Blog
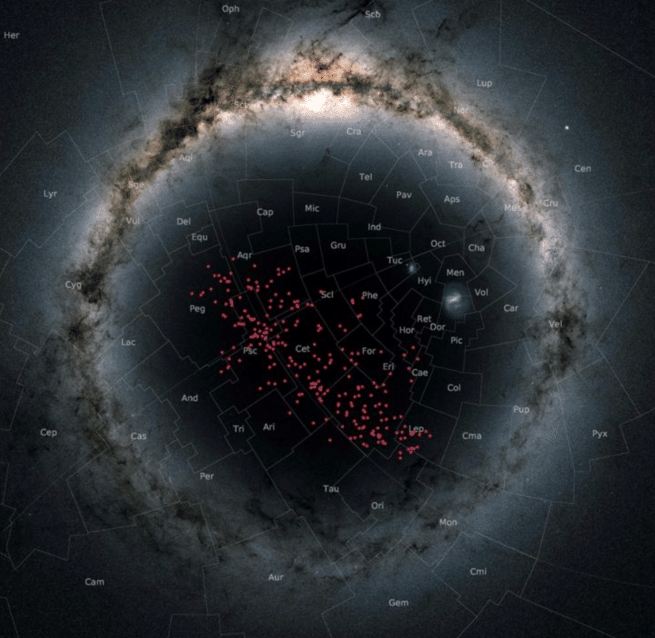
A new study published this month in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics details new observations of a 1,300-light-year-long cluster of more than 4,000 stars that have been moving together through the southern sky for about a billion years now. Distributed like a river of bright lights, a cluster like this has never been found so close to Earth, and could create some useful opportunities for learning about the structure and evolution of the galaxy.
“Similar stream-like structures have been known for quite a while now,” says Stefan Meingast, a researcher from the University of Vienna and the lead author of the new study. They are typically considered remnants of more globular clusters or dwarf galaxies that have been pulled apart and distorted over time, but still share a pattern of movement that hint at a shared origin.
Previous streams have been found in the outskirts of the Milky Way. “Our stream, however, is the first one that was found inside the galaxy, in the immediate vicinity of the sun,” says Meingast. “It therefore is a unique probe for studying the evolution of clusters and for measuring the gravity field of the galaxy.”
There had been previous hints that such a stream existed, through some scattered observations. But this latest investigation is the first to confirm that this is a big, coherent structure. What changed? The European Space Agency’s Gaia mission. An audacious project launched in 2013, Gaia plans to catalog over 1 billion astronomical objects and provide the most precise 3D map of the galaxy ever made.
Yes, it’s a bit strange to think a cluster of stars this large was simply hiding in plain sight for so long, but astronomers know better than to feel embarrassed. When you think about how extraordinarily large space is, trying to locate even several thousand stars streaming through the galaxy is “truly like searching for the needle in the haystack,” says Meingast.
The team was initially tasked with simply using the Gaia data to locate groups of stars that were moving together, and eventually they came across the “structure” of these stars that were moving as a group. The team pinpointed only about 200 stars; the 4,000 figure, and their 1-billion-year age, are extrapolations based on an analysis of stellar brightness, distance, and other factors.
more...Najwa Karam (Arabic: نجوى كرم Lebanese pronunciation: [ˈnaʒwa ˈkaɾam]; born 26 February 1966) is a Lebanese singer and songwriter. She has sold upwards of 60 million records in the world, with each album becoming a best-seller. Karam, widely known for her vocal powerhouse dabka talents, gained an international audience for her distinct blend of traditional Lebanese music and contemporary sounds and contributed to the spread of the Lebanese dialect in Arabic Music. In 2011, Karam debuted as a judge on the reality competition television series, Arabs Got Talent; she has since appeared on all five of its seasons. Najwa Karam is one of the highest selling Arabic language singers and holds the records for highest selling Arabic language album during the years of 1999, 2000, 2001, 2003, 2004, 2008 and 2011. In 2017, Forbes Middle East ranked Karam number 5 on the list of “The Top 100 Arab Celebrities” with 26.58 million social media followers. In 2018, Cosmopolitan included Karam on their list of “The 15 Most Inspiring Women In The Middle East”, and Forbes included Najwa Karam on their list of the “Top 10 of Arab Stars On The Global Stage”.
