Blog
Fred Anderson (March 22, 1929 – June 24, 2010) was an American jazz tenor saxophonist who was based in Chicago, Illinois. Anderson’s playing was rooted in the swing music and hard bop idioms, but he also incorporated innovations from free jazz.[4] Anderson was also noted for having mentored numerous young musicians.Critic Ben Ratliff called him “a father figure of experimental jazz in Chicago”. Writer John Corbett referred to him as “scene caretaker, underground booster, indefatigable cultural worker, quiet force for good.” In 2001, author John Litweiler called Anderson “the finest tenor saxophonist in free jazz/underground jazz/outside jazz today.”
more...eorge Washington Benson (born March 22, 1943 Pittsburg) is an American jazz fusionguitarist, singer, and songwriter. He began his professional career at the age of 19 as a jazz guitarist.
A former child prodigy, Benson first came to prominence in the 1960s, playing soul jazzwith Jack McDuff and others. He then launched a successful solo career, alternating between jazz, pop, R&B singing, and scat singing. His album Breezin’ was certified triple-platinum, hitting No. 1 on the Billboard album chart in 1976. His concerts were well attended through the 1980s, and he still has a large following. Benson has won ten Grammy Awards and has been honored with a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame.
more...Aurelio Martínez Suazo, the Honduran musician who championed his country’s Garifuna people (also known as the Garínagu) and brought the music to wider international attention, has died. Martínez was one of 13 people killed last night (Monday, March 17) in a small plane crash off the coast of the Caribbean island of Roatán, according to The Associated Press. He was 55 years old.
Born in the isolated town of Plaplaya, in Honduras’ Gracias a Dios district, in 1969, Martínez participated in traditional Garifuna rituals from a young age. Typically performed on acoustic guitar with percussive accompaniment, Garifuna songs combine West African rhythms with Latin, reggae, and calypso music. At the age of 14, Martínez moved to the port city La Ceiba, where he began performing in various latin jazz ensembles. Eventually, he formed his first group, Lita Ariran, whose 1995 album, Songs of the Garifuna, made them one of the first Garifuna bands distributed on an international label.
Two years later, Martínez met Andy Palacio, a fellow rising star in Garifuna music from Belize, when the two recorded the duet “Lánarime Lamiselu” for Stonetree Records’ compilation Paranda: Africa in Central America. He put out his debut solo album, Garifuna Soul, in 2004, and, in 2005, was elected as the first member of African descent in the National Congress of Honduras, where he fought for the rights of the Garifuna community. Following Palacio’s death, in 2008, however, Martínez returned to music, and would go on to release three more studio LPs under the moniker Aurelio: Laru Beya, in 2011, Lándini, in 2014, and Darandi, in 2017. Last year, Lándini was named as one of the best Latin American albums of all time in the Los 600 discos de Latinoamérica, a list project compiled by music journalists from the region.
Aurelio Martínez Suazo (26 September 1969 – 17 March 2025), professionally known as Aurelio, was a Honduran singer-songwriter and politician. Known for his Garifuna music, he was considered a cultural ambassador of the Garifuna people. According to The Guardian, he became the leading Garifuna performer after the death of musician Andy Palacio. His acclaimed album “Laru Beya” was considered among the best albums of Latin American music, according to Los 600 de Latinoamérica, a 2024 ranking made by Latin American music critics.
more...Friday March 21st Hiddur Mitzvah service with Hannah Regal, Erin Roe, Renae Goldman and mick laBriola.
