Blog
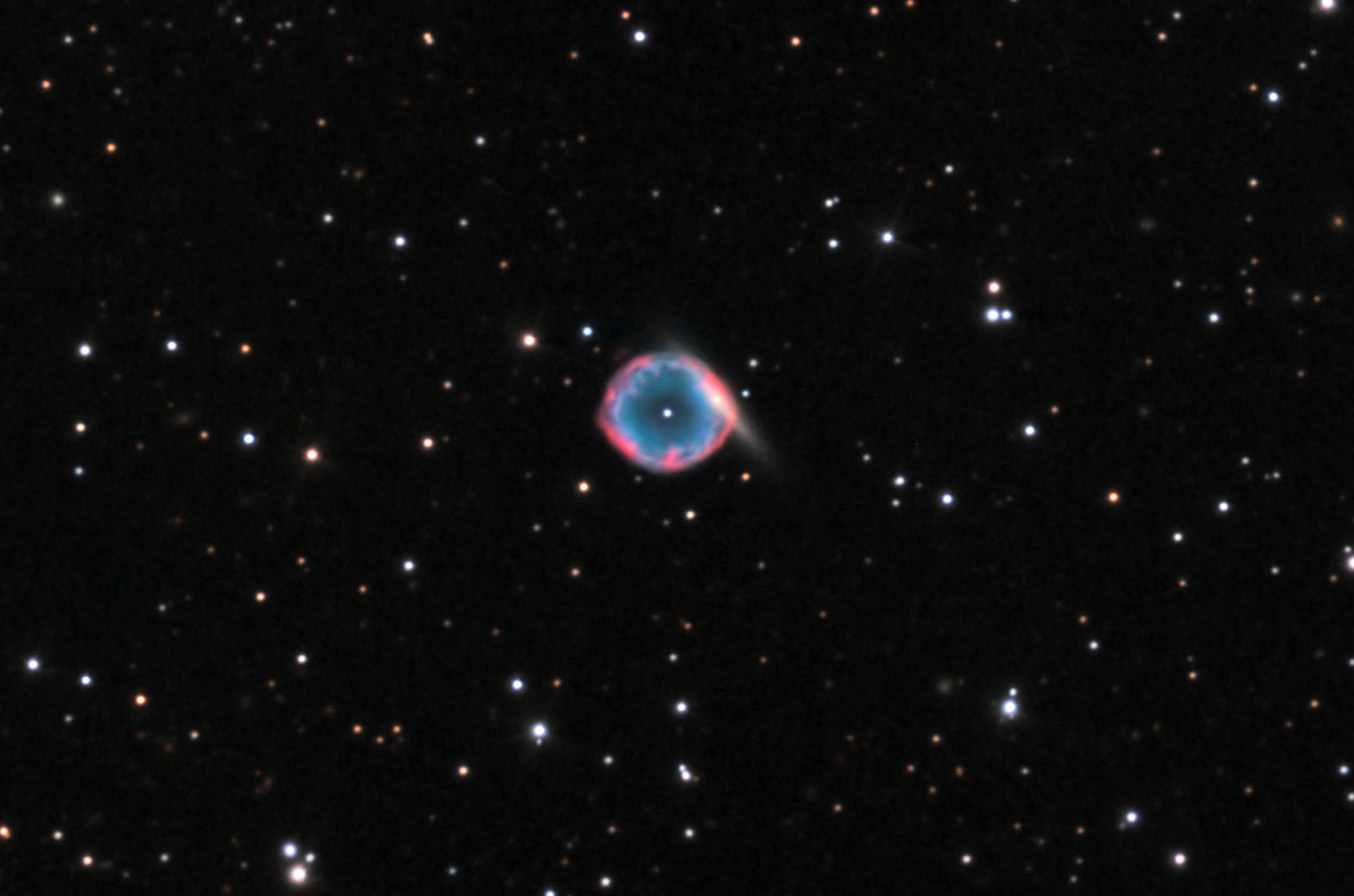
Abell 70 is a slightly elongated planetary nebula located 13,500-17,500 light years away in the constellation of Aquila. It is approaching the earth at 79 kilometers per second and expanding 38 kilometers per second. There is a galaxy named PMN J2033-0656 behind Abell 70, giving it a “diamond ring” effect.

