large neighbouring galaxy.
NGC 1055 is an edge-on spiral galaxy located in the constellation Cetus that has a prominent nuclear bulge crossed by a wide, knotty, dark lane of dust and gas. The spiral arm structure appears to be elevated above the galaxy’s plane and obscures the upper half of the bulge. Discovered on December 19, 1783 by William Herschel from his home in Slough England.
It is a binary system together with the bright spiral galaxy M77 (NGC 1068). These two are the largest galaxies of a small galaxy group that also includes NGC 1073, and five other small irregular galaxies.
NGC 1087, NGC 1090, and NGC 1094 appear close, but they simply appear in the field of view and are background galaxies.
Based on the published red shift, (Hubble Constant of 62 km/s per Mpc) a rough distance estimate for NGC 1055 is 52 million light-years, with a diameter of about 115,800 light-years. The separation between NGC 1055 and M77 is about 442,000 light-years.
NGC 1055 is a bright infrared and radio source, particularly in the wavelength for warm carbon monoxide. Astronomers believe that this results from unusually active star formation. It most likely has a transitional nucleus, however, there is a small chance that it could be a LINER.
more...
Stephanie Lynn Nicks (born May 26, 1948) is an American singer-songwriter.
Nicks is best known for her work as a songwriter and vocalist with Fleetwood Mac, and also for her chart-topping solo career. She is known for her distinctive voice, mystical stage persona and poetic, symbolic lyrics. Collectively, her work both as a member of Fleetwood Mac and as a solo artist has produced over 40 top-50 hits and sold over 140 million records, making her one of the best selling music acts of all time with Fleetwood Mac.
Nicks has been named one of the 100 Greatest Songwriters of All Time, and as one of the world’s top “100 Greatest Singers of All Time” by Rolling Stone. As a member of Fleetwood Mac, she was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1998. She has garnered eight Grammy Award nominations and two American Music Award nominations as a solo artist. She has won numerous awards with Fleetwood Mac, including a Grammy Award and five Grammy Award nominations.
Stephanie “Stevie” Nicks was born at Good Samaritan Hospital in Phoenix, Arizona, to Jess Nicks (July 2, 1925 – August 10, 2005), former president of Greyhound’s Armour-Dial, and Barbara Nicks (November 12, 1927 – December 29, 2011), a homemaker. Nicks’s grandfather, Aaron Jess “A.J.” Nicks, Sr. (May 18, 1892 – August 1, 1974), a struggling country music singer, taught Nicks to sing duets with him by the time she was four years old. Nicks’s mother was so protective that she kept her at home “more than most people” and during that time fostered in her daughter a love of fairy tales. The infant Stephanie could pronounce her own name only as “tee-dee,” which led to her nickname of “Stevie”. Her father’s frequent relocation as a food business executive had the family living in Phoenix, Albuquerque, El Paso, Salt Lake City, Los Angeles, and San Francisco during Nicks’s youth. With the Goya guitar that she received for her 16th birthday, Nicks wrote her first song, “I’ve Loved and I’ve Lost, and I’m Sad But Not Blue”. She spent her adolescence playing records constantly, and lived in her “own little musical world.
more...Mark Lavon “Levon” Helm (May 26, 1940 – April 19, 2012) was an American musician and actor who achieved fame as the drummer and one of the vocalists for The Band. Helm was known for his deeply soulful, country-accented voice, multi-instrumental ability, and creative drumming style, highlighted on many of the Band’s recordings, such as “The Weight“, “Up on Cripple Creek“, and “The Night They Drove Old Dixie Down“.
Helm also had a successful career as a film actor, appearing as Loretta Lynn‘s father in Coal Miner’s Daughter, as Chuck Yeager‘s friend and colleague Captain Jack Ridley in The Right Stuff, and as a Tennessee firearms expert in Shooter.