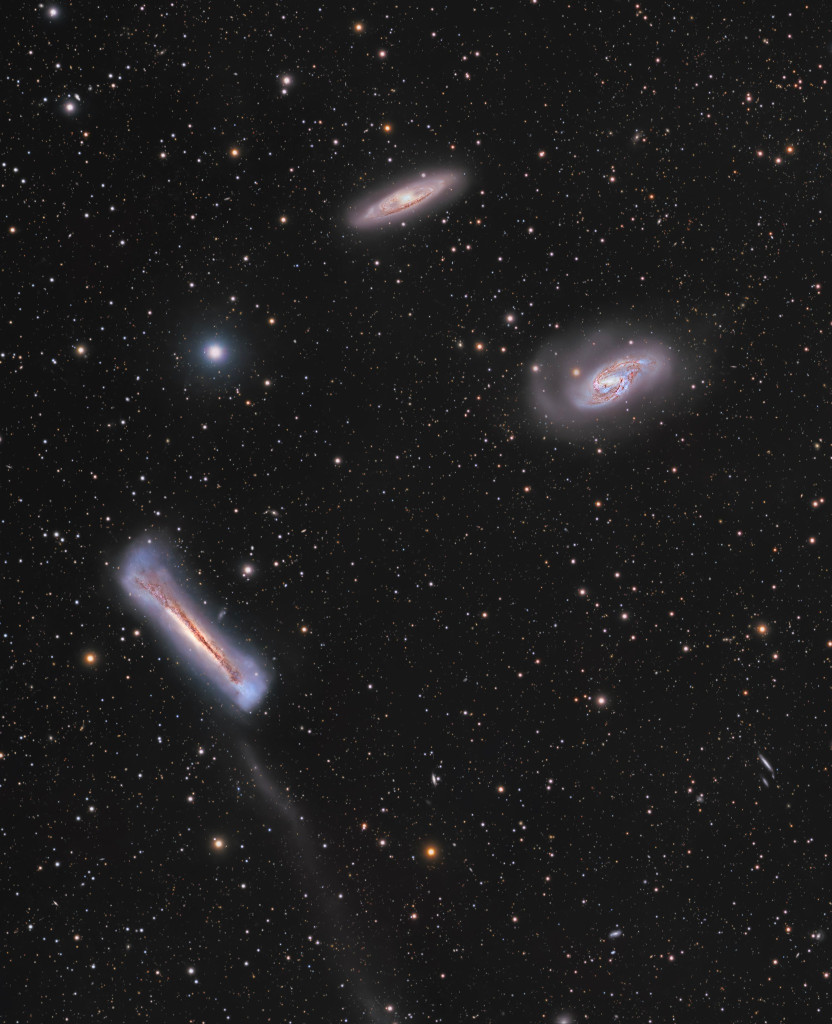
more...March equinox and the northern hemisphere spring. Famous as the Leo Triplet, the three magnificent galaxies found in the prominent constellation Leo gather here in one astronomical field of view. Crowd pleasers when imaged with even modest telescopes, they can be introduced individually as NGC 3628 (bottom left), M66 (middle right), and M65 (top center). All three are large spiral galaxies but tend to look dissimilar, because their galactic disks are tilted at different angles to our line of sight. NGC 3628, also known as the Hamburger Galaxy, is temptingly seen edge-on, with obscuring dust lanes cutting across its puffy galactic plane. The disks of M66 and M65 are both inclined enough to show off their spiral structure. Gravitational interactions between galaxies in the group have left telltale signs, including the tidal tails and warped, inflated disk of NGC 3628 and the drawn out spiral arms of M66. This gorgeous view of the region spans over 1 degree (two full moons) on the sky. Captured with a telescope from Sawda Natheel, Qatar, planet Earth, the frame covers over half a million light-years at the Leo Trio’s estimated 30 million light-year distance.

more...
Solomon Vincent McDonald Burke (born James Solomon McDonald, March 21, 1940 – October 10, 2010) was an American singer who shaped the sound of rhythm and blues as one of the founding fathers of soul music in the 1960s. He has been called “a key transitional figure bridging R&B and soul”, and was known for his “prodigious output”.
He had a string of hits including “Cry to Me“, “If You Need Me“, “Got to Get You Off My Mind“, “Down in the Valley“, and “Everybody Needs Somebody to Love“. Burke was referred to honorifically as “King Solomon”, the “King of Rock ‘n’ Soul”, “Bishop of Soul”, and the “Muhammad Ali of Soul”. Due to his minimal chart success in comparison to other soul music greats such as James Brown, Wilson Pickett, and Otis Redding, Burke has been described as the genre’s “most unfairly overlooked singer” of its golden age. Atlantic Records executive Jerry Wexler referred to Burke as “the greatest male soul singer of all time”.
more...Ustad Bismillah Khan (born Qamaruddin Khan, 21 March 1916 – 21 August 2006), often referred to by the title Ustad, was an Indian musician credited with popularizing the shehnai, a reeded woodwind instrument. His virtuosity made him a leading Hindustani classical music artist, indelibly linking his name with the woodwind instrument. While the shehnai had importance as a folk instrument played primarily by musicians schooled in traditional ceremonies, Khan elevated its status and brought it to the concert stage.
Khan was a devout Muslim but performed at both Hindu and Muslim ceremonies, and was considered a symbol of religious harmony. Owing to his fame, he was selected to perform for the ceremony at Delhi’s historic Red Fort as the Indian flag unfurled at the hour of India’s independence on 15 August 1947. His music was played (in Raag Kafi) on television every Independence Day. Khan turned down invitations to perform in other countries before 1966, when the Indian government insisted that he play at the Edinburgh International Festival. This gained him a following in the West, and he continued to appear in Europe and North America thereafter.