Karam rose to stardom throughout the 1990s, earning the moniker, Shams el-Ghinnieh (“The Sun of Song”), from her eponymous album and topping the charts throughout the Arab Worldwith her albums, Naghmet Hob, Ma Bassmahlak, Maghroumeh, and Rouh Rouhi. In 2000, Karam’s tenth album Oyoun Qalbi became her highest selling album. In 2001 her album Nedmaneh sold millions of copies worldwide, earning Karam a Murex d’Or award for Best Arabic Artist and Rotana Records awards including, Artist of the Year, Album of the Year, and Highest-Selling Album of the Year. By the time her record Saharni was released in 2003, she had established herself as one of the most prominent Lebanese singers and as a Middle Eastern pop icon.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gCAzCs7eiI8
more...Johnny Cash (born J.R. Cash, February 26, 1932 – September 12, 2003 Kingsland, AR) was an American singer-songwriter, guitarist, actor, and author. He is one of the best-selling music artists of all time, having sold more than 90 million records worldwide. Although primarily remembered as a country music icon, his genre-spanning songs and sound embraced rock and roll, rockabilly, blues, folk, and gospel. This crossover appeal won Cash the rare honor of being inducted into the Country Music, Rock and Roll, and Gospel Music Halls of Fame.
Cash was known for his deep, calm bass-baritone voice, the distinctive sound of his Tennessee Three backing band characterized by train-sound guitar rhythms, a rebelliousness coupled with an increasingly somber and humble demeanor, free prison concerts,[8][9] and a trademark, all-black stage wardrobe, which earned him the nickname “The Man in Black.” He traditionally began his concerts by simply introducing himself, “Hello, I’m Johnny Cash,” followed by his signature song “Folsom Prison Blues“.
Much of Cash’s music contained themes of sorrow, moral tribulation, and redemption, especially in the later stages of his career.[4][12] His other signature songs include “I Walk the Line“, “Ring of Fire“, “Get Rhythm“, and “Man in Black“. He also recorded humorous numbers like “One Piece at a Time” and “A Boy Named Sue“; a duet with his future wife, June Carter, called “Jackson” (followed by many further duets after their wedding); and railroad songs including “Hey, Porter“, “Orange Blossom Special“, and “Rock Island Line“. During the last stage of his career, Cash covered songs by several late 20th-century rock artists, notably “Hurt” by Nine Inch Nails and “Rusty Cage” by Soundgarden.
more...Antoine “Fats” Domino Jr. (February 26, 1928 – October 24, 2017) was an American pianist and singer-songwriter. One of the pioneers of rock and roll music, Domino sold more than 65 million records.Between 1955 and 1960, he had eleven Top 10 hits. His humility and shyness may be one reason his contribution to the genre has been overlooked.
During his career, Domino had 35 records in the U.S. Billboard Top 40, and five of his pre-1955 records sold more than a million copies, being certified gold. His musical style was based on traditional rhythm and blues, accompanied by saxophones, bass, piano, electric guitar, and drums.
His 1949 release “The Fat Man” is widely regarded as the first million-selling Rock ‘n Roll record. One of his most famous songs is “Blueberry Hill”.