In 1998, Helm was diagnosed with throat cancer, which caused him to lose his singing voice. After treatment, his cancer eventually went into remission, and he gradually regained the use of his voice. His 2007 comeback album Dirt Farmer earned the Grammy Award for Best Traditional Folk Album in February 2008, and in November of that year, Rolling Stone magazine ranked him No. 91 in its list of 100 Greatest Singers of All Time. In 2010, Electric Dirt, his 2009 follow-up to Dirt Farmer, won the first Grammy Award for Best Americana Album, a category inaugurated in 2010. In 2011, his live album Ramble at the Ryman won the Grammy in the same category. On April 17, 2012, his wife and daughter announced on Helm’s website that he was “in the final stages of his battle with cancer” and thanked fans while requesting prayers. Two days later, Helm died at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City.
Born in Elaine, Arkansas, Helm grew up in Turkey Scratch, a hamlet of Marvell, Arkansas. His parents, Nell and Diamond Helm, were cotton farmers and great lovers of music. They encouraged their children to play and sing at a young age. Young Lavon (as he was christened) began playing the guitar at the age of eight and also played drums during his formative years. He saw Bill Monroe and His Blue Grass Boys at the age of six and decided then to become a musician.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RDnlU6rPfwY
more...Miles Dewey Davis III (May 26, 1926 – September 28, 1991) was an American jazz trumpeter, bandleader, and composer. He is among the most influential and acclaimed figures in the history of jazz and 20th century music. Davis adopted a variety of musical directions in his five-decade career which kept him at the forefront of a number of major stylistic developments in jazz.
Born and raised in Illinois, Davis left his studies at The Juilliard School in New York City and made his professional debut as a member of saxophonist Charlie Parker‘s bebop quintet from 1944 to 1948. Shortly after, he recorded the Birth of the Cool sessions for Capitol Records, which were instrumental to the development of cool jazz. In the early 1950s, Davis recorded some of the earliest hard bop music while on Prestige Records but did so haphazardly due to a heroin addiction. After a widely acclaimed comeback performance at the Newport Jazz Festival in 1955, he signed a long-term contract with Columbia Records and recorded the 1957 album ‘Round About Midnight. It was his first work with saxophonist John Coltrane and bassist Paul Chambers, key members of the sextet he led into the early 1960s. During this period, he alternated between orchestral jazz collaborations with arranger Gil Evans, such as the Spanish-influenced Sketches of Spain (1960), and band recordings, such as Milestones (1958) and Kind of Blue (1959). The latter recording remains one of the most popular jazz albums of all time, having sold over four million copies in the U.S.
Miles Dewey Davis III was born on May 26, 1926, to an affluent African-American family in Alton, Illinois, fifteen miles north of St. Louis. He had an older sister, Dorothy Mae (born 1925), and a younger brother, Vernon (born 1929). His mother, Cleota Mae Henry of Arkansas, was a music teacher and violinist, and his father, Miles Dewey Davis Jr., also of Arkansas, was a dentist. They owned a 200-acre estate near Pine Bluff, Arkansas with a profitable pig farm. In Pine Bluff, he and his siblings fished, hunted, and rode horses. In 1927, the family moved to East St. Louis, Illinois. They lived on the second floor of a commercial building behind a dental office in a predominantly white neighborhood. From 1932 to 1934, Davis attended John Robinson Elementary School, an all-black school, then Crispus Attucks, where he performed well in mathematics, music, and sports. At an early age he liked music, especially blues, big bands, and gospel.