In 2001, Bismillah Khan was awarded the Bharat Ratna, India’s highest civilian honour, and the country observed a national day of mourning following his death in 2006. He became the third classical musician of India after M. S. Subbalakshmi and Ravi Shankarto be awarded the Bharat Ratna.
more...Modest Petrovich Mussorgsky (21 March [O.S. 9 March] 1839 – 28 March [O.S. 16 March] 1881) was a Russian composer, one of the group known as “The Five.” He was an innovator of Russian music in the Romantic period and strove to achieve a uniquely Russian musical identity, often in deliberate defiance of the established conventions of Western music.
Many of Mussorgsky’s works were inspired by Russian history, Russian folklore, and other national themes. Such works include the opera Boris Godunov, the orchestral tone poem Night on Bald Mountain and the piano suite Pictures at an Exhibition.
For many years, Mussorgsky’s works were mainly known in versions revised or completed by other composers. Many of his most important compositions have posthumously come into their own in their original forms, and some of the original scores are now also available.
more...Otis Spann (March 21, 1924, or 1930 – April 24, 1970 Belzoni,MS) was an American bluesmusician many consider the leading postwar Chicago blues pianist. By age 14, he was playing in bands in the Jackson area. He moved to Chicago in 1946, where Big Maceo Merriweather mentored him. Spann performed solo with the guitarist Morris Pejoe, working a regular spot at the Tic Toc Lounge. Spann was known for his distinctive piano style. He became Muddy Waters‘ piano player in late 1952 and participated in his first recording session with the band on September 24, 1953. He played on many of Waters’ most famous songs, including the blues standards “Hoochie Coochie Man,” “I’m Ready,” and “Got My Mojo Working.” During his tenure with the group, he continued to record as a solo artist and session player with other musicians, including Bo Diddley and Howlin’ Wolf. He stayed with Muddy Waters until 1968.
more...Edward James “Son” House Jr. (March 21, 1902 – October 19, 1988) was an American Delta blues singer and guitarist, noted for his highly emotional style of singing and slide guitar playing.
After years of hostility to secular music, as a preacher and for a few years also working as a church pastor, he turned to blues performance at the age of 25. He quickly developed a unique style by applying the rhythmic drive, vocal power and emotional intensity of his preaching to the newly learned idiom. In a short career interrupted by a spell in Parchman Farm penitentiary, he developed his musicianship to the point that Charley Patton, the foremost blues artist of the Mississippi Delta region, invited him to share engagements and to accompany him to a 1930 recording session for Paramount Records.
Issued at the start of the Great Depression, the records did not sell and did not lead to national recognition. Locally, House remained popular, and in the 1930s, together with Patton’s associate Willie Brown, he was the leading musician of Coahoma County. There he was a formative influence on Robert Johnson and Muddy Waters. In 1941 and 1942, House and the members of his band were recorded by Alan Lomax and John W. Work for the Library of Congress and Fisk University. The following year, he left the Delta for Rochester, New York, and gave up music.
In 1964, Alan Wilson, co-founder of the band Canned Heat, found House and had him listen to his old recordings. He encouraged him to find his way back to the music and from this collaboration, Father of Folk Blues was born. Wilson even played second guitar on “Empire State Express” and the harp on ”Levee Camp Moan”. Son’s manager Dick Waterman said,” Al Wilson helped Son House find Son House”. He relearned his repertoire and established a career as an entertainer, performing for young, mostly white audiences in coffeehouses, at folk festivals and on concert tours during the American folk music revival, billed as a “folk blues” singer. He recorded several albums and some informally taped concerts have also been issued as albums. In 2017, his single “Preachin’ the Blues” was inducted into the Blues Hall of Fame.
more...More Posts
- Don’t Lose Your Head
- Protect Our Children
- Introspection
- Canadian Solidarity
- Cosmo NGC 4941
- Joseph Haydn
- Johann Sebastian Bach
- Herb Alpert
- Freddie Green
- Big Maceo
- World Music Kamini Natarajan
- Daily Roots Scientist
- Tracy Chapman
- Cosmo IC 1871
- Frankie Laine
- “Sonny Boy” Williamson I
- Norah Jones
- Eric Clapton
- World Music Nusrat Fateh Ali Khan
- Daily Roots Barrington Levy