Antoine Domino Jr, was born and raised in New Orleans, Louisiana, the youngest of eight children born to Antoine Caliste Domino (1879–1964) and Marie-Donatille Gros (1886–1971). The Domino family was of French Creole background, and Louisiana Creole was his first language.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dm6MjDXydWo
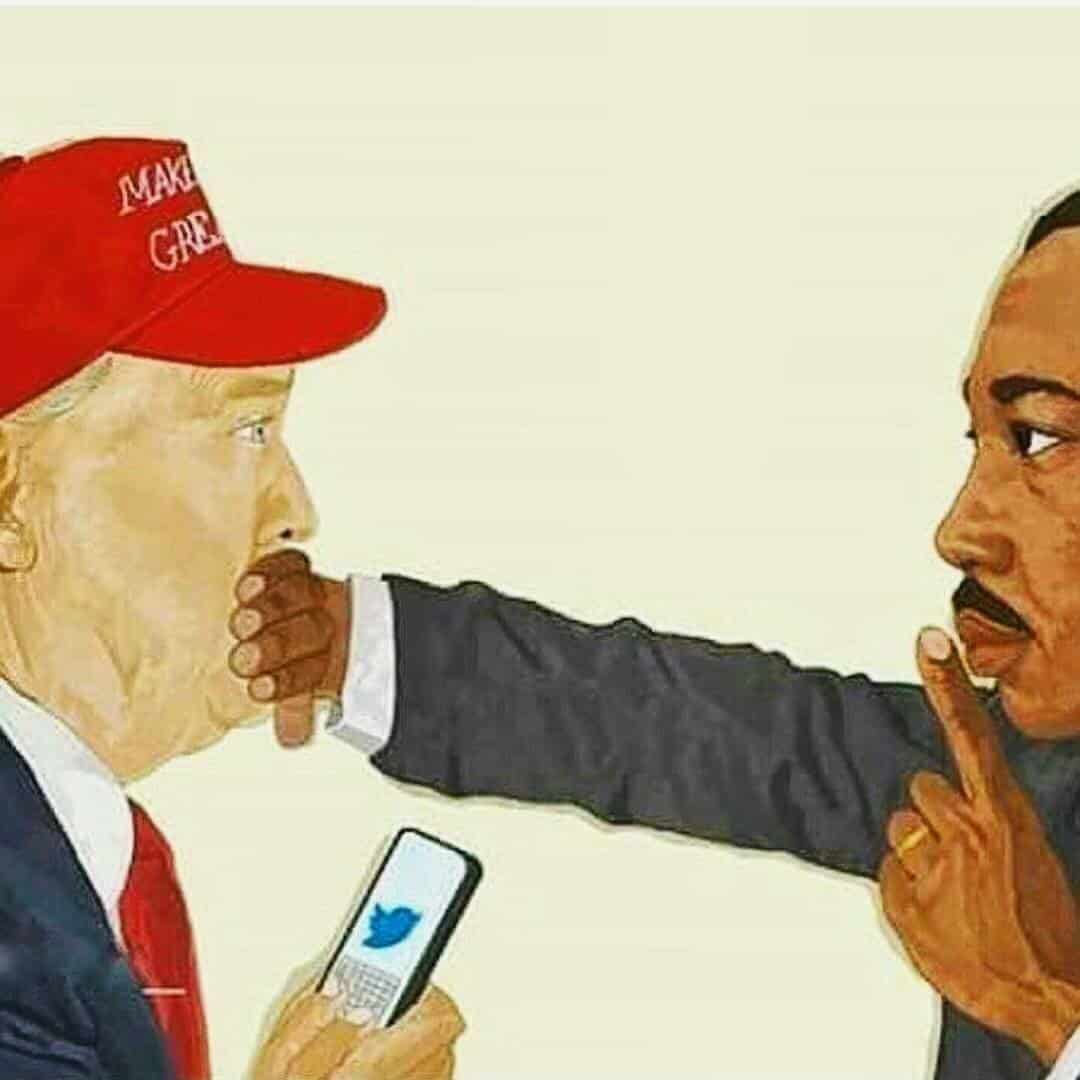
more...This is the last post of ECHOS OF FREEDOM. I created the posts in response to the incredulous and immoral WH administration of our current day; continually discrediting the foundation and moral fiber of our constitution and premise of the United States of America. Let us continue to hear the Echos of Freedom expressed by our historic & present heroes for Freedom, Free Speech, Free Press, Scientific & Medical Freedom and the ultimate objective and brilliant light of truth and justice for all Americans and People of All Cultures.