more...Cindy Le Coeur is a recording artist, singer, and dancer from the Democratic Republic of the Congo. She is a member of the Congolese band Quartier Latin International, formed and led by musician Koffi Olomide
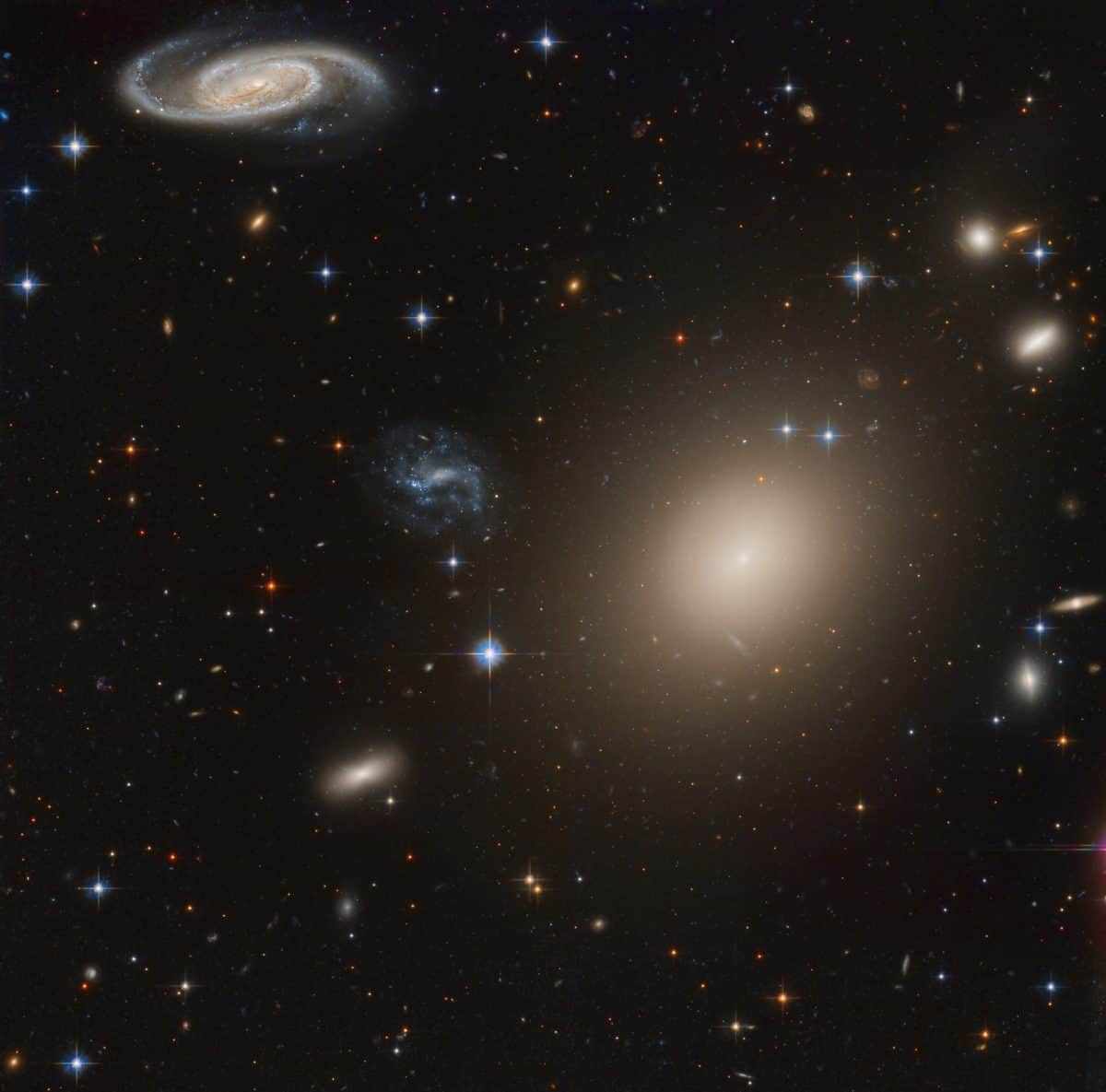
more...This stunning group of galaxies is far, far away, about 450 million light-years from planet Earth and cataloged as galaxy cluster Abell S0740. Dominated by the cluster’s large central elliptical galaxy (ESO 325-G004), this reprocessed Hubble Space Telescope view takes in a remarkable assortment of galaxy shapes and sizes with only a few spiky foreground stars scattered through the field. The giant elliptical galaxy (right of center) spans over 100,000 light years and contains about 100 billion stars, comparable in size to our own spiral Milky Way galaxy. The Hubble data can reveal a wealth of detail in even these distant galaxies, including arms and dust lanes, star clusters, ring structures, and gravitational lensing arcs.
more...Wallace Roney (born May 25, 1960, Philadelphia) is an American jazz (hard bop and post-bop) trumpeter.
Roney took lessons from Clark Terry and Dizzy Gillespie and studied with Miles Davis from 1985 until the latter’s death in 1991. Wallace credits Davis as having helped to challenge and shape his creative approach to life as well as being his music instructor, mentor, and friend; he was the only trumpet player Davis personally mentored.