Signe Toly Anderson ( born Signe Toly; September 15, 1941 – January 28, 2016) was an American singer who was one of the founding members of the American rock band Jefferson Airplane.
Signe Toly was born in Seattle, Washington on September 15, 1941. Her parents divorced when she was three, and her mother raised her in Portland, Oregon. Toly sang in a band with three male musicians she had known in high school, under the name Three Guys and a Gal. The group performed at a campaign event for John F. Kennedy in November 1959.
Toly was a locally-known and well-respected jazz and folk singer in San Francisco, where Marty Balin heard her perform and invited her to join his band, soon named Jefferson Airplane.
more...Arvell Shaw (September 15, 1923 – December 5, 2002) was an American jazzdouble-bassist, best known for his work with Louis Armstrong.
He was born on September 15, 1923, in St. Louis, Missouri. Shaw learned to play tuba in high school, but switched to bass soon after. In 1942 he worked with Fate Marable on riverboats traveling on the Mississippi River, then served in the Navy from 1942 to 1945. After his discharge he played with Armstrong in his last big band, from 1945 to 1947. Shaw and Sid Catlett then joined the Louis Armstrong All-Stars until 1950, when Shaw broke off to study music. He returned to play with Armstrong from 1952 to 1956, and performed in the 1956 musical, High Society.
Shaw performed with Louis Armstrong and his All Stars with Velma Middleton singing vocals for the ninth Cavalcade of Jazz concert held at Wrigley Field in Los Angeles. The concert was produced by Leon Hefflin, Sr. on June 7, 1953. Also featured that day were Roy Brown and his Orchestra, Don Tostiand His Mexican Jazzmen, Earl Bostic, Nat “King” Cole, and Shorty Rogers and his Orchestra.
Following this he worked at CBS with Russ Case, did time in Teddy Wilson‘s trio, and played with Benny Goodman at the 1958 Brussels World’s Fair. After a few years in Europe, he played again with Goodman on a tour of Central America in 1962. From 1962–64 Shaw played again with Armstrong, and occasionally accompanied him through the end of the 1960s. After the 1960s, Shaw mostly freelanced in New York, and kept playing until his death. He recorded only once as a leader, a live concert from 1991 of his Satchmo Legacy Band. Shaw died in Roosevelt, New York, on December 5, 2002, at the age of 79.
more...Julian Edwin “Cannonball” Adderley (September 15, 1928 – August 8, 1975 Tampa, FL) was an American jazzalto saxophonist of the hard bop era of the 1950s and 1960s.
Adderley is perhaps best remembered for the 1966 soul jazz single “Mercy, Mercy, Mercy“, which was written for him by his keyboardist Joe Zawinul and became a major crossover hit on the pop and R&B charts. A cover version by the Buckinghams, who added lyrics, also reached No. 5 on the charts. Adderley worked with Miles Davis, first as a member of the Davis sextet, appearing on the seminal records Milestones (1958) and Kind of Blue (1959), and then on his own 1958 album Somethin’ Else. He was the elder brother of jazz trumpeter Nat Adderley, who was a longtime member of his band. In July 1975, Adderley suffered a stroke from a cerebral hemorrhage and died four weeks later, on August 8, 1975, at St. Mary Methodist Hospital in Gary, Indiana. He was 46 years old.