“I say to you that our goal is freedom, and I believe we are going to get there because however much she strays away from it, the goal of America is freedom. Abused and scorned though we may be as a people, your destiny is tied up in the destiny of America.” MLK
more...
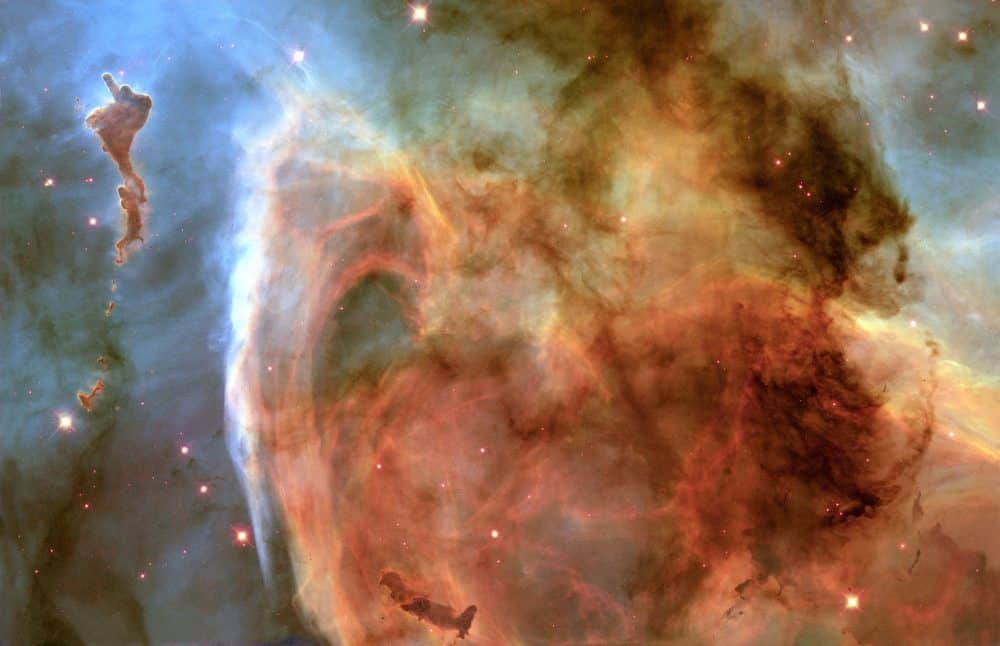
Previously unseen details of a mysterious, complex structure within the Carina Nebula (NGC 3372) are revealed by this image of the ‘Keyhole Nebula, ‘ obtained with the Hubble Space Telescope. The picture is a montage assembled from four different April 1999 telescope pointings with Hubble’s Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which used six different colour filters. The picture is dominated by a large, approximately circular feature, which is part of the Keyhole Nebula, named in the 19th century by Sir John Herschel. This region, about 8000 light-years from Earth, is located adjacent to the famous explosive variable star Eta Carinae, which lies just outside the field of view toward the upper right. The Carina Nebula also contains several other stars that are among the hottest and most massive known, each about 10 times as hot, and 100 times as massive, as our Sun.
more...George Harrison MBE (25 February 1943 – 29 November 2001) was an English musician, singer-songwriter, music and film producer who achieved international fame as the lead guitarist of the Beatles. Often referred to as “the quiet Beatle”, Harrison embraced Indian culture and helped broaden the scope of popular music through his incorporation of Indian instrumentation and Hindu-aligned spirituality in the Beatles’ work. Although the majority of the band’s songs were written by John Lennon and Paul McCartney, most Beatles albums from 1965 onwards contained at least two Harrison compositions. His songs for the group included “Taxman“, “Within You Without You“, “While My Guitar Gently Weeps“, “Here Comes the Sun” and “Something“.