Roney was born in Philadelphia and attended Howard University and Berklee College of Music in Boston, Massachusetts, after graduating from the Duke Ellington School of the Arts of the D. C. Public Schools, where he studied trumpet with Langston Fitzgerald of the Baltimore Symphony Orchestra. Found to have perfect pitch at the age of four, Wallace began his musical and trumpet studies at Philadelphia’s Settlement School of Music.
more...Jimmy Hamilton (May 25, 1917 – September 20, 1994) was an American jazz clarinetist, tenor saxophonist, arranger, composer, and music educator, best known for his twenty-five years with Duke Ellington.
Hamilton was born in Dillon, South Carolina, and grew up in Philadelphia. Having originally learned to play piano and brass instruments, in the 1930s he started playing the latter in local bands, before switching to clarinet and saxophone. In 1939 he played with Lucky Millinder, Jimmy Mundy, and Bill Doggett, going on to join the Teddy Wilson sextet in 1940. After two years with Wilson, he played with Eddie Heywood and Yank Porter.
In 1943, he replaced Barney Bigard in the Duke Ellington orchestra, and stayed with Ellington until 1968. His style was very different on his two instruments: on tenor saxophone he had an R&B sound, while on clarinet he was much more precise and technical. He wrote some of his own material in his time with Ellington.
more...Bill “Bojangles” Robinson (May 25, 1878 – November 25, 1949) was an American tap dancer and actor, the best known and most highly paid African-American entertainer in the first half of the twentieth century. His long career mirrored changes in American entertainment tastes and technology. He started in the age of minstrel shows and moved to vaudeville, Broadway, the recording industry, Hollywood, radio, and television. According to dance critic Marshall Stearns, “Robinson’s contribution to tap dance is exact and specific. He brought it up on its toes, dancing upright and swinging”, giving tap a “…hitherto-unknown lightness and presence.”His signature routine was the stair dance, in which Robinson would tap up and down a set of stairs in a rhythmically complex sequence of steps, a routine that he unsuccessfully attempted to patent. Robinson is also credited with having introduced a new word, copacetic, into popular culture, via his repeated use of it in vaudeville and radio appearances.
A popular figure in both the black and white entertainment worlds of his era, he is best known today for his dancing with Shirley Temple in a series of films during the 1930s, and for starring in the musical Stormy Weather (1943), loosely based on Robinson’s own life, and selected for preservation in the National Film Registry. Robinson used his popularity to challenge and overcome numerous racial barriers, including becoming the following:
- one of the first minstrel and vaudeville performers to appear without the use of blackface makeup
- one of the earliest African-American performers to go solo, overcoming vaudeville’s two colored rule
- a headliner in Broadway shows
- the first African American to appear in a Hollywood film in an interracial dance team (with Temple in The Little Colonel, 1935)
- the first African American to headline a mixed-race Broadway production
- Luther Robinson was born in Richmond, Virginia, and raised in its Jackson Ward neighborhood. His parents were Maxwell, a machine-shop worker, and Maria Robinson, a choir singer. His grandmother raised him after both parents died in 1884 when he was six years old—his father from chronic heart disease and his mother from natural causes. Details of Robinson’s early life are known only through legend, much of it perpetuated by Robinson himself. He claimed he was christened “Luther”—a name he did not like. He suggested to his younger brother Bill that they should exchange names. Eventually, the exchange between the names of both brothers was made. The brother subsequently adopted the name of “Percy” and under that name achieved recognition as a musician.
more...
World Music on Flamenco Fridays with Cantaora: María Ángeles Martínez Guitarra: Eduardo Rebollar
performing Alegrias.
Alegrías (Spanish pronunciation: [aleˈɣɾi.as]) is a flamenco palo or musical form, which has a rhythm consisting of 12 beats. It is similar to Soleares. Its beat emphasis is as follows: 1 2 [3] 4 5 [6] 7 [8]9 [10] 11 [12]. Alegrías originated in Cádiz. Alegrías belongs to the group of palos called Cantiñas and it is usually played in a lively rhythm (120-170 beats per minute). The livelier speeds are chosen for dancing, while quieter rhythms are preferred for the song alone.