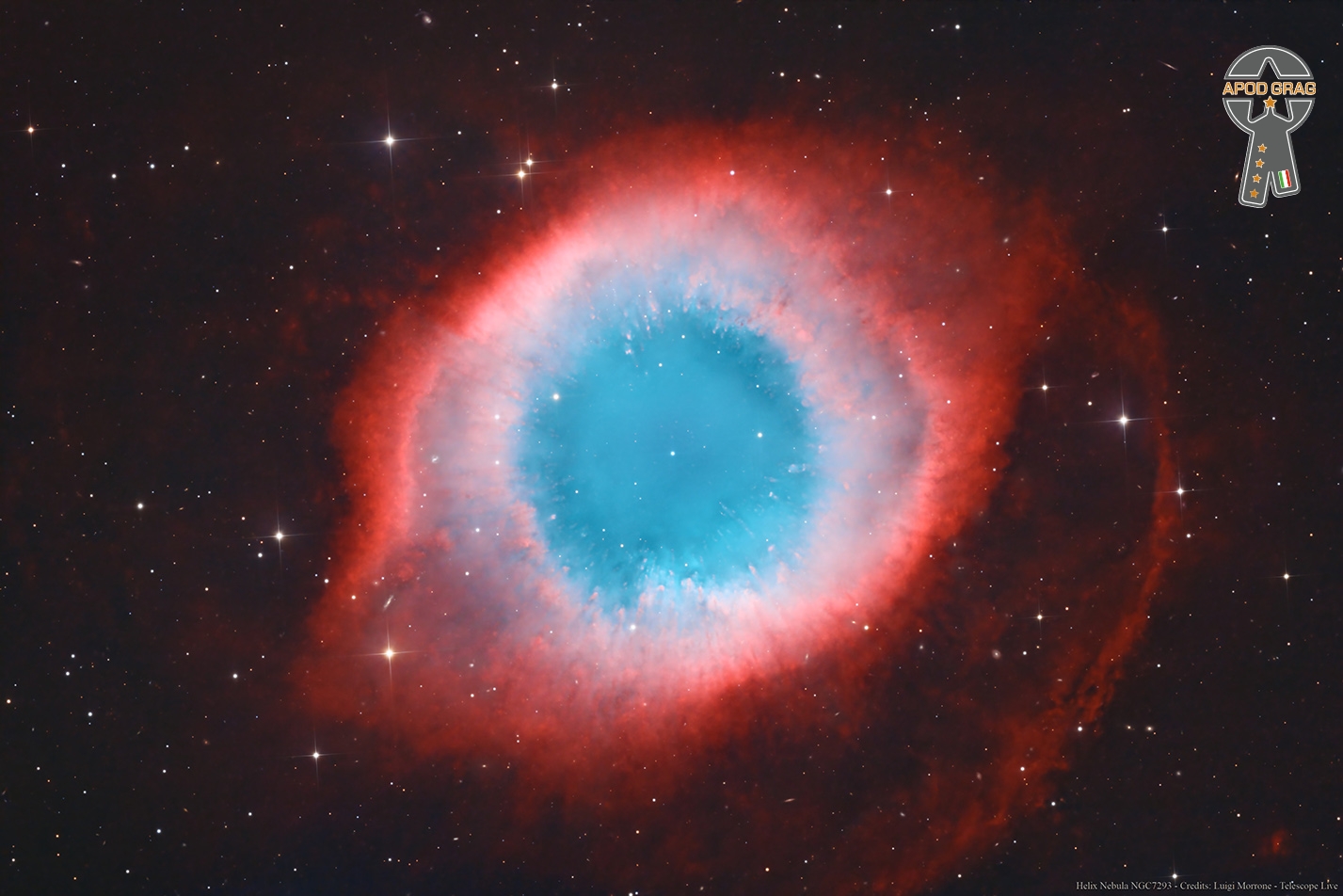
more...The Helix Nebula (also known as NGC 7293 or Caldwell 63) is a planetary nebula(PN) located in the constellation Aquarius. Discovered by Karl Ludwig Harding, most likely before 1824, this object is one of the closest of all the bright planetary nebulae to Earth. The distance, measured by the Gaia mission, is 655±13 light-years. It is similar in appearance to the Cat’s Eye Nebula and the Ring Nebula, whose size, age, and physical characteristics are similar to the Dumbbell Nebula, varying only in its relative proximity and the appearance from the equatorial viewing angle. The Helix Nebula has sometimes been referred to as the “Eye of God” in pop culture, as well as the “Eye of Sauron“.
Joseph Jarman (September 14, 1937 – January 9, 2019 Pine Bluff, AK) was an American jazzmusician, composer, poet, and Shinshu Buddhist priest. He was one of the first members of the Association for the Advancement of Creative Musicians and a member of the Art Ensemble of Chicago. After he was discharged from the Army in 1958, Jarman attended Wilson Junior College, where he met bassist Malachi Favors Maghostut and saxophonists Roscoe Mitchell, Henry Threadgill, and Anthony Braxton. These men would often perform long jam sessions at the suggestion of their professor, Richard Wang (now with Illinois University). Mitchell introduced Jarman to pianist Muhal Richard Abrams, and Jarman, Mitchell, and Maghostut joined Abrams’ Experimental Band, a private, non-performing ensemble, when that group was founded in 1961. The same group of musicians continued to play together in a variety of configurations, and went on to found the Association for the Advancement of Creative Musicians (AACM) in 1965, along with Fred Anderson and Phil Cohran.