Harrison’s earliest musical influences included George Formby and Django Reinhardt; Carl Perkins, Chet Atkins and Chuck Berry were subsequent influences. By 1965, he had begun to lead the Beatles into folk rock through his interest in Bob Dylan and the Byrds, and towards Indian classical music through his use of the sitar on “Norwegian Wood (This Bird Has Flown)“. Having initiated the band’s embracing of Transcendental Meditation in 1967, he subsequently developed an association with the Hare Krishna movement. After the band’s break-up in 1970, Harrison released the triple album All Things Must Pass, a critically acclaimed work that produced his most successful hit single, “My Sweet Lord“, and introduced his signature sound as a solo artist, the slide guitar. He also organised the 1971 Concert for Bangladesh with Indian musician Ravi Shankar, a precursor to later benefit concerts such as Live Aid. In his role as a music and film producer, Harrison produced acts signed to the Beatles’ Apple record label before founding Dark Horse Records in 1974 and co-founding HandMade Films in 1978.
Harrison released several best-selling singles and albums as a solo performer. In 1988, he co-founded the platinum-selling supergroup the Traveling Wilburys. A prolific recording artist, he was featured as a guest guitarist on tracks by Badfinger, Ronnie Wood and Billy Preston, and collaborated on songs and music with Dylan, Eric Clapton, Ringo Starr and Tom Petty, among others. Rolling Stone magazine ranked him number 11 in their list of the “100 Greatest Guitarists of All Time”. He is a two-time Rock and Roll Hall of Fame inductee – as a member of the Beatles in 1988, and posthumously for his solo career in 2004.[3]
Harrison’s first marriage, to model Pattie Boyd in 1966, ended in divorce in 1977. The following year he married Olivia Arias, with whom he had a son, Dhani. Harrison died from lung cancer in 2001 at the age of 58, two years after surviving a knife attack by an intruder at his Friar Park home. His remains were cremated and the ashes were scattered according to Hindu traditionin a private ceremony in the Ganges and Yamuna rivers in India. He left an estate of almost £100 million.
more...Hal Blaine (born Harold Simon Belsky; February 5, 1929) is an American drummer and session musician.
He is most known for his work with the Wrecking Crew, a group of musicians who recorded prolifically in the Los Angeles music scene and played behind a large number of musicians in the 1960s and ’70s. Blaine played on numerous hits by popular groups, including Nancy Sinatra, Jan and Dean, Elvis Presley, John Denver, the Ronettes, Simon & Garfunkel, the Carpenters, the Beach Boys, the Grass Roots, the 5th Dimension, the Monkees, the Partridge Family, and Steely Dan. He has played on 40 number one hit singles, 150 top ten hits and has performed on, by his own accounting, over 35,000 recorded tracks. He is widely regarded as one of the most prolific drummers in rock and roll history, having “certainly played on more hit records than any drummer in the rock era”.
Blaine is a member of the Rock & Roll Hall of Fame, Musicians Hall of Fame and Museum, and the Percussive Arts Society Hall of Fame. He was inducted into the Modern DrummerHall of Fame in 2010.
Blaine was born to Jewish Eastern European immigrants, Meyer and Rose Belsky, in Holyoke, Massachusetts.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hp1FBfjH60g
more...René Thomas (25 February 1927 – 3 January 1975) was a jazz guitarist from Belgium.
In the early 1950s, he moved to Paris and became part of the modern jazz scene, playing in the style of Jimmy Raney. Back in Europe in 1962, he toured and recorded with Chet Baker, Bobby Jaspar, Kenny Clarke, Eddy Louiss, Stan Getz, Lucky Thompson, Sonny Criss, Jacques Pelzer, Lou Bennett, Charles “Lolo” Bellonzi, and Ingfried Hoffmann.