One of the structurally strictest forms of flamenco, a traditional dance in alegrías must contain each of the following sections: a salida (entrance), paseo (walkaround), silencio (similar to an adagio in ballet), castellana (upbeat section) zapateado (Literally “a tap of the foot”) and bulerías. This structure though, is not followed when alegrías are sung as a standalone song (with no dancing). In that case, the stanzas are combined freely, sometimes together with other types of cantiñas.
Recommended listenings for this palo include most singers from Cádiz, like Chano Lobato, La Perla de Cádiz, Aurelio Sellé, but also general singers like Manolo Caracol or La Niña de los Peines.
Also, you can listen “Mar Amargo” from Camarón and “La Tarde es Caramelo” from Vicente Amigo.
It is one of the cante chico forms of flamenco. The word Alegrías literally means “joys.”
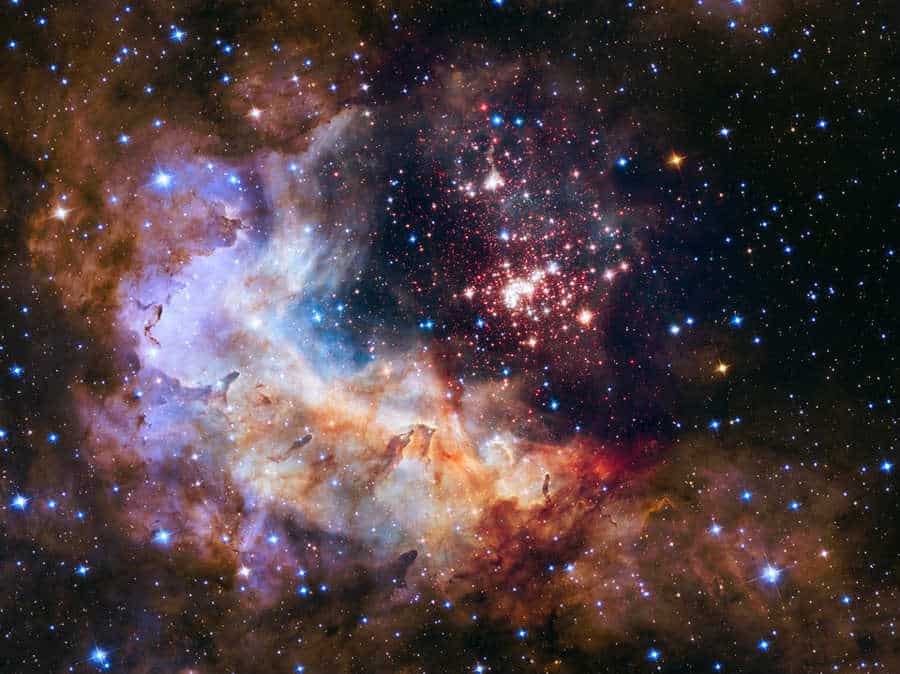
more...The Gum Nebula (Gum 12) is an emission nebula that extends across 40° in the southern constellations Vela and Puppis. It lies roughly 400 parsecsfrom the Earth. Hard to distinguish, it is believed to be the greatly expanded (and still expanding) remains of a supernova that took place about a million years ago. It contains the smaller and younger Vela Supernova Remnant, along with the Vela Pulsar.
It is named after its discoverer, the Australian astronomer Colin Stanley Gum (1924–1960). Gum had published his findings in 1955 in a work called A study of diffuse southern H-alpha nebulae (see Gum catalog).
Distance 1470 ly
more...Bob Dylan (born Robert Allen Zimmerman, May 24, 1941) is an American singer-songwriter, author, and painter who has been an influential figure in popular music and culture for more than five decades. Much of his most celebrated work dates from the 1960s, when he became a reluctant “voice of a generation” with songs such as “Blowin’ in the Wind” and “The Times They Are a-Changin’” that became anthems for the Civil Rights Movementand anti-war movement. In 1965, he controversially abandoned his early fan-base in the American folk music revival, recording a six-minute single, “Like a Rolling Stone“, which enlarged the scope of popular music.