Jarman’s solo recording career began at this time, with two releases on the Delmark label which included material, such as spoken word and “little instruments”, that would later characterize the sound of the Art Ensemble. The band he fronted and used during these recordings between 1966 and 1968, included Fred Anderson (tenor sax), Billy Brimfield (trumpet), Charles Clark (bass), Christopher Gaddy (piano) and Thurman Barker (drums). However, in 1969, Clark and Gaddy both died and Jarman disbanded his group.
more...
Israel López Valdés (September 14, 1918 – March 22, 2008), better known as Cachao, was a Cuban double bassist and composer. Cachao is widely known as the co-creator of the mambo and a master of the descarga (improvised jam sessions). Throughout his career he also performed and recorded in a variety of music styles ranging from classical music to salsa. An exile in the United States since the 1960s, he only achieved international fame following a career revival in the 1990s.
Born into a family of musicians in Havana, Cachao and his older brother Orestes were the driving force behind one of Cuba’s most prolific charangas, Arcaño y sus Maravillas. As members of the Maravillas, Cachao and Orestes pioneered a new form of ballroom music derived from the danzón, the danzón-mambo, which subsequently developed into an international genre, mambo. In the 1950s, Cachao became famous for popularizing improvised jam sessions known as descargas. He emigrated to Spain in 1962, and moved to the United States in 1963, starting a career as a session and live musician for a variety of bands in New York during the rise of boogaloo, and later, salsa.
In the 1970s, Cachao fell into obscurity after moving to Las Vegas and later Miami, releasing albums sporadically as a leader. In the 1990s, he was re-discovered by actor Andy García, who brought him back to the forefront of the Latin music scene with the release of a documentary and several albums. Before his death in 2008, Cachao had earned a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame and several Grammy Awards. He is ranked number 24 on Bass Player magazine’s list of “The 100 Greatest Bass Players of All Time”.
more...Oliver Lake (born September 14, 1942) is an American jazz saxophonist, flutist, composer, poet, and visual artist. He is known mainly for alto saxophone, but he also performs on soprano and flute. During the 1960s, Lake worked with the Black Artists Group in St. Louis. In 1977, he founded the World Saxophone Quartet with David Murray, Julius Hemphill, and Hamiet Bluiett. Lake worked in the group Trio 3 with Reggie Workmanand Andrew Cyrille. Lake has appeared on more than 80 albums as a bandleader, co-leader, and side musician. He is the father of drummer Gene Lake. Lake has been a resident of Montclair, New Jersey.
more...Temple Israel Tot Shabbat service Friday September 13th 2024 6pm. Music with Inbal Sharett-Singer, Jayson Rodovsky, Jeff Bailey, Pete Whitman and mick laBriola.
more...Even though this theory is in dispute, the story is intriguing.
One of the most popular theories, however, links Friday the 13th with the fall of a fearsome group of legendary warriors—the Knights Templar. Founded around 1118 as a monastic military order devoted to the protection of pilgrims traveling to the Holy Land following the Christian capture of Jerusalem during the First Crusade, the Knights Templar quickly became one of the richest and most influential groups of the Middle Ages, thanks to lavish donations from the crowned heads of Europe, eager to curry favor with the fierce Knights. By the turn of the 14th century, the Templars had established a system of castles, churches and banks throughout Western Europe. And it was this astonishing wealth that would lead to their downfall. For the Templars, that end began in the early morning hours of Friday, October 13, 1307.