Thomas died of a heart attack in Santander, Spain at the age of 47 on 3 January 1975.
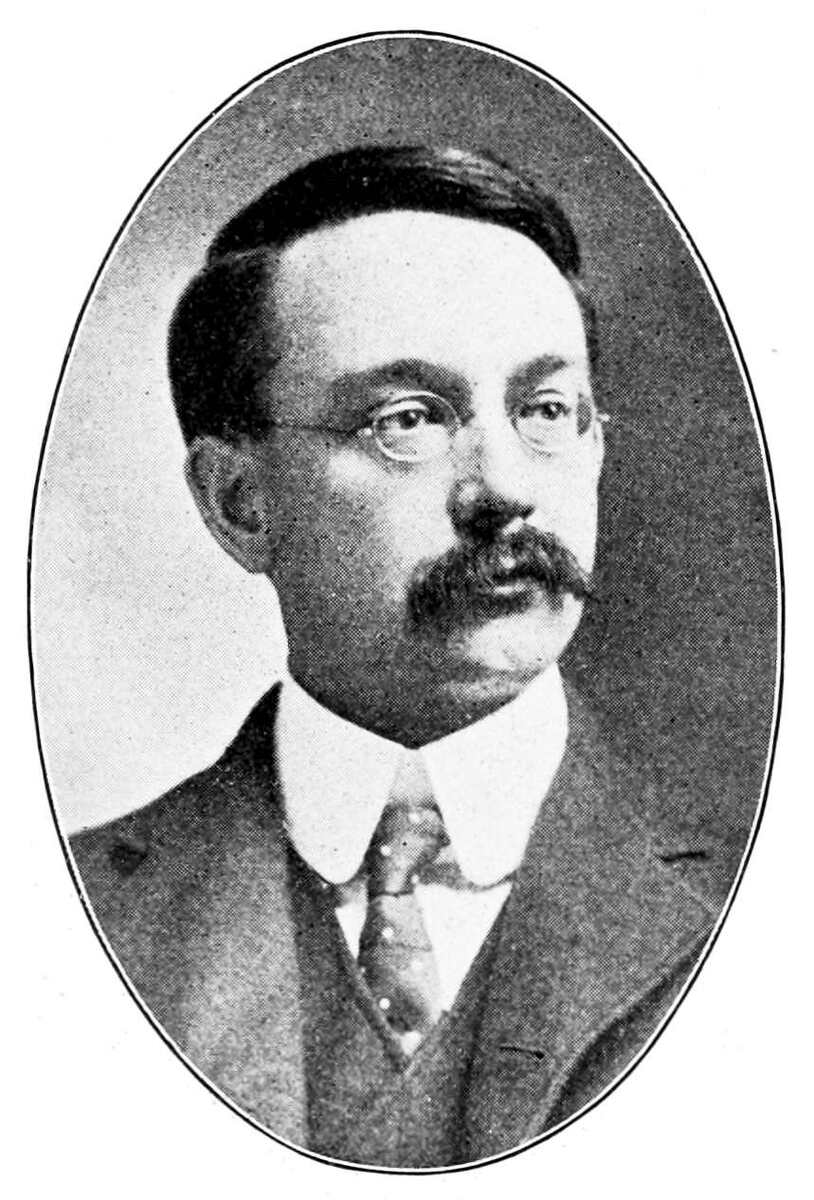
more...“Dictators seek to control men’s thoughts as well as their bodies and so they attempt to dictate science, education and religion. But dictated education is usually propaganda, dictated history is often mythology, dictated science is pseudo-science.” Edwin Grant Conklin
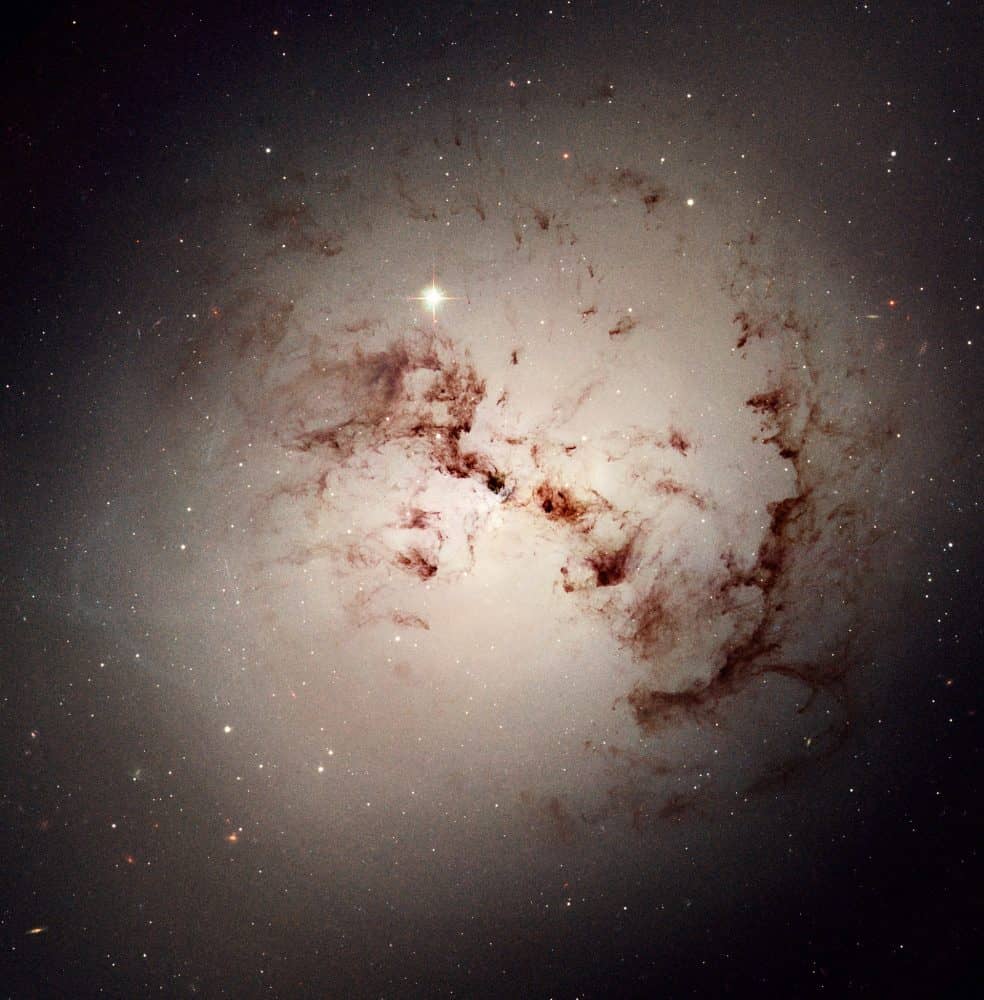
more...Surprisingly complex loops and blobs of cosmic dust lie hidden in the giant elliptical galaxy NGC 1316. This image made from data obtained with the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope reveals the dust lanes and star clusters of this giant galaxy that give evidence that it was formed from a past merger of two gas-rich galaxies.
NGC 1316 (also known as Fornax A) is a lenticular galaxy about 60 million light-years away in the constellation Fornax It is a radio galaxy and at 1400 MHz is the fourth-brightest radio source in the sky.
more...
Nicholas Christian Hopkins (24 February 1944 – 6 September 1994) was an English pianist and organist. Hopkins recorded and performed on many notable British and American pop and rock music releases from the 1960s through the 1990s including many songs by The Rolling Stones, The Kinks and The Who.
David “Fathead” Newman (February 24, 1933 – January 20, 2009) was an American jazz and rhythm-and-blues saxophonist who made numerous recordings as a session musician and leader, but is best known for his work as a sideman on seminal 1950s and early 1960s recordings by singer-pianist Ray Charles.