Dylan’s lyrics incorporate a wide range of political, social, philosophical, and literary influences. They defied existing pop-music conventions and appealed to the burgeoning counterculture. Initially inspired by the performances of Little Richard and the songwriting of Woody Guthrie, Robert Johnson, and Hank Williams, Dylan has amplified and personalized musical genres. In his recording career, Dylan has explored many of the traditions in American song—from folk, blues, and country to gospel, and rock and roll, and from rockabilly to English, Scottish, and Irish folk music, embracing even jazz and the Great American Songbook. Dylan performs on guitar, keyboards, and harmonica. Backed by a changing lineup of musicians, he has toured steadily since the late 1980s on what has been dubbed “the Never Ending Tour“. His accomplishments as a recording artist and performer have been central to his career, but his songwriting is considered his greatest contribution.
Following his self-titled debut album in 1962, which mainly consisted of traditional folk songs, Dylan made his breakthrough as a songwriter with the release of the 1963 album The Freewheelin’ Bob Dylan, featuring “Blowin’ in the Wind” and the thematically complex composition “A Hard Rain’s a-Gonna Fall,” alongside several other enduring songs of the era. Dylan went on to release the politically charged The Times They Are a-Changin’ and the more lyrically abstract and introspective Another Side of Bob Dylan in 1964. In 1965 and 1966 Dylan encountered controversy when he adopted the use of electrically amplified rock instrumentation and in the space of 15 months recorded three of the most important and influential rock albums of the 1960s, Bringing It All Back Home, Highway 61 Revisited and Blonde on Blonde.
Bob Dylan was born Robert Allen Zimmerman (Hebrew name שבתאי זיסל בן אברהם [Shabtai Zisl ben Avraham]) in St. Mary’s Hospital on May 24, 1941, in Duluth, Minnesota, and raised in Hibbing, Minnesota, on the Mesabi Range west of Lake Superior. He has a younger brother, David. Dylan’s paternal grandparents, Zigman and Anna Zimmerman, emigrated from Odessa, in the Russian Empire (now Ukraine), to the United States following the anti-Semitic pogroms of 1905. His maternal grandparents, Ben and Florence Stone, were Lithuanian Jews who arrived in the United States in 1902.In his autobiography, Chronicles: Volume One, Dylan wrote that his paternal grandmother’s maiden name was Kirghiz and her family originated from the Kağızman district of Kars Province in northeastern Turkey.
more...Archie Shepp (born May 24, 1937) is an American jazz saxophonist.
Shepp was born in Fort Lauderdale, Florida, but raised in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He studied piano, clarinet, and alto saxophone before focusing on tenor saxophone. He occasionally plays soprano saxophone and piano. He studied drama at Goddard College from 1955 to 1959.
He played in a Latin jazz band for a short time before joining the band of avant-garde pianist Cecil Taylor. Shepp’s first recording under his own name, Archie Shepp – Bill Dixon Quartet, was released on Savoy Records in 1962 and featured a composition by Ornette Coleman. Along with John Tchicaiand Don Cherry, he was a member of the New York Contemporary Five. John Coltrane‘s admiration led to recordings for Impulse! Records, the first of which was Four for Trane in 1964, an album of mainly Coltrane compositions on which he was joined by trombonist Roswell Rudd, bassist Reggie Workman and alto player John Tchicai.
Shepp participated in the sessions for Coltrane’s A Love Supreme in late 1964, but none of the takes he participated in were included on the final LP release (they were made available for the first time on a 2002 reissue). However, Shepp, along with Tchicai and others from the Four for Tranesessions, then recorded Ascension with Coltrane in 1965, and his place alongside Coltrane at the forefront of the avant-garde jazz scene was epitomized when the pair split a record (the first side a Coltrane set, the second a Shepp set) entitled New Thing at Newport released in late 1965.
more...More Posts
- Cees See
- Alvin Ailey
- Elizabeth Cotten
- World Music with Gájanas
- Daily Roots with Sylford Walker feat. Rachaad Amarjii
- Surviving the Pandemic and Realizing Racial Justice
- The Cosmos with NGC 2217
- John Mclaughlin
- Frank Wess
- Slim Gaillard
- World Music with Antibalas
- Daily Roots with Prince Alla
- Surviving the Pandemic and Realizing Racial Justice
- The Cosmos with the Phoenix Aurora
- John Paul Jones
- Stephen Stills
- John Jenkins
- Herbie Nichols
- World Music with Bombino
- Daily Roots with Joe Gibbs & The Professionals