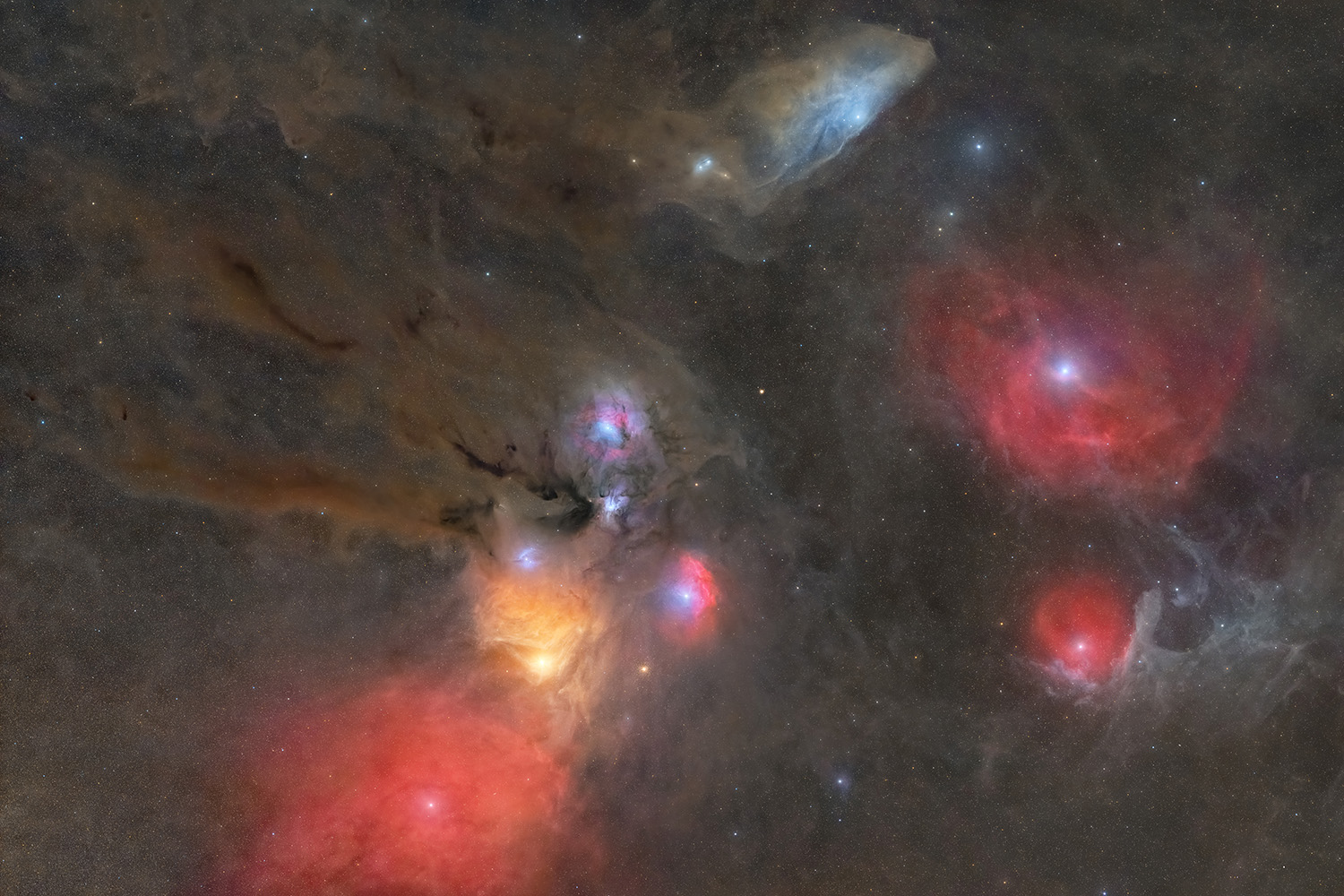
Project 49’ was the name code for our second project with the ‘Altaïr of Atlas Astrophotographers’ team, an idea that looked a bit crazy on paper, but that we knew could only be achieved under optimum conditions… The idea was to produce an ultra-detailed image of the Rho Ophiuchi complex, as well as some of its neighbours in the Scorpius constellation, using remotely our setup in Morocco. As this region is about 15° higher in the sky than our home in France, this dream became a reality ! With our instrument in place in the Atlas Mountains, we had to make a 7*7 mosaic (49 tiles), to achieve our goal. A project of this kind already takes up a huge amount of time and material resources (post-processing), so we set ourselves the challenge of producing all our tiles in a single exposure for each filter, without any stacking, and all in LHaRGB using a monochrome camera. 358ly distant.

William Smith Monroe (September 13, 1911 – September 9, 1996) was an American mandolinist, singer, and songwriter, and created the bluegrass music genre. Because of this, he is often called the “Father of Bluegrass“.
The genre takes its name from his band, the Blue Grass Boys, who named their group for the bluegrass of Monroe’s home state of Kentucky. He described the genre as “Scottish bagpipes and ole-time fiddlin’. It’s Methodist and Holiness and Baptist. It’s blues and jazz, and it has a high lonesome sound.”