The AllMusic Guide to Jazz wrote that “there have not been many saxophonists and flutists more naturally soulful than David “Fathead” Newman,” and that “one of jazz’s and popular music’s great pleasures is to hear, during a vocalist’s break, the gorgeous, huge Newman tones filling the space…” Newman is sometimes cited as a leading exponent of the so-called “Texas Tenor” saxophone style, which refers to the many big-toned, bluesy jazz tenor players from that state.
Newman was born in Corsicana, Texas, on February 24, 1933, but grew up in Dallas, where he studied first the piano and then the saxophone. According to one account, he got his nickname “Fathead” in school when “an outraged music instructor used it as an epithet after catching Mr. Newman playing a Sousa march from memory rather than from reading the sheet music, which rested upside down on the stand.”
Inspired by the jump blues bandleader Louis Jordan, Newman took up the alto saxophone in the seventh grade, and was mentored by former Count Basie saxophonist Buster Smith. He went off to Jarvis Christian College on a music and theology scholarship but quit school after three years and began playing professionally, mostly jazz and blues, with a number of musicians, including Smith, pianist Lloyd Glenn, and guitarist bandleaders Lowell Fulson and T-Bone Walker.
more...Mayotte-It consists of a main island, Grande-Terre (or Maore), a smaller island, Petite-Terre (or Pamanzi), and several islets around these two. The archipelago is located in the northern Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean off the coast of Southeast Africa, between northwestern Madagascar and northeastern Mozambique. The department status of Mayotte is recent and the region remains, by a significant margin, the poorest in France. Mayotte is nevertheless much more prosperous than the other countries of the Mozambique Channel, making it a major destination for illegal immigration.
more...https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vmos2JLOSnU
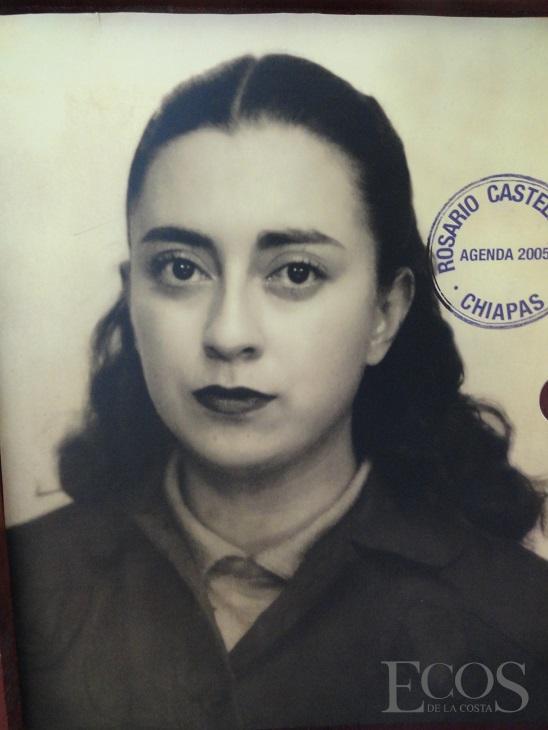
more...“We have to laugh. Because laughter, we already know, is the first evidence of freedom.” Rosario Castellanos
more...
More Posts
- Lost Radio Hour music by Ed Volker of the Radiators
- Cosmos Phoenix Aurora over Iceland
- Hal Blaine
- René Thomas
- Oumou Sangaré
- George Harrison
- Ida Cox
- World Music La Yegros
- Daily Roots Message
- Revolution & Dancing
- Cosmos RCW 16
- Nicky Hopkins
- David “Fathead” Newman
- World Music CHAKANA
- Daily Roots U Roy
- CELESTIAL ANTIQUITY Event 3-28-24
- Mt Zion Shabbat for the Soul
- Cosmos NGC 2736
- Wayne Escoffery
- Rusty Young