Monroe was born on his family’s farm near Rosine, Kentucky, the youngest of eight children of James Buchanan “Buck” and Malissa (Vandiver) Monroe. His mother and her brother, James Pendleton “Pen” Vandiver, were both musically talented, and Monroe and his family grew up playing and singing at home.
Bill was of Scottish and English heritage. Because his older brothers Birch and Charliealready played the fiddle and guitar, Bill was resigned to playing the less desirable mandolin. He recalled that his brothers insisted that he remove four of the mandolin’s eight strings so he would not play too loudly.
more...Leon Brown “Chu” Berry (September 13, 1908 – October 30, 1941 Wheeling, WV) was an American jazz tenor saxophonist during the 1930s. He is perhaps best known for his time as a member of singer Cab Calloway‘s big band.
According to music critic Gary Giddins, musicians called him “Chu” either because he chewed on the mouthpiece of his saxophone or because he had a Fu Manchu mustache. Berry died at 33 on October 30, 1941, in Conneaut, Ohio, after being in a car accident.
more...
Arnold Schoenberg or Schönberg (13 September 1874 – 13 July 1951) was an Austrian and American composer, music theorist, teacher and writer. He was among the first modernists who transformed the practice of harmony in 20th-century classical music, and a central element of his music was its use of motives as a means of coherence. He propounded concepts like developing variation, the emancipation of the dissonance, and the “unity of musical space“.
Schoenberg’s early works, like Verklärte Nacht (1899), represented a Brahmsian–Wagnerian synthesis on which he built. Mentoring Anton Webern and Alban Berg, he became the central figure of the Second Viennese School. They consorted with visual artists, published in Der Blaue Reiter, and wrote atonal, expressionist music, attracting fame and stirring debate. In his String Quartet No. 2 (1907–1908), Erwartung (1909), and Pierrot lunaire (1912), Schoenberg visited extremes of emotion; in self-portraits he emphasized his intense gaze. While working on Die Jakobsleiter (from 1914) and Moses und Aron (from 1923), Schoenberg confronted popular antisemitism by returning to Judaism and substantially developed his twelve-tone technique. He systematically interrelated all notes of the chromatic scale in his twelve-tone music, often exploiting combinatorial hexachords and sometimes admitting tonal elements.
Schoenberg resigned from the Prussian Academy of Arts (1926–1933), emigrating as the Nazis took power; they banned his (and his students’) music, labeling it “degenerate“. He taught in the US, including at the University of California, Los Angeles (1936–1944), where facilities are named in his honor. He explored writing film music (as he had done idiosyncratically in Begleitungsmusik zu einer Lichtspielscene, 1929–1930) and wrote more tonal music, completing his Chamber Symphony No. 2 in 1939. With citizenship (1941) and US entry into World War II, he satirized fascist tyrants in Ode to Napoleon (1942, after Byron), deploying Beethoven’s fate motif and the Marseillaise. Post-war Vienna beckoned with honorary citizenship, but Schoenberg was ill as depicted in his String Trio (1946). As the world learned of the Holocaust, he memorialized its victims in A Survivor from Warsaw (1947). The Israel Conservatory and Academy of Music elected him honorary president (1951).
His innovative music was among the most influential and polemicized of 20th-century classical music. At least three generations of composers extended its somewhat formal principles. His aesthetic and music-historical views influenced musicologists Theodor W. Adorno and Carl Dahlhaus. The Arnold Schönberg Center collects his archival legacy.
more...More Posts
- Percy Heath Day
- Reverend Gary Davis Day
- World Music with Clave y Guaguancó
- Daily Roots with Don Carlos
- Mayday Ceremony rehearsal 4-29-18
- The Cosmos with M17
- Ray Barretto Day
- Toots Thielemans Day
- Duke Ellington Day
- World Music with Hossein Omoumi
- Daily Roots with Mad Professor
- The Cosmos with the Small Magellanic Cloud
- Mickey Tucker Day
- John Tchicai Day
- Mario Bauza Day
- World Music with Mahmoud Ahmed
- Daily Roots with Justin Hines and the Dominos
- Community Band performance 4-27-18
- The Cosmos with NGC 6946
- Freddie Waits